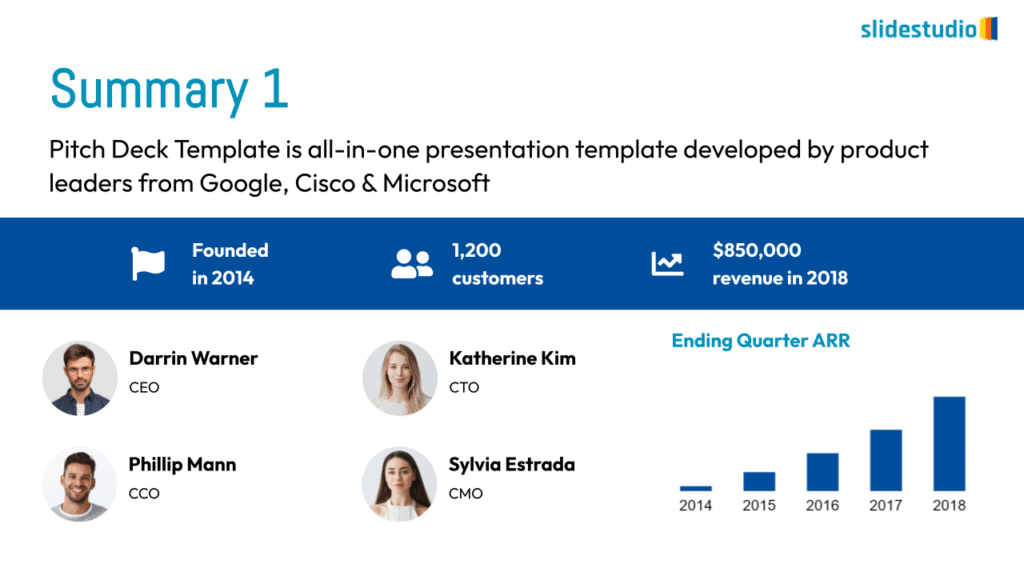
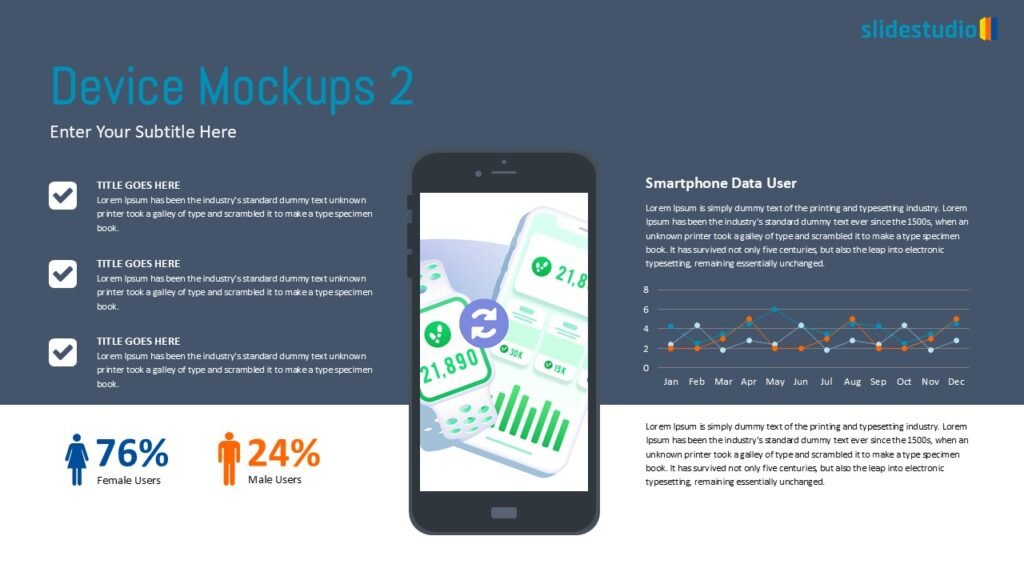
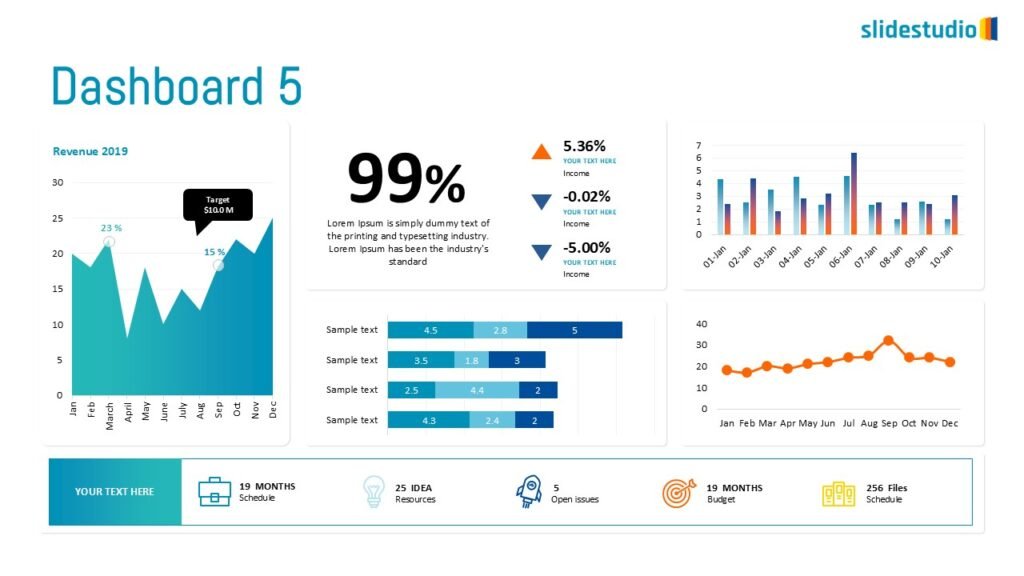
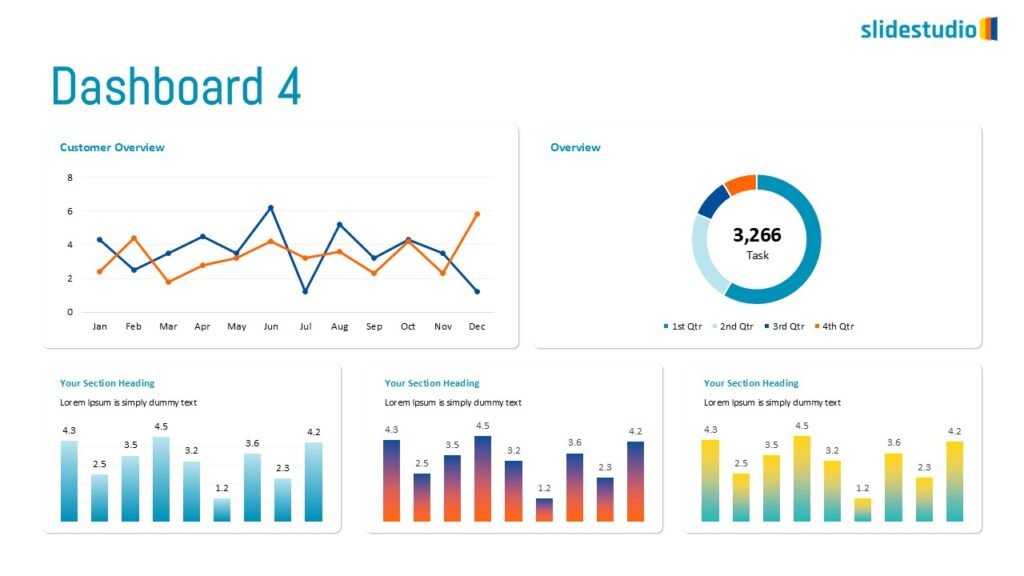
Your Data, Powerfully Presented.
Elevate your most important presentations with sharp visuals that command attention.
Each template transforms complex data into compelling frameworks visualized through high-impact infographics. Accelerate understanding, secure buy-in, and propel your initiatives forward. Master data and strategy with ease.
Ready to use. Customizable. No design skills required.

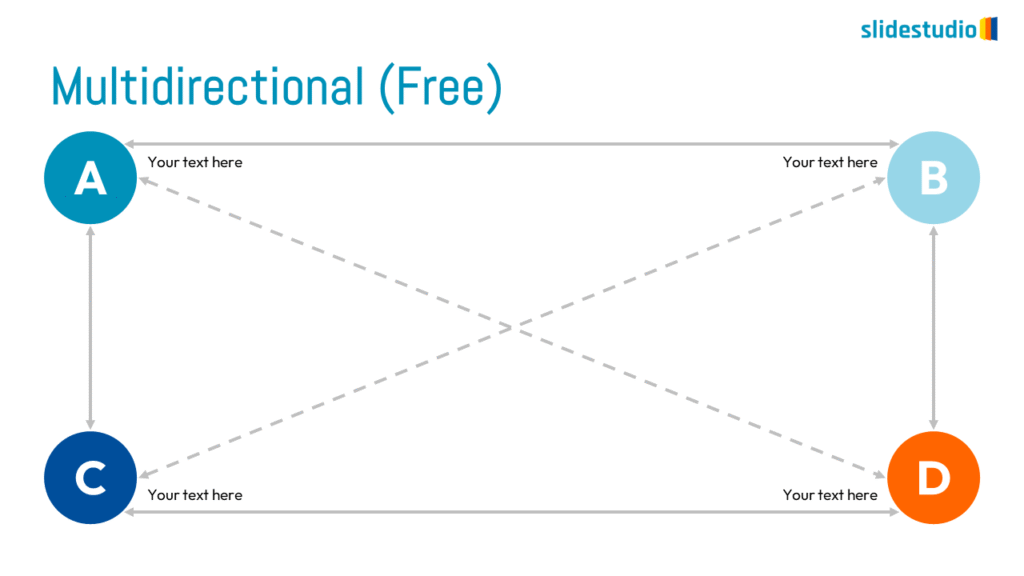
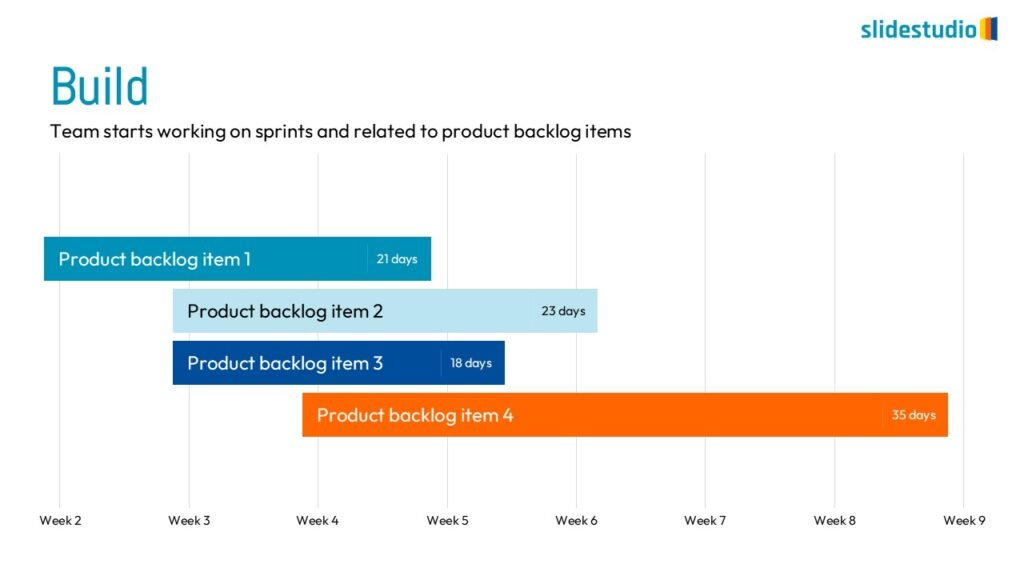
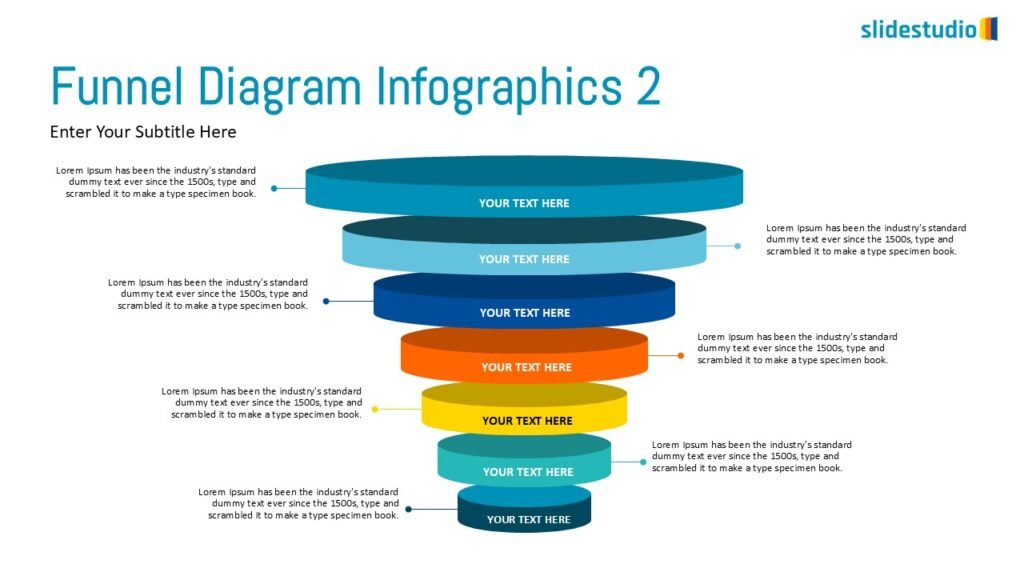
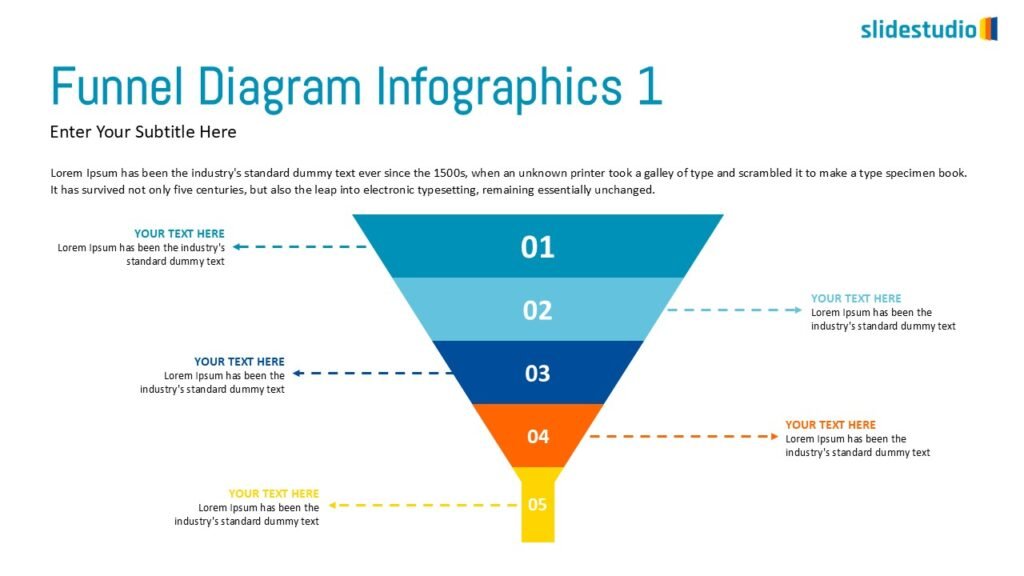
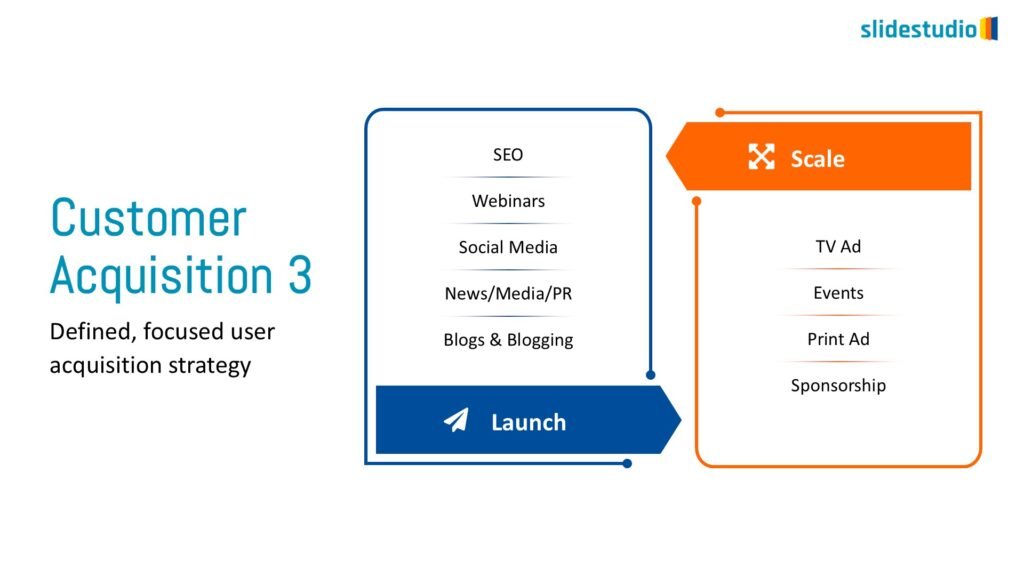
Flow
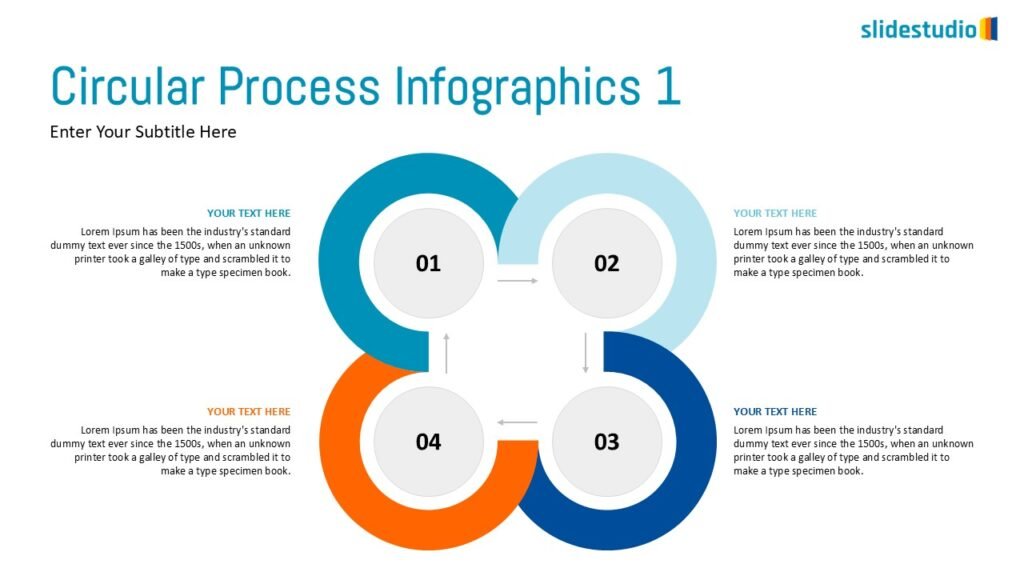
This concept focuses on illustrating the movement or progression of information. It can be represented in various forms, such as linear, circular, divergent/convergent, or multidirectional pathways, to convey how elements progress or connect in a sequence.
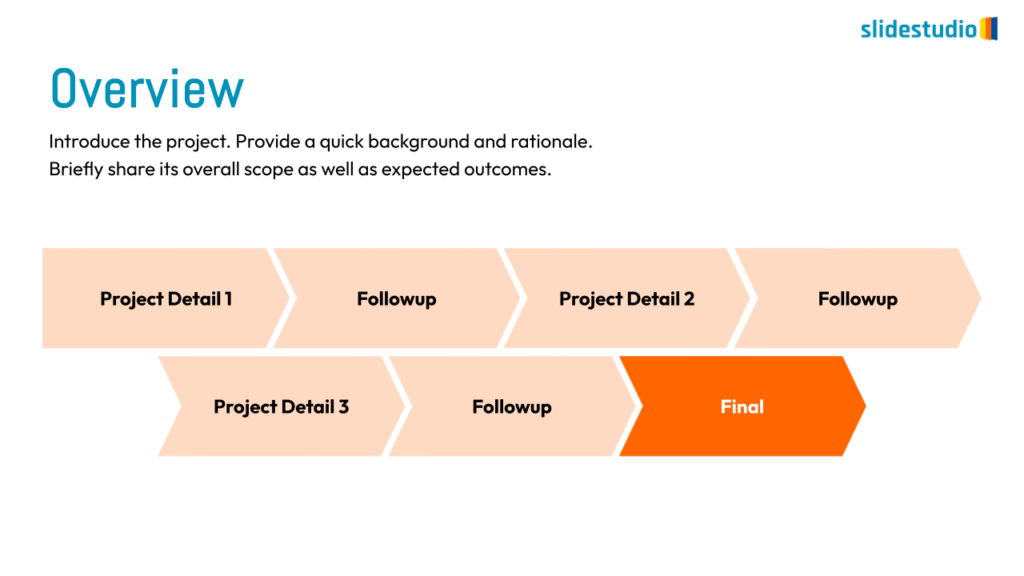
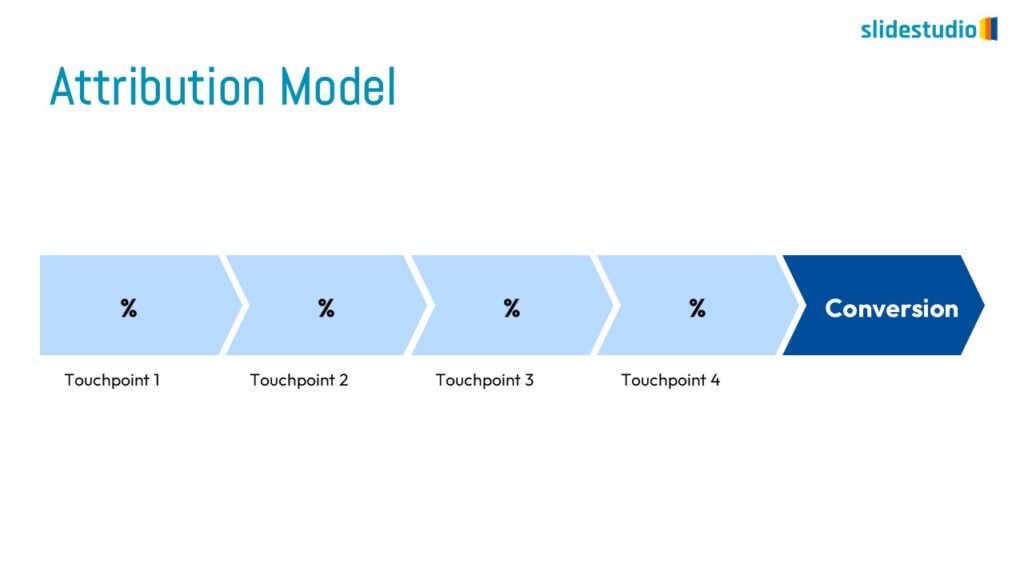
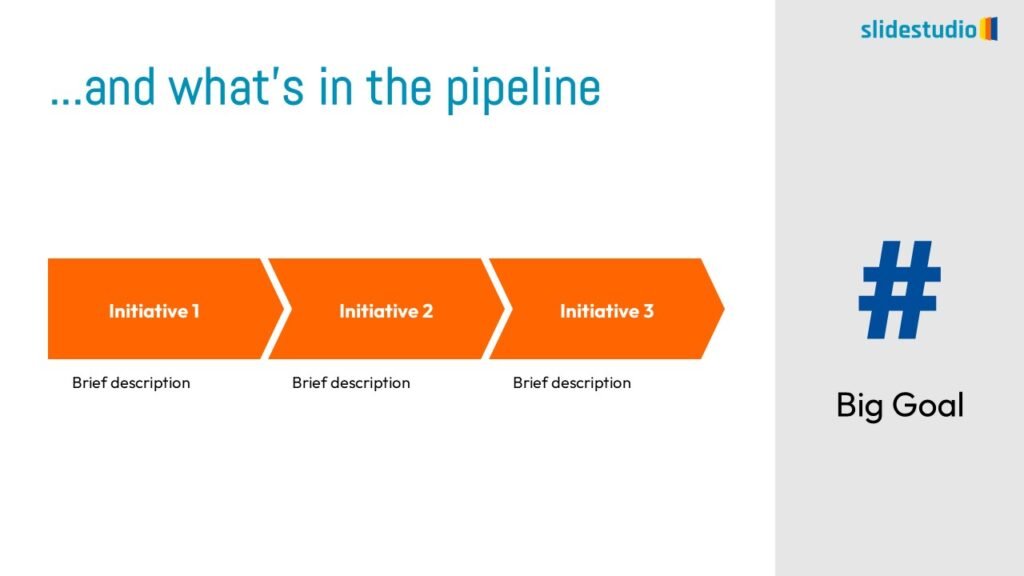
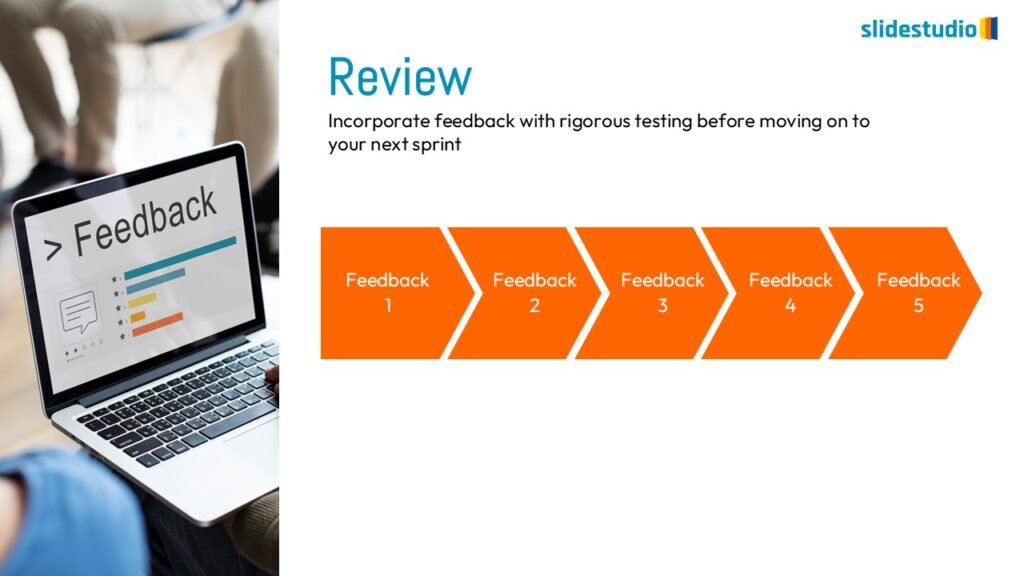
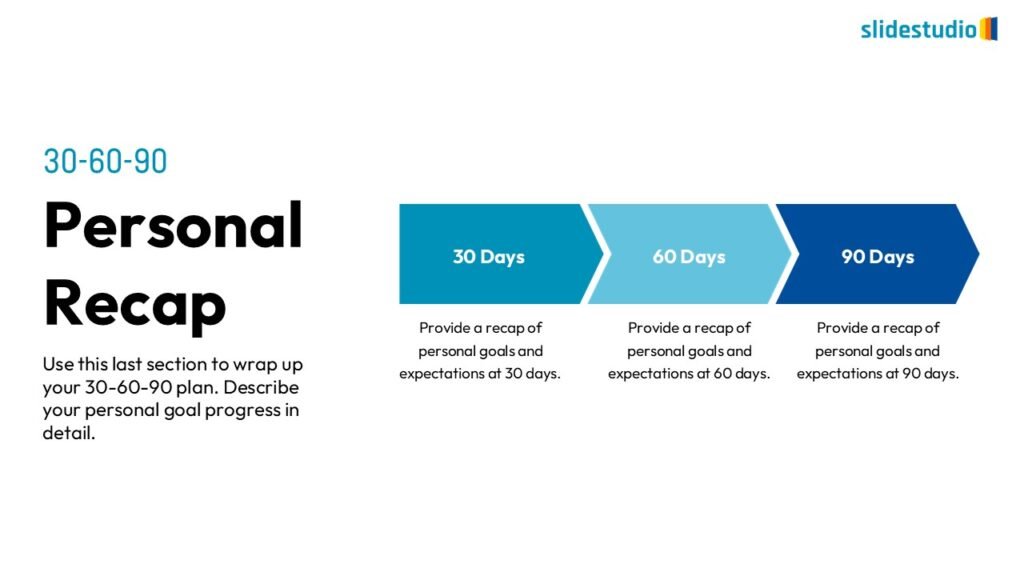
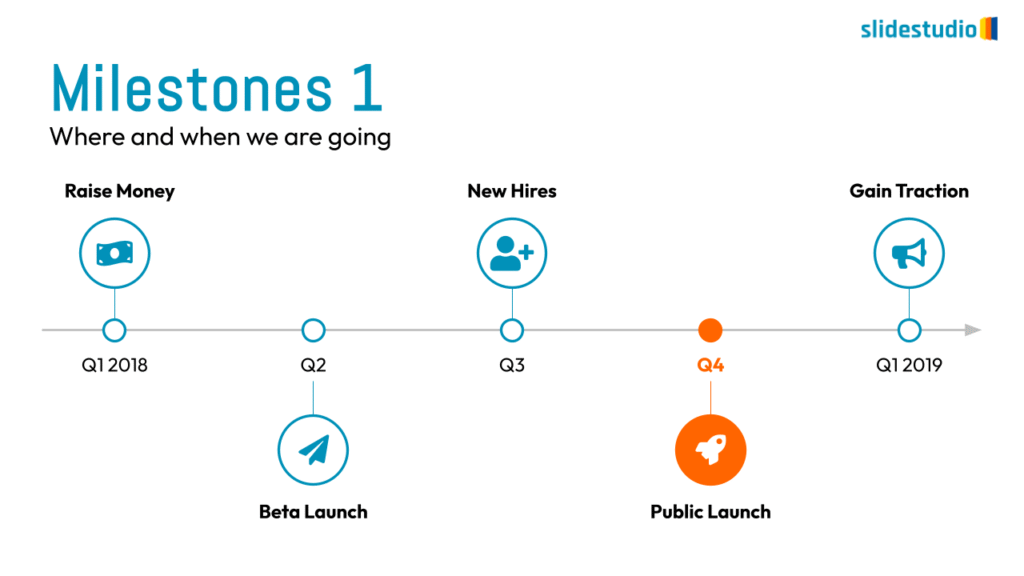
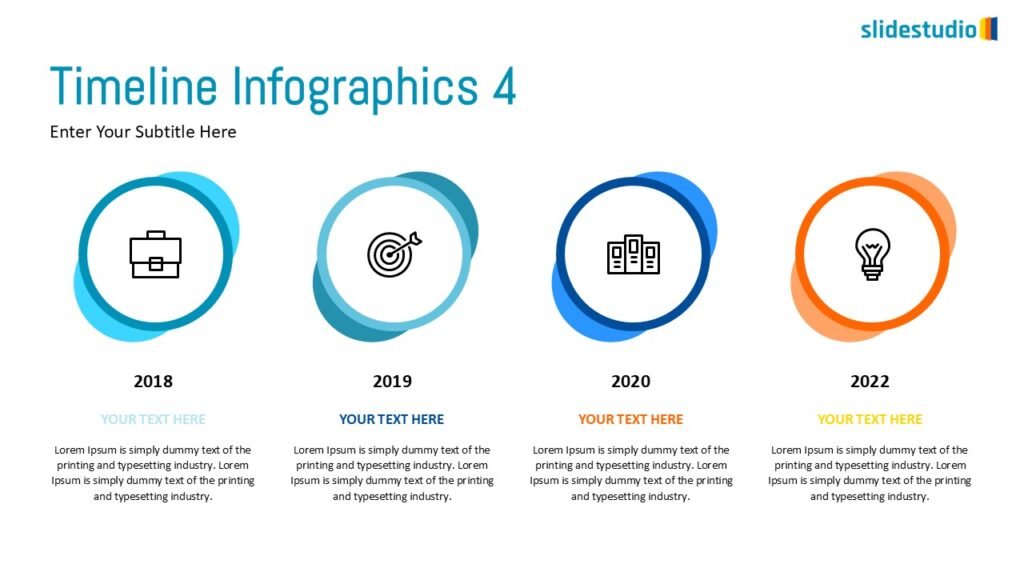
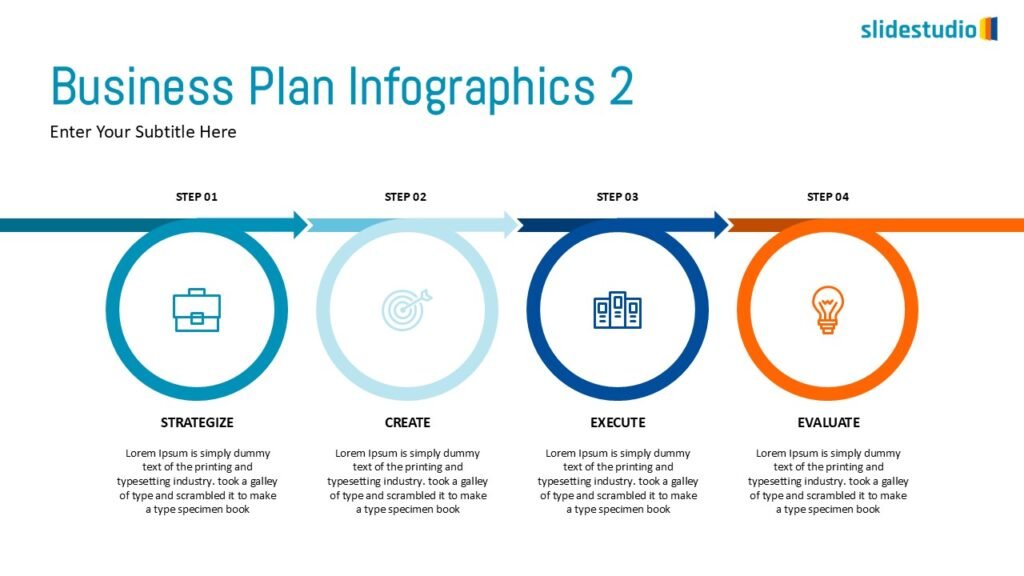
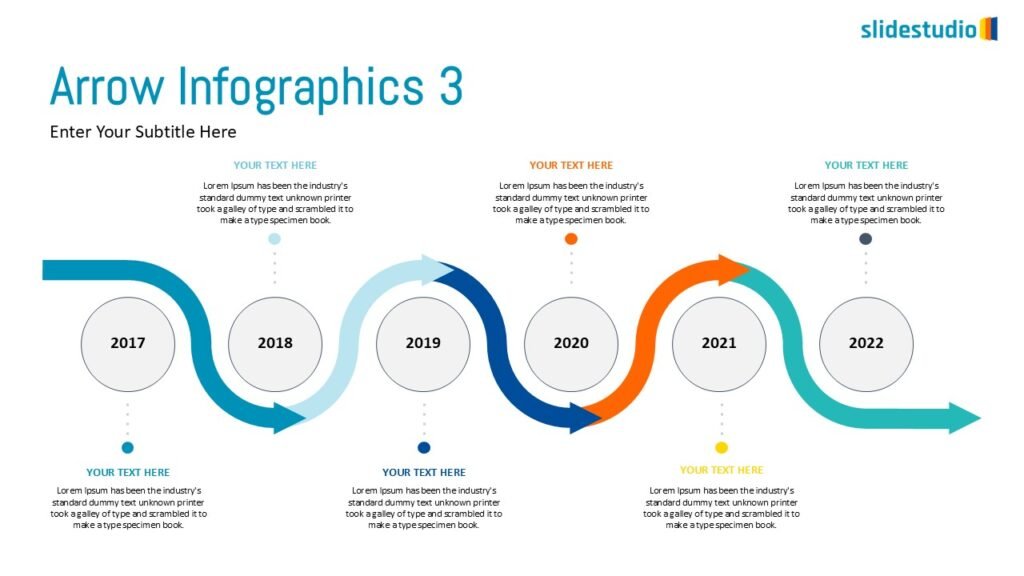
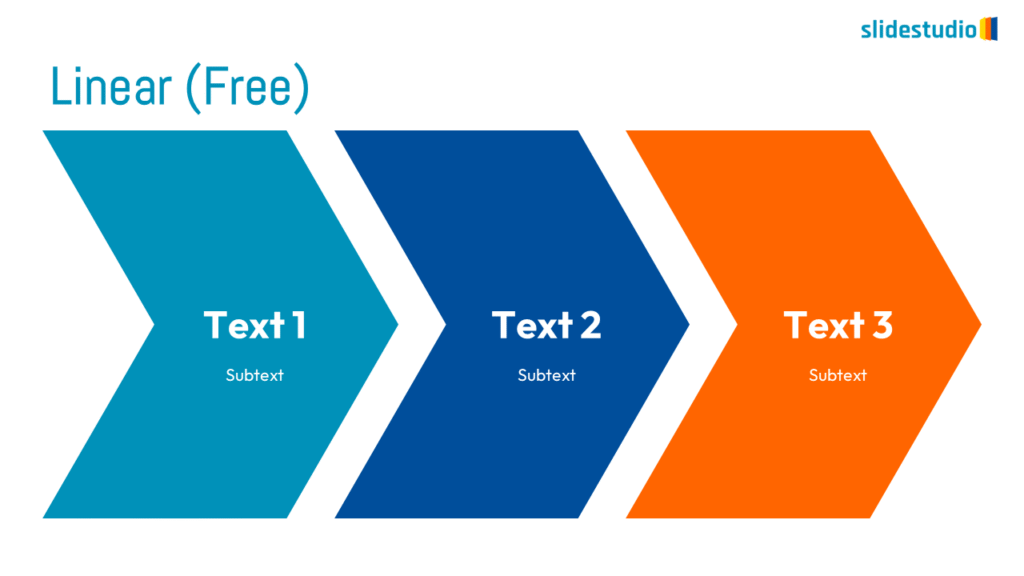
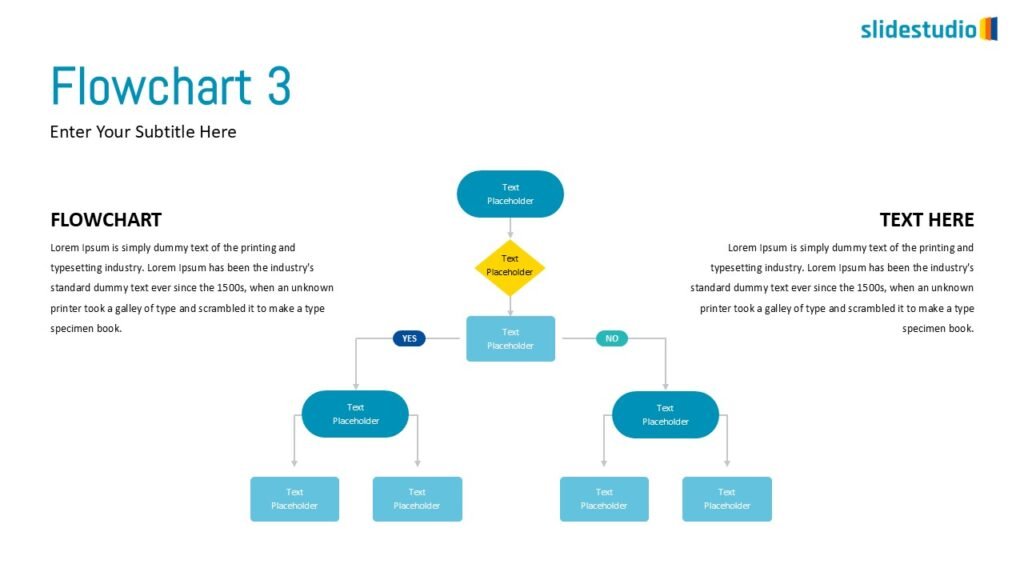
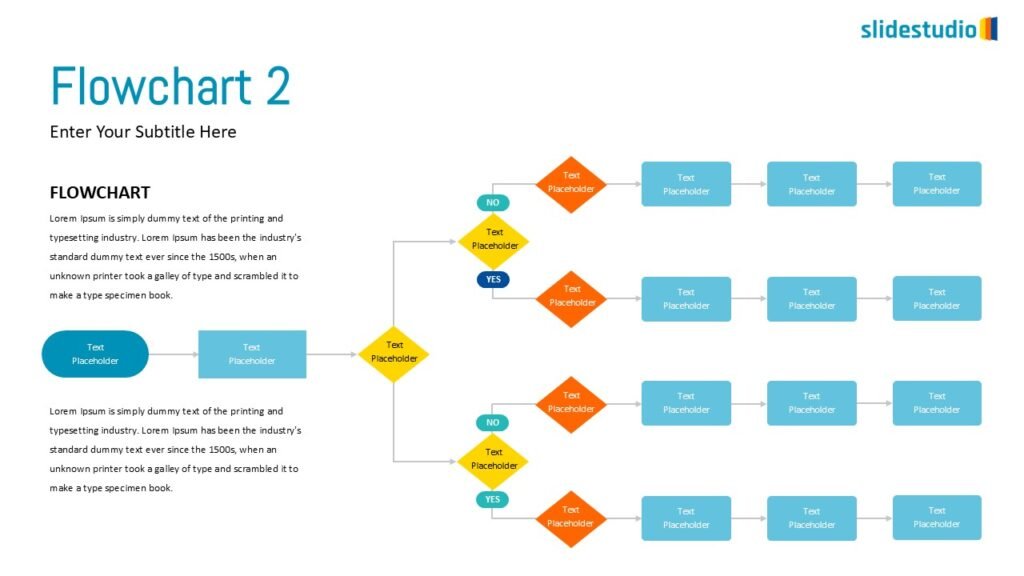
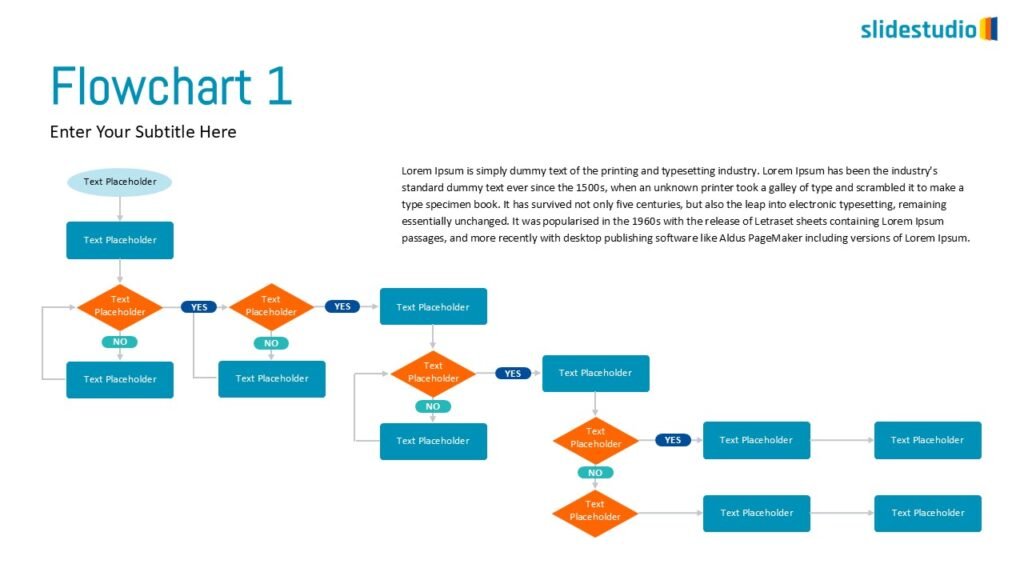
Linear
A step-by-step structure that illustrates a straightforward progression from start to finish.
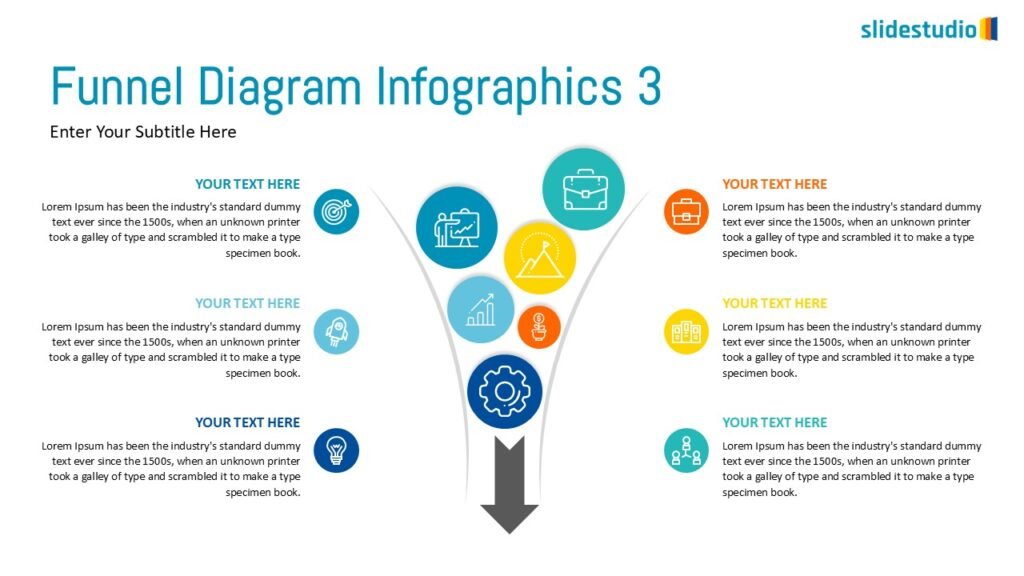
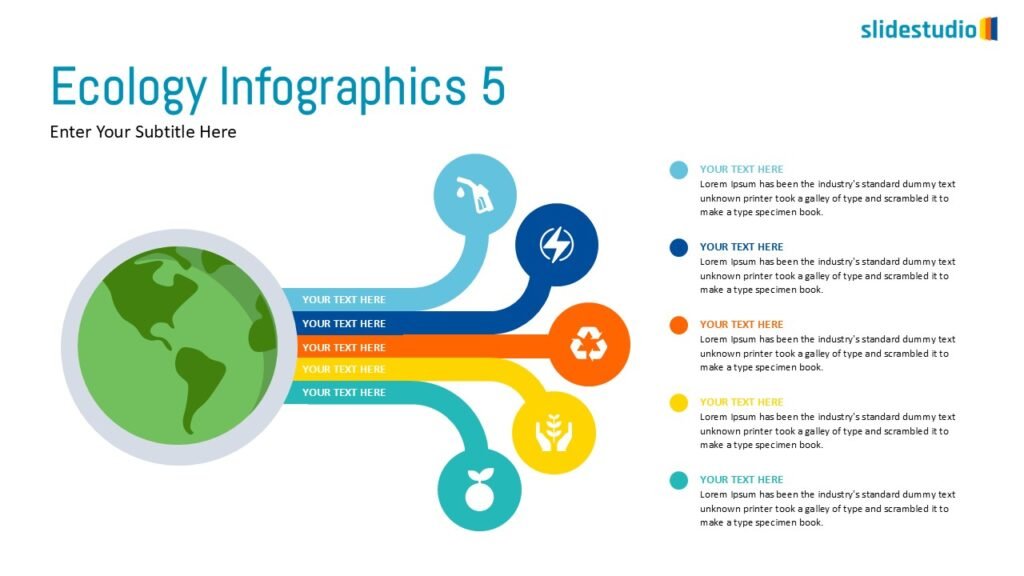
DIVERGENT/CONVERGENT
A flow that branches out or converges, ideal for showing multiple pathways or merging ideas.
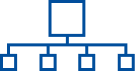
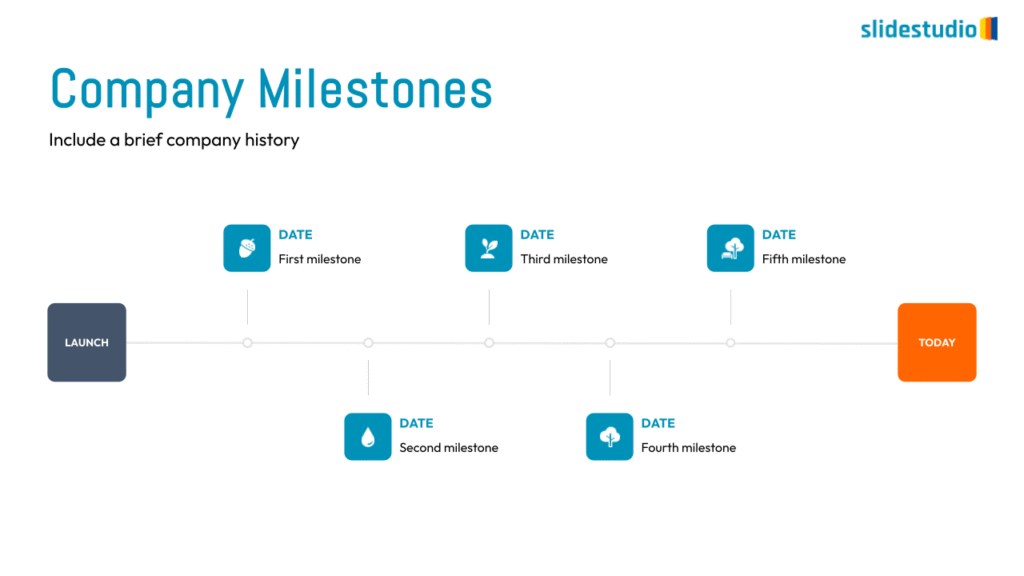
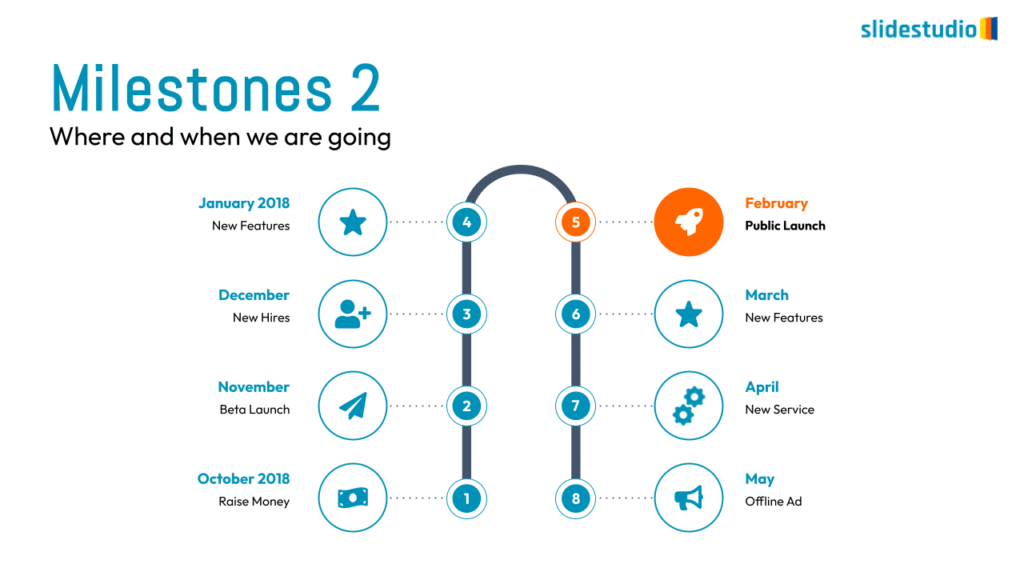
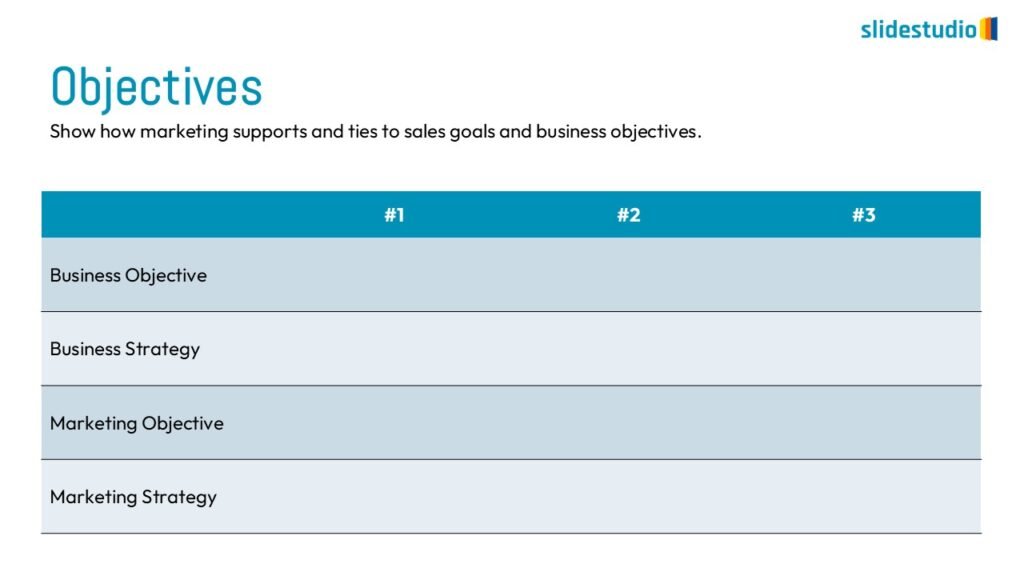
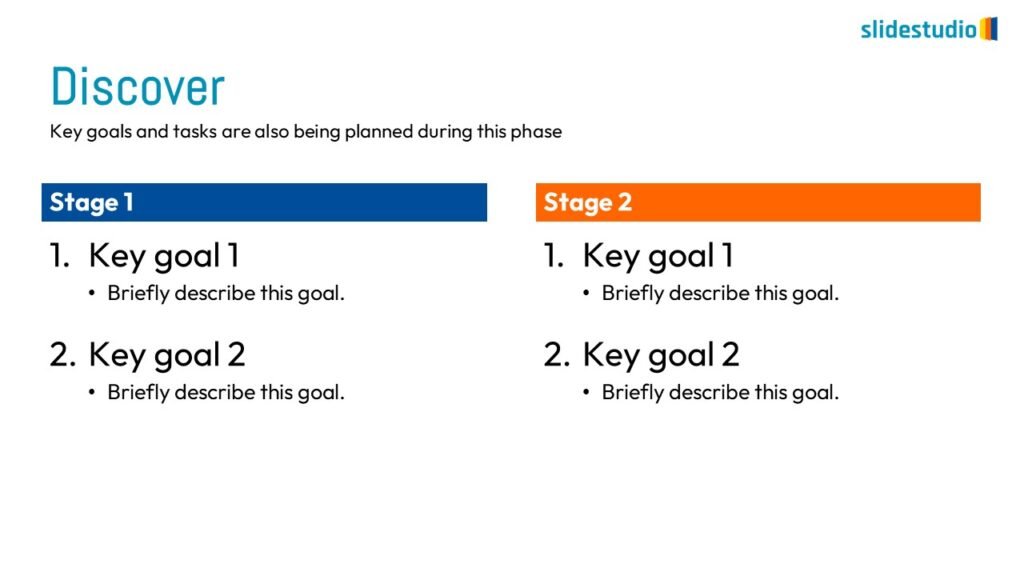
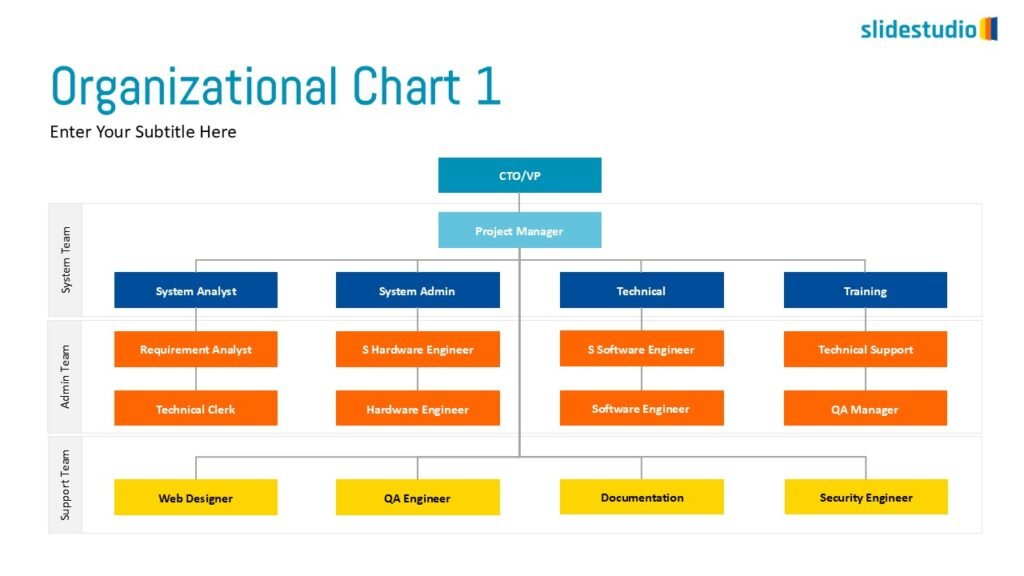
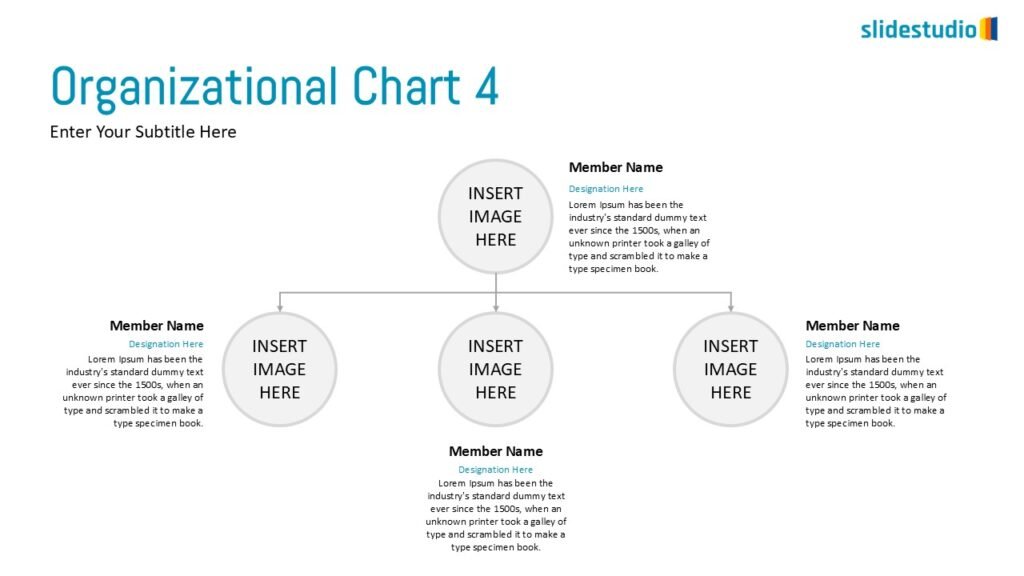
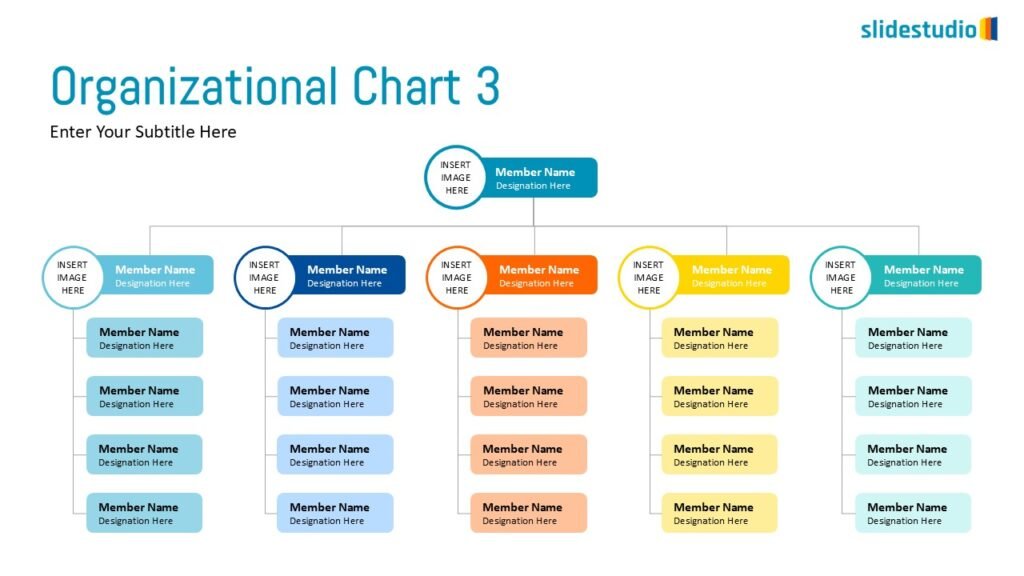
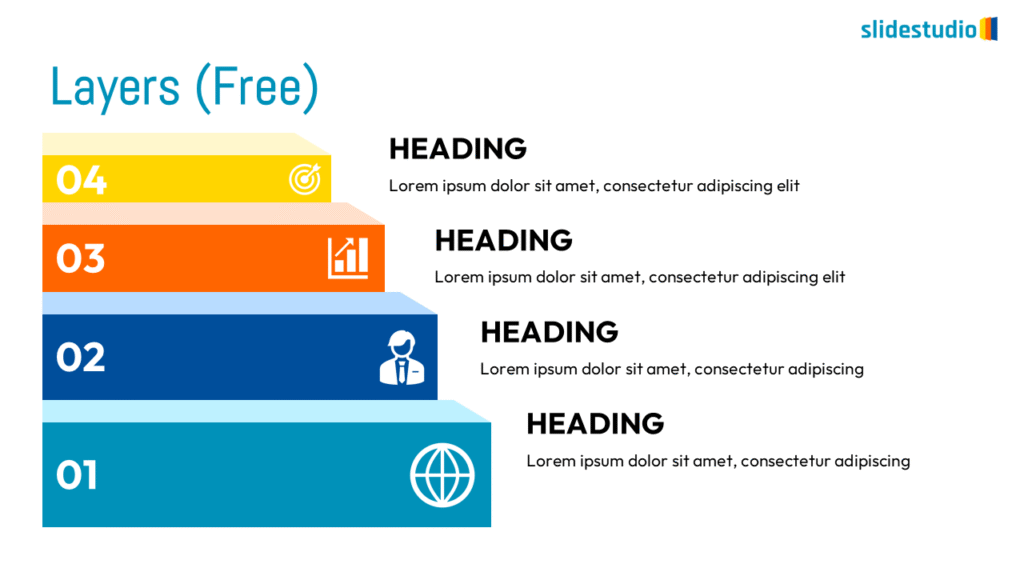
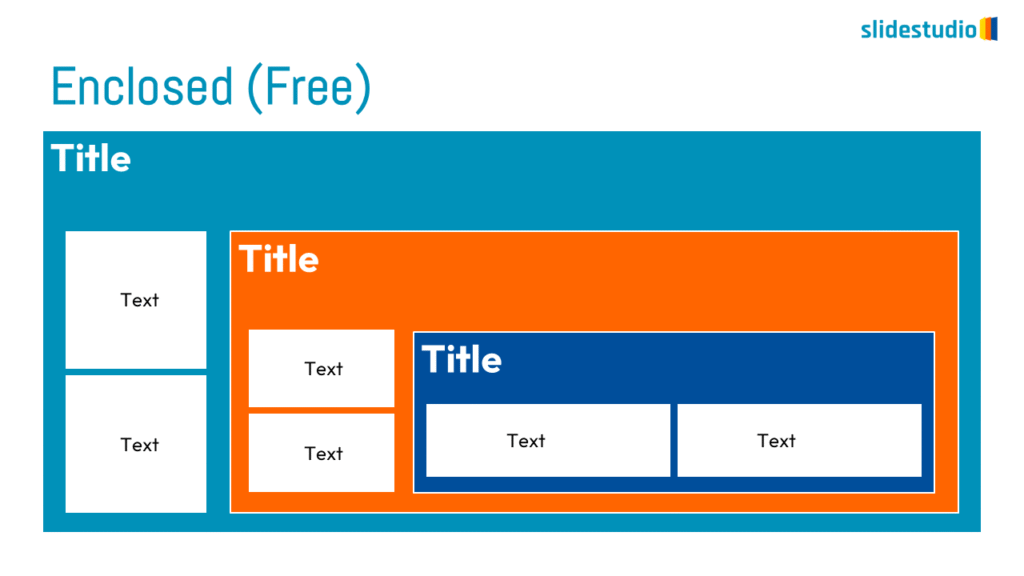
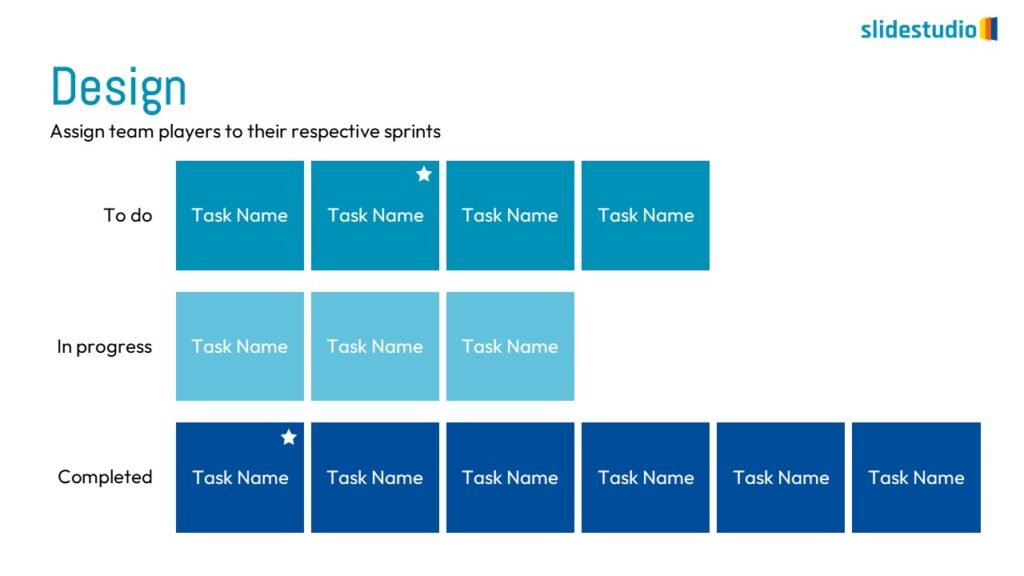
Structure
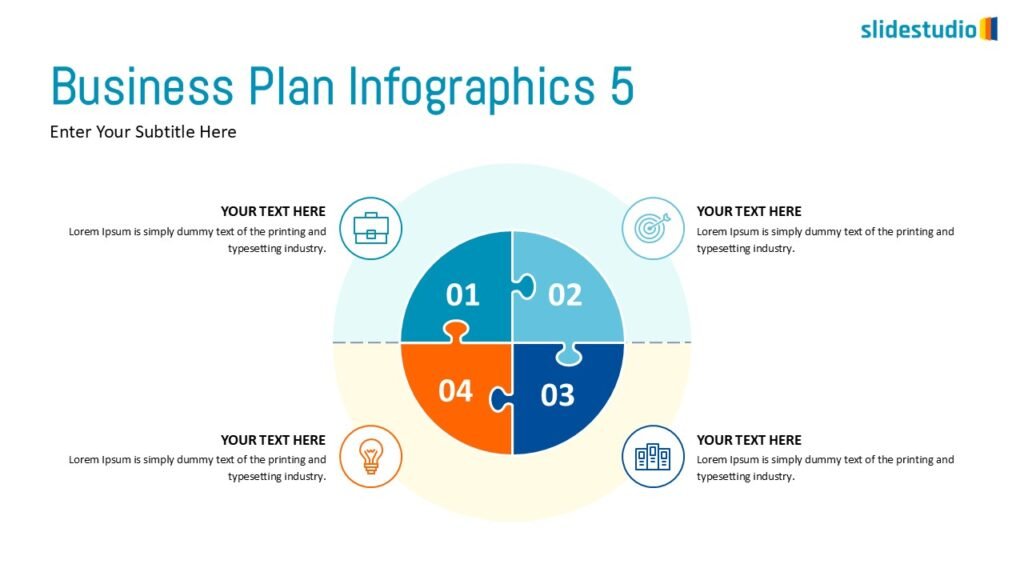
This concept organizes information hierarchically or categorically, often using matrices, trees, or layered arrangements. It helps to present the framework or arrangement of components within a system or process.
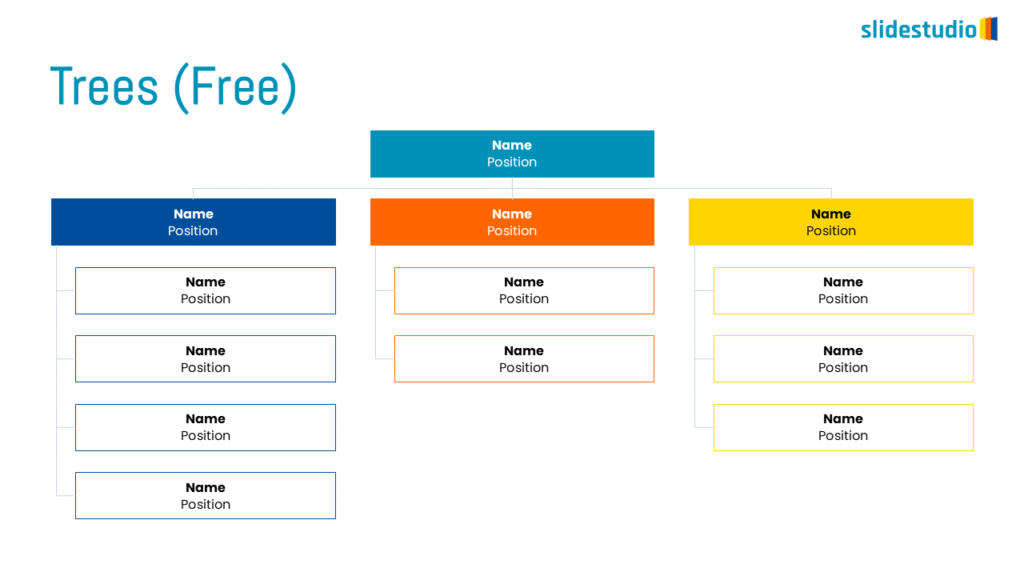
TREES
A hierarchical layout that maps out connections, such as organizational charts or family trees.
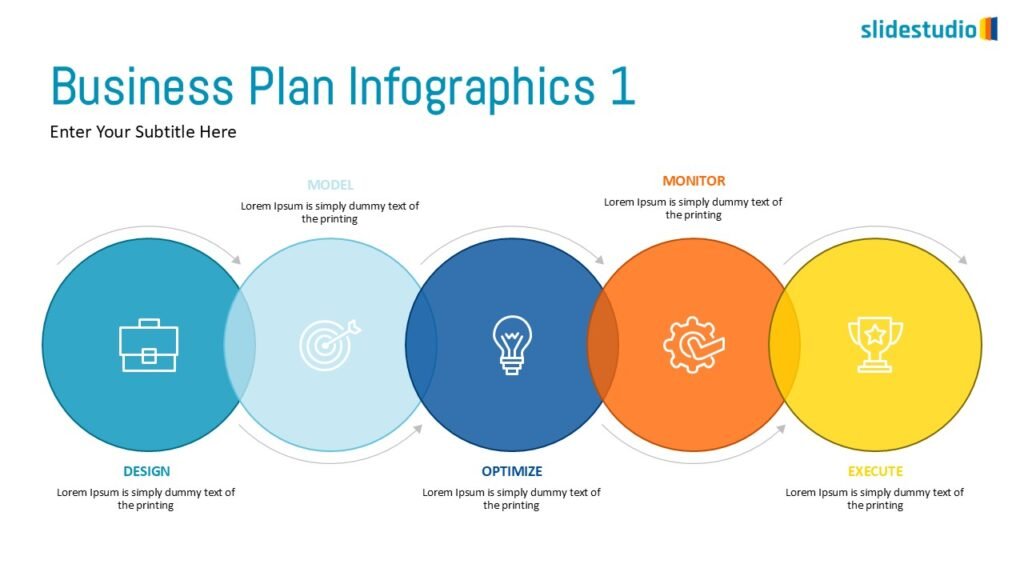
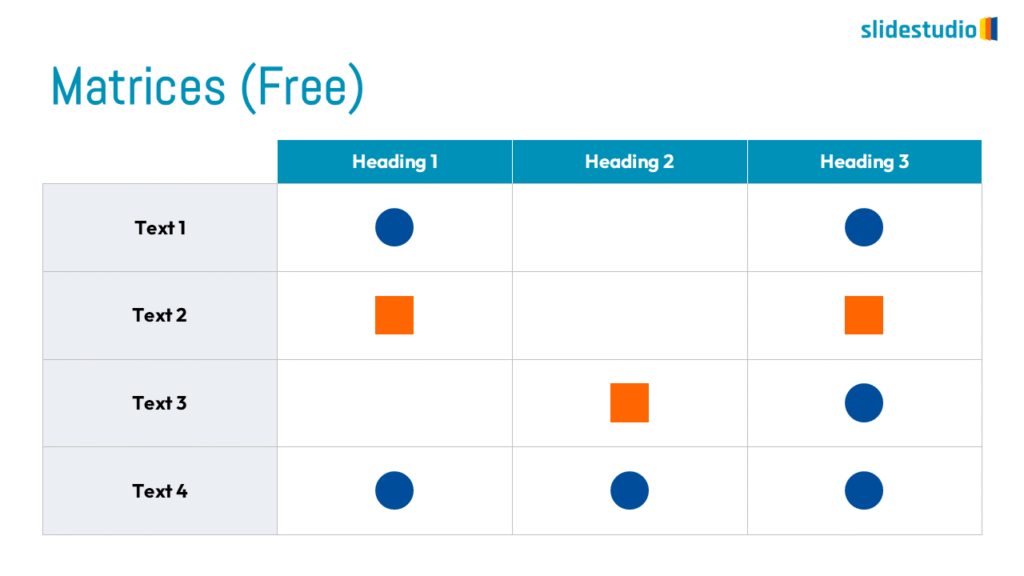
Cluster
This concept visually groups related items together, showing associations or overlaps. Cluster designs c to represent elements that belong together within a context or theme.
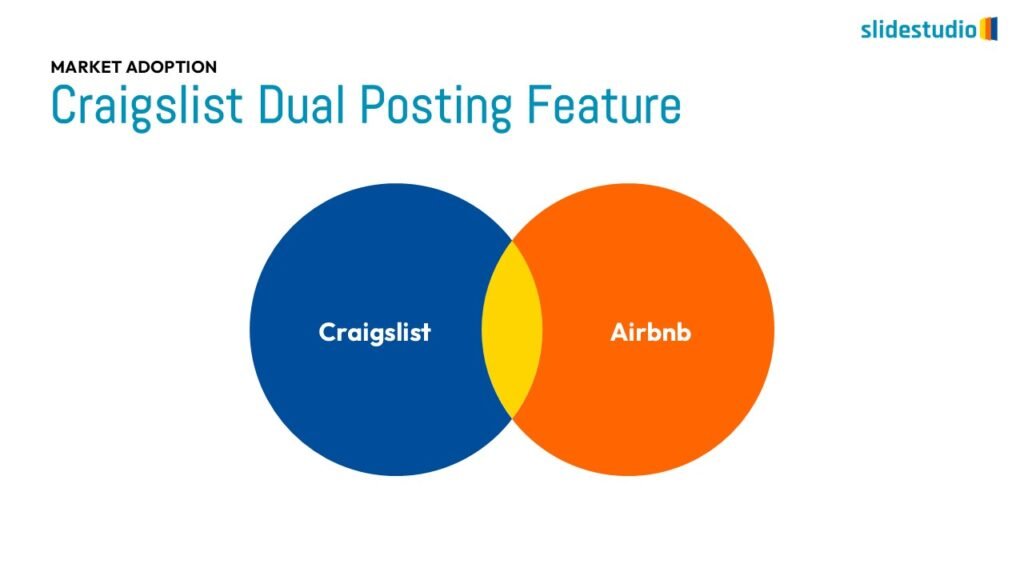
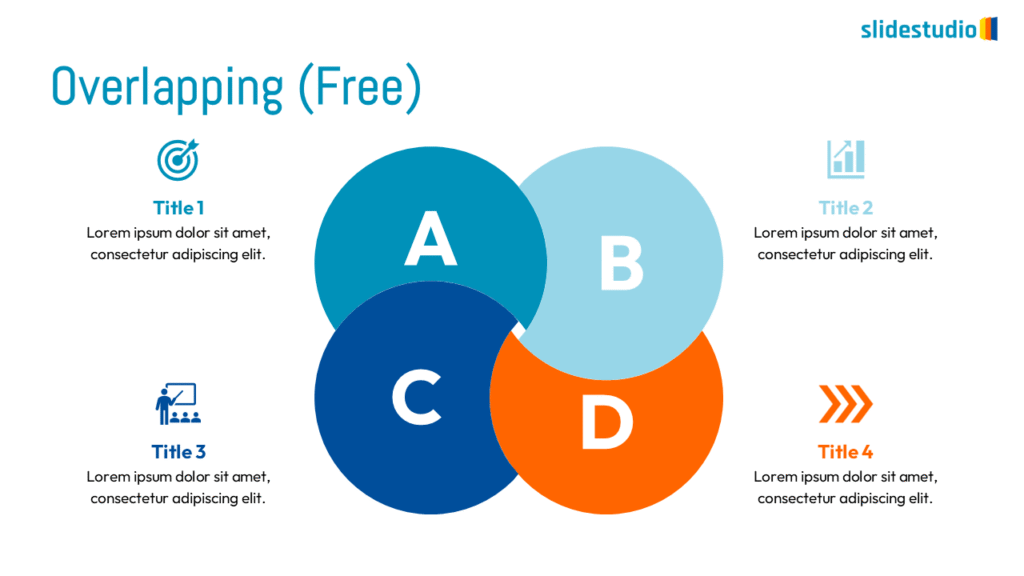
OVERLAPPING
Displays shared areas or intersections, useful for showing commonalities in Venn diagrams.
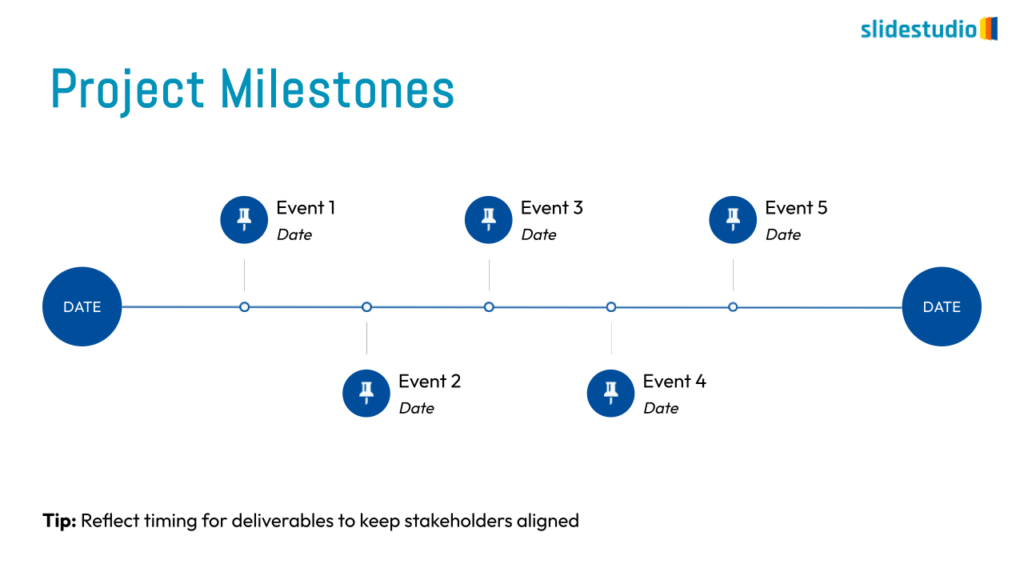
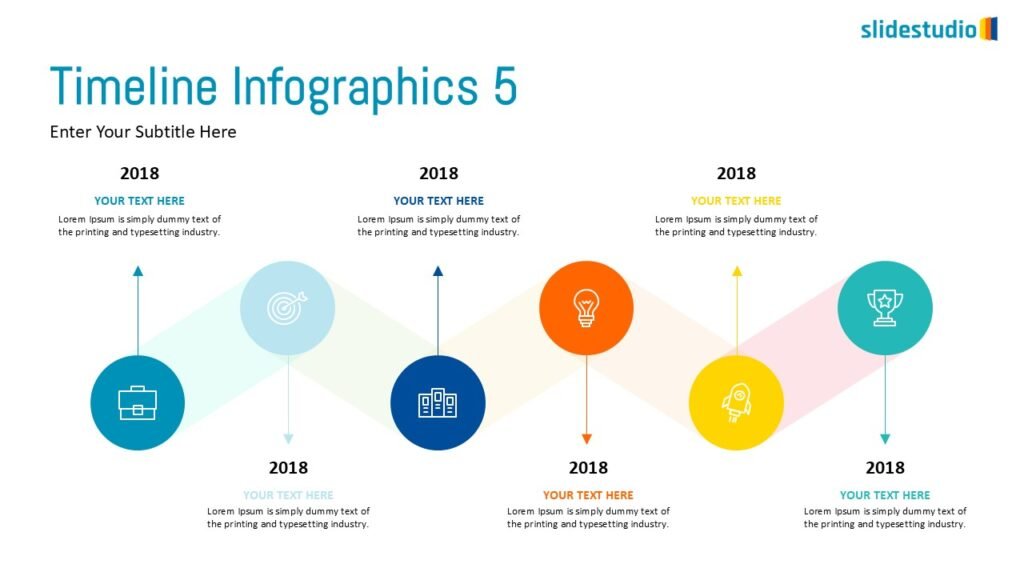
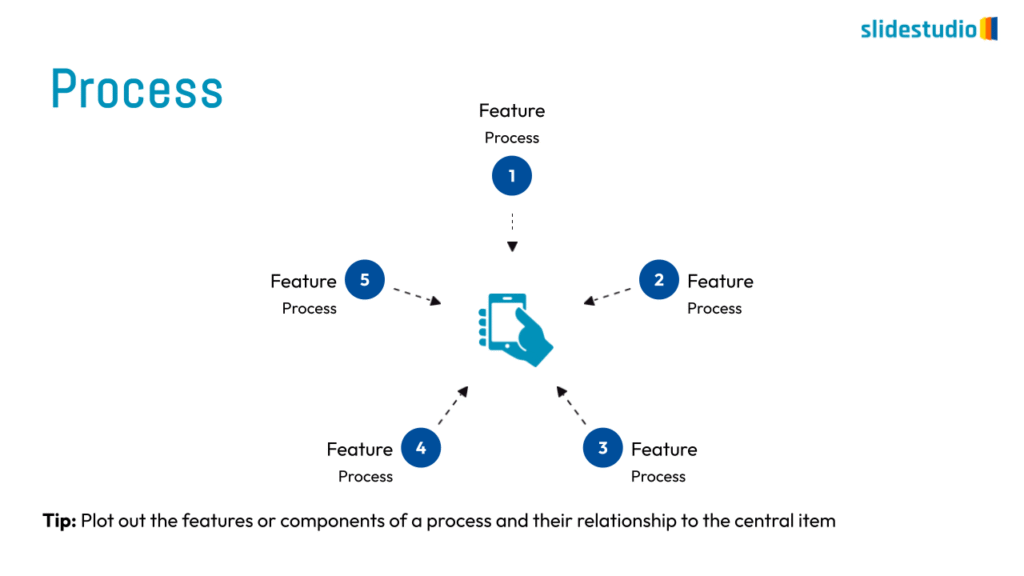
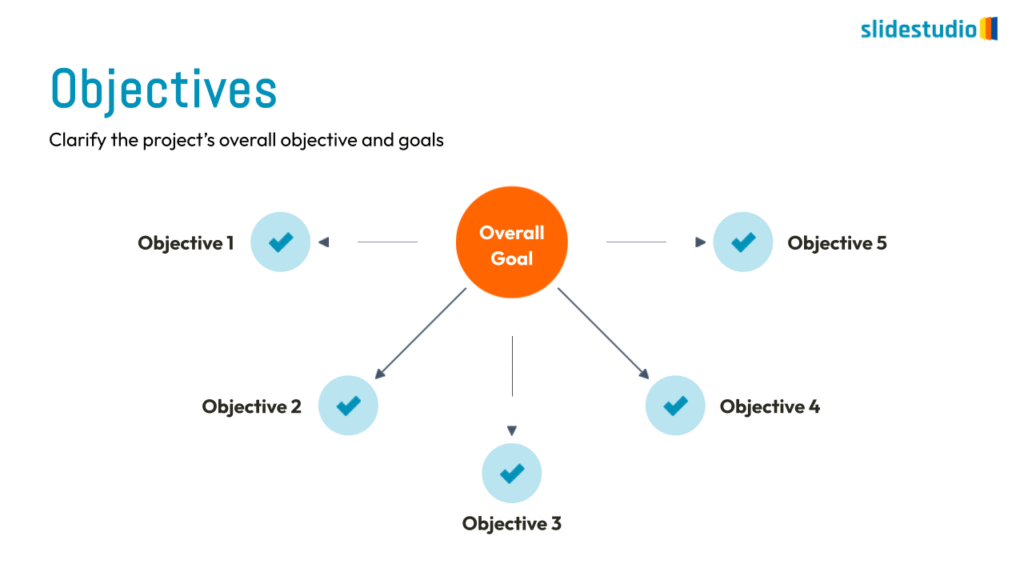
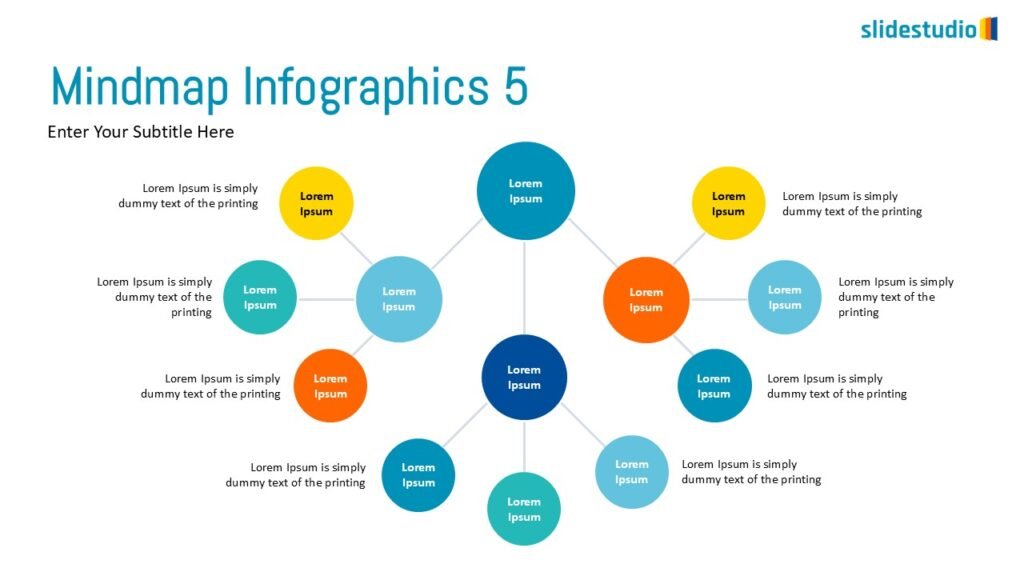
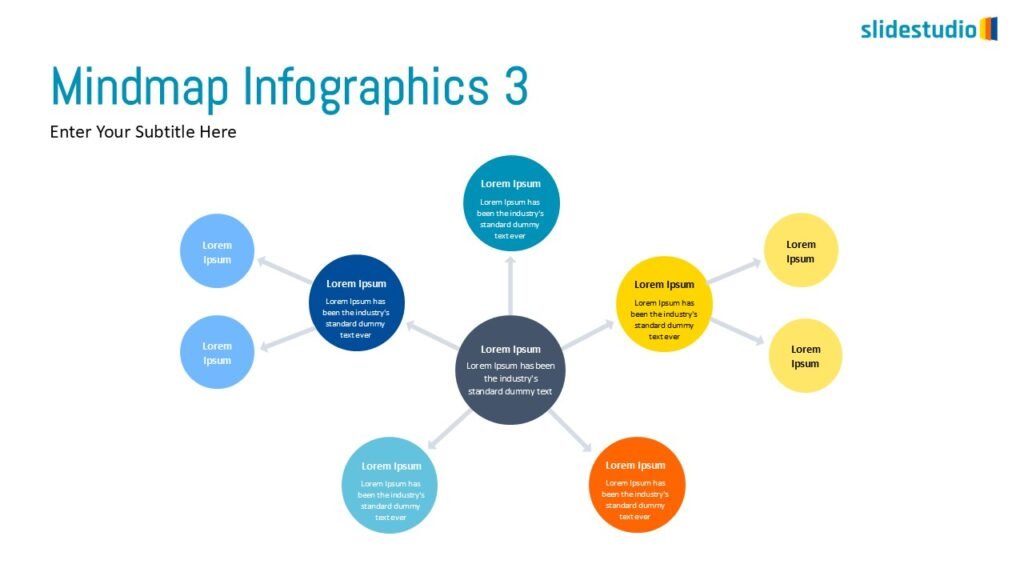
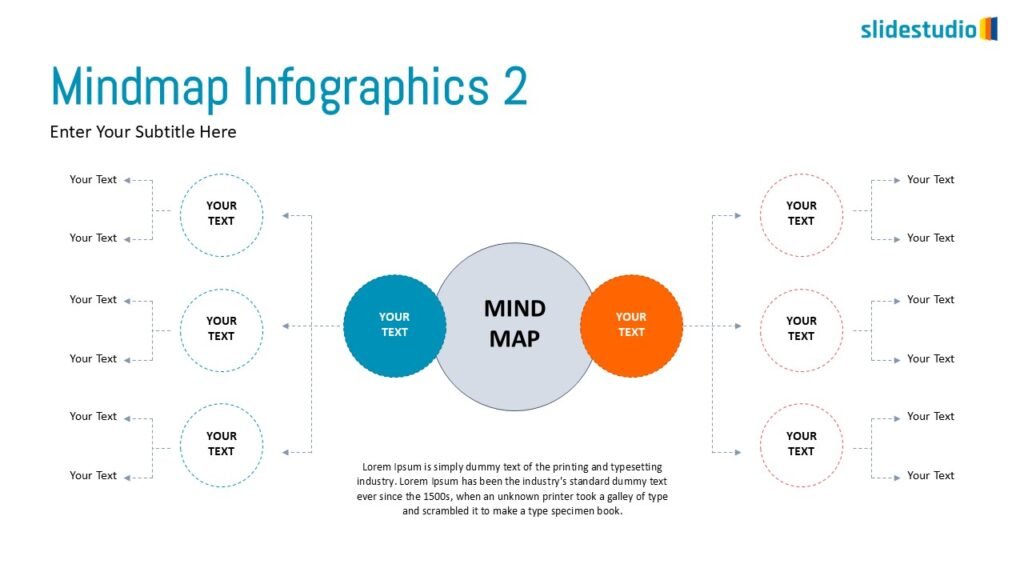
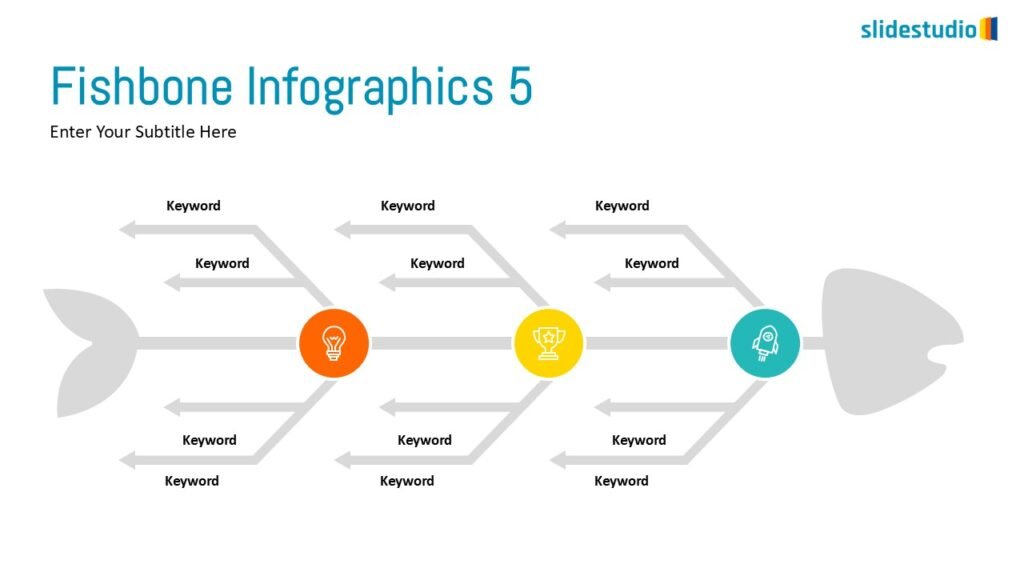
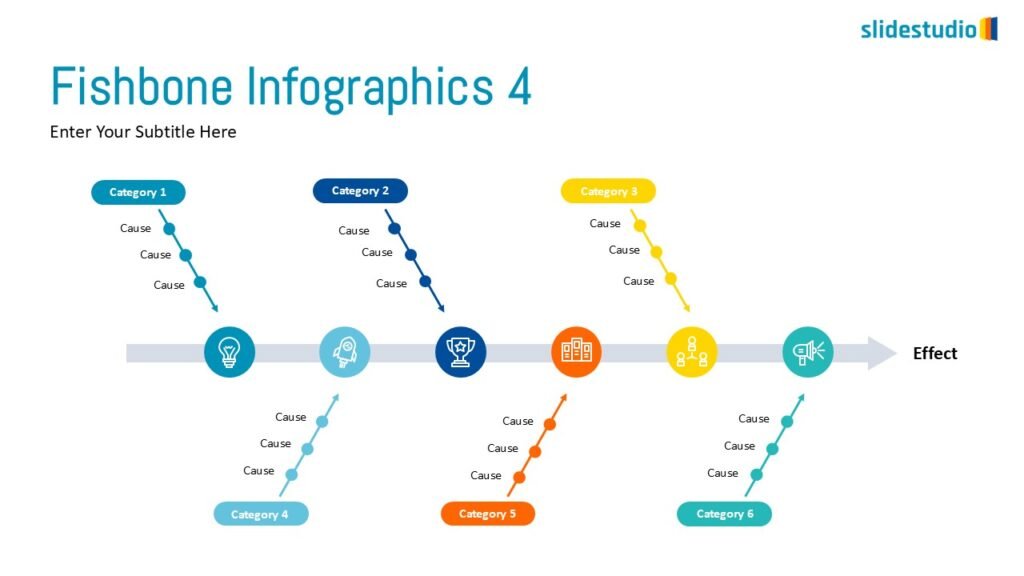
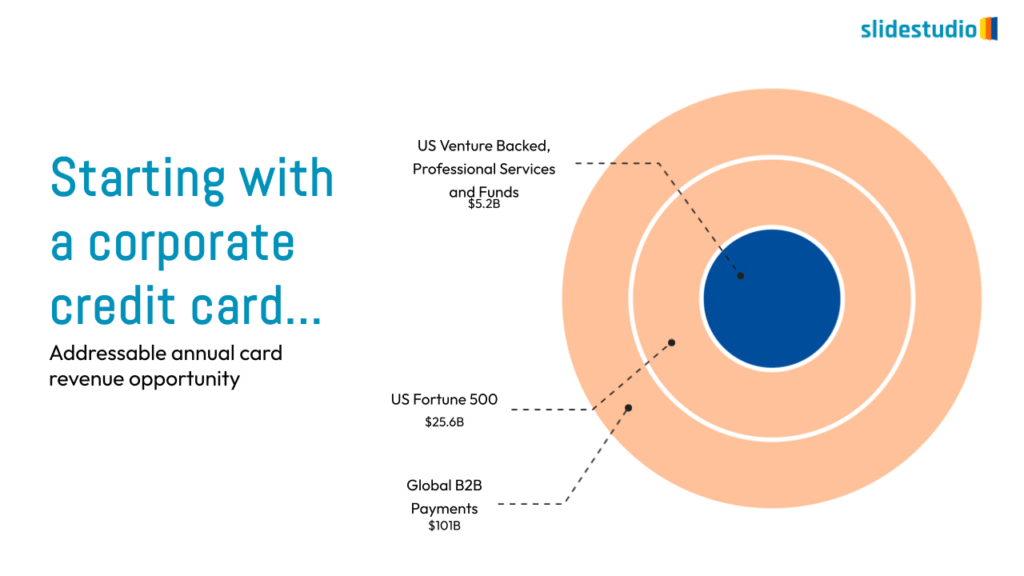
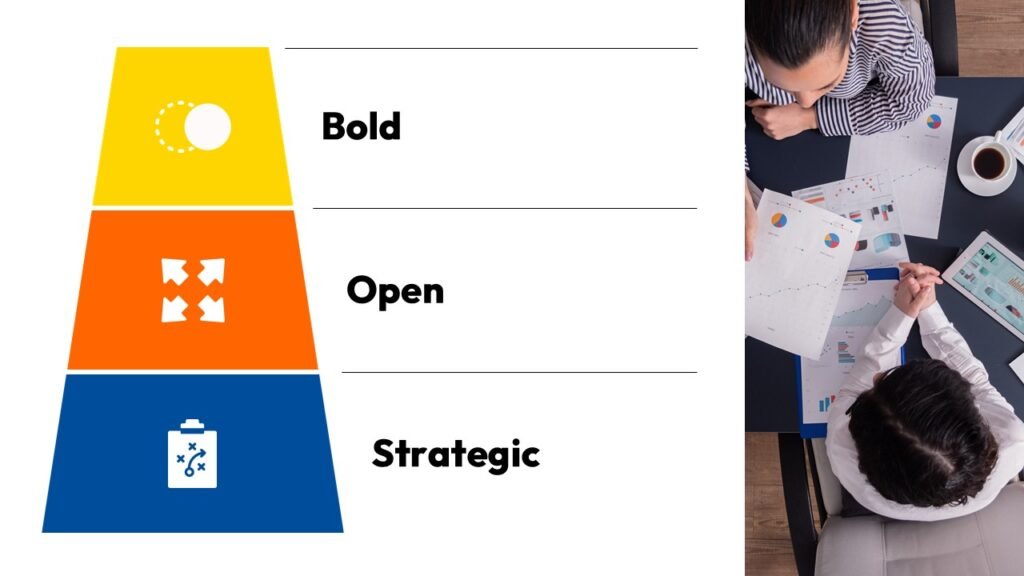
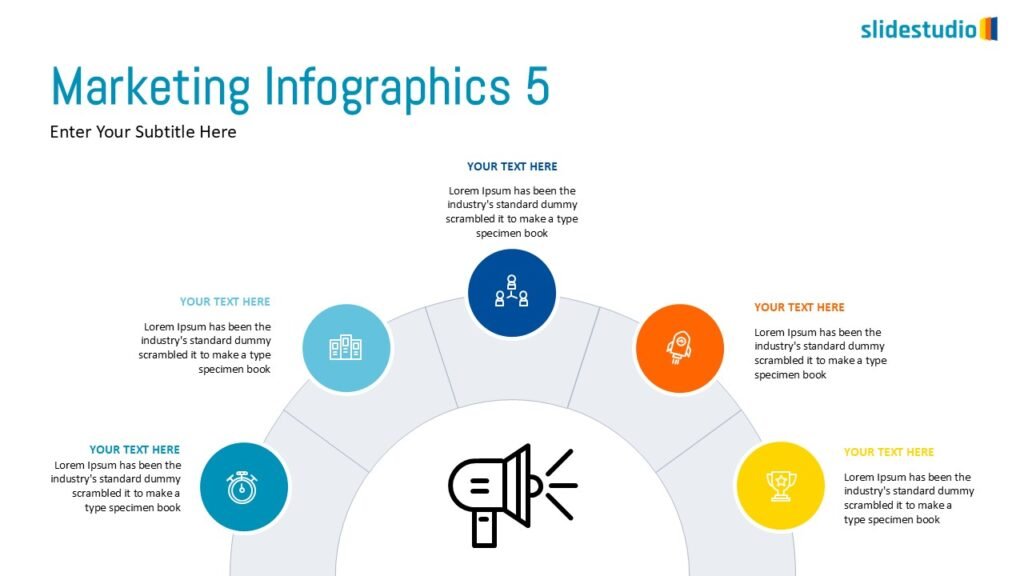
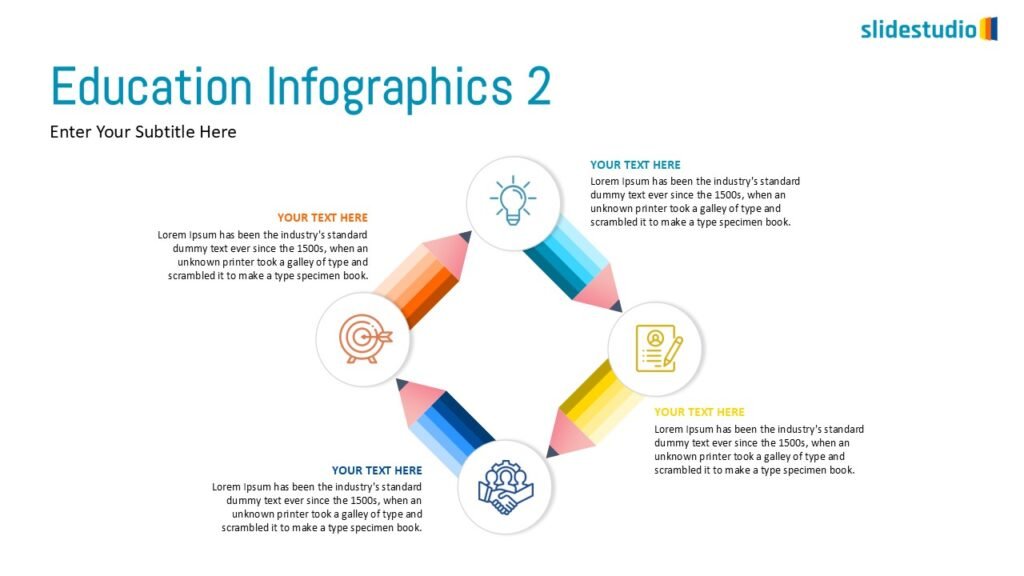
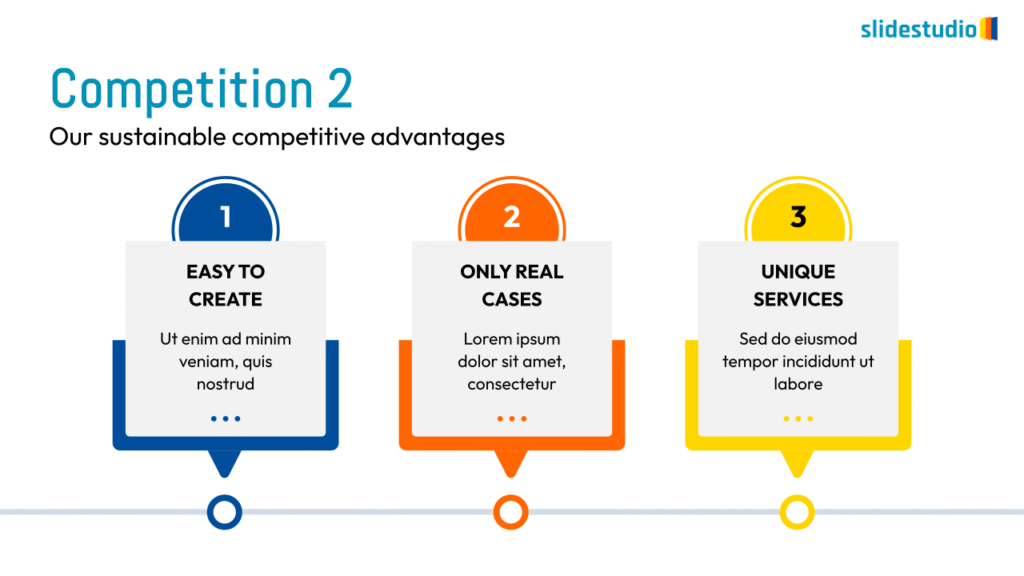
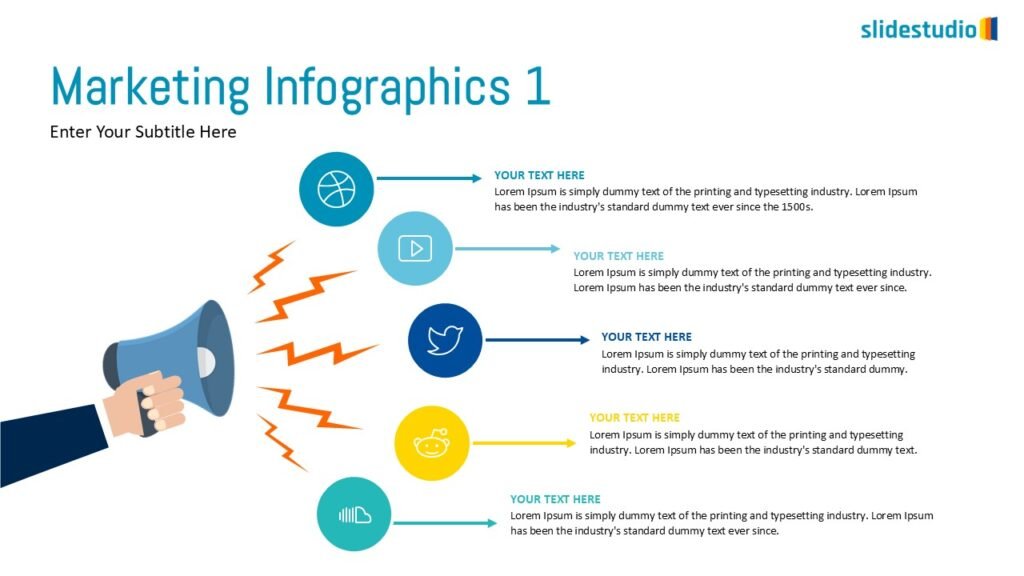
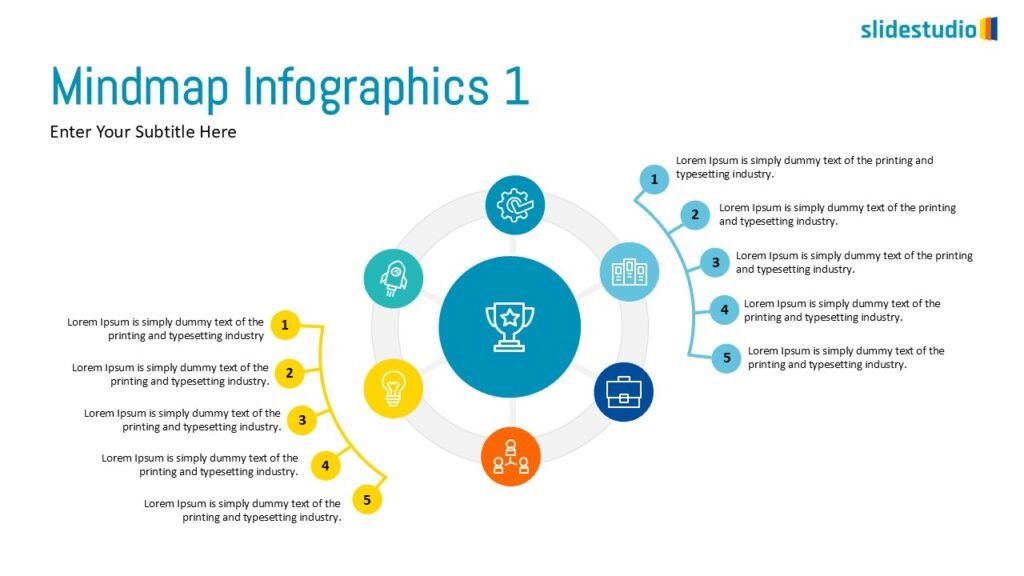
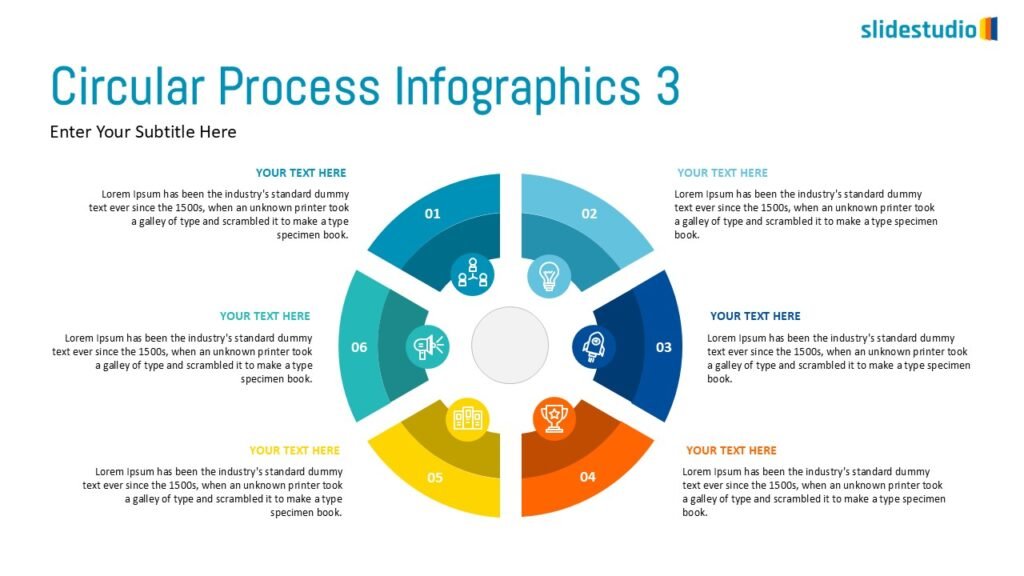
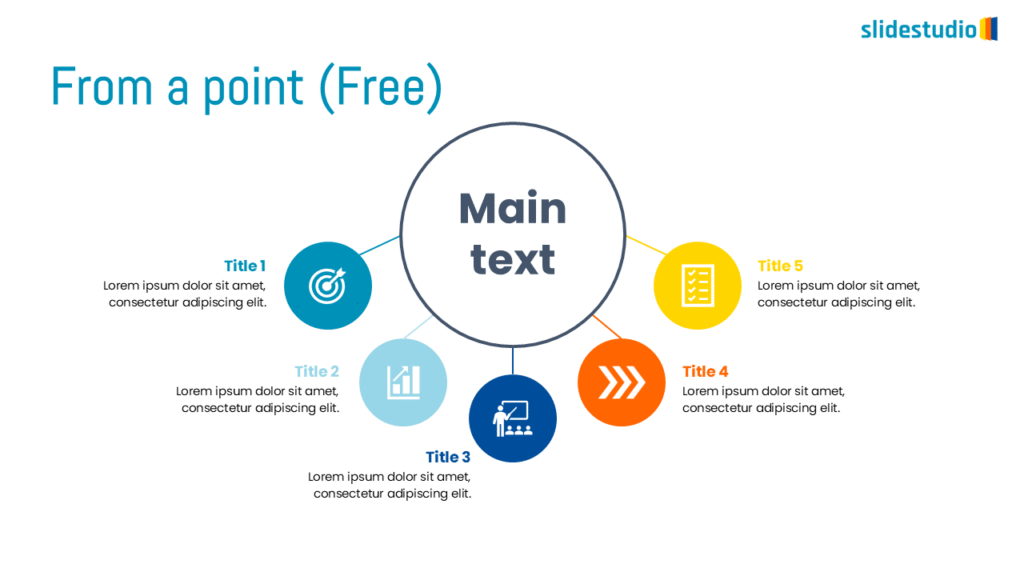
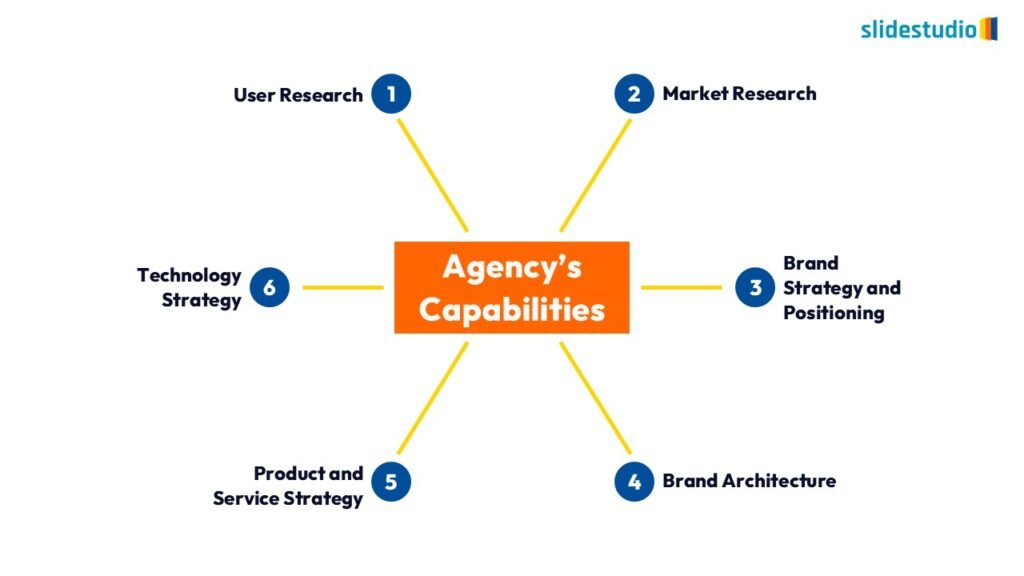
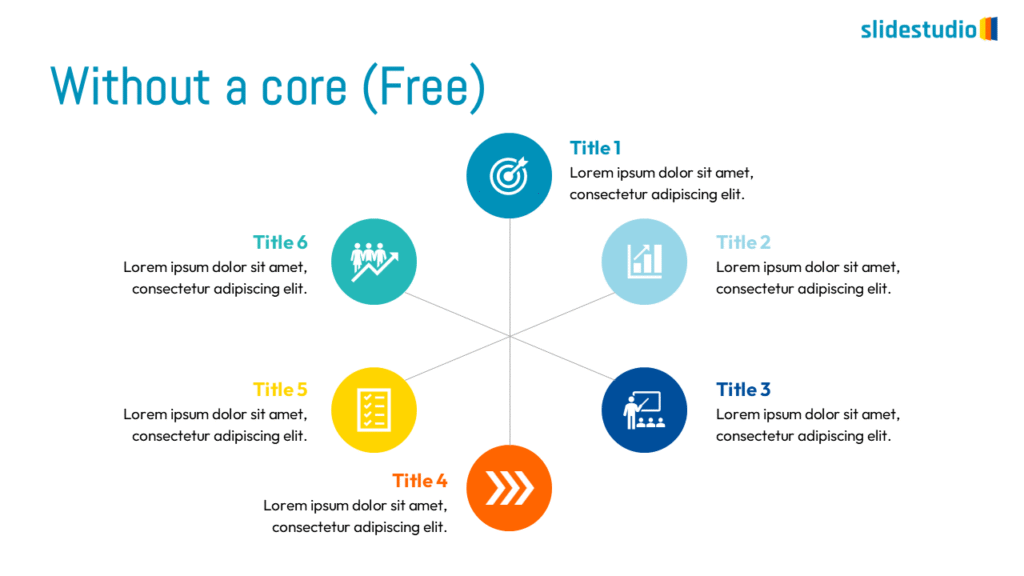
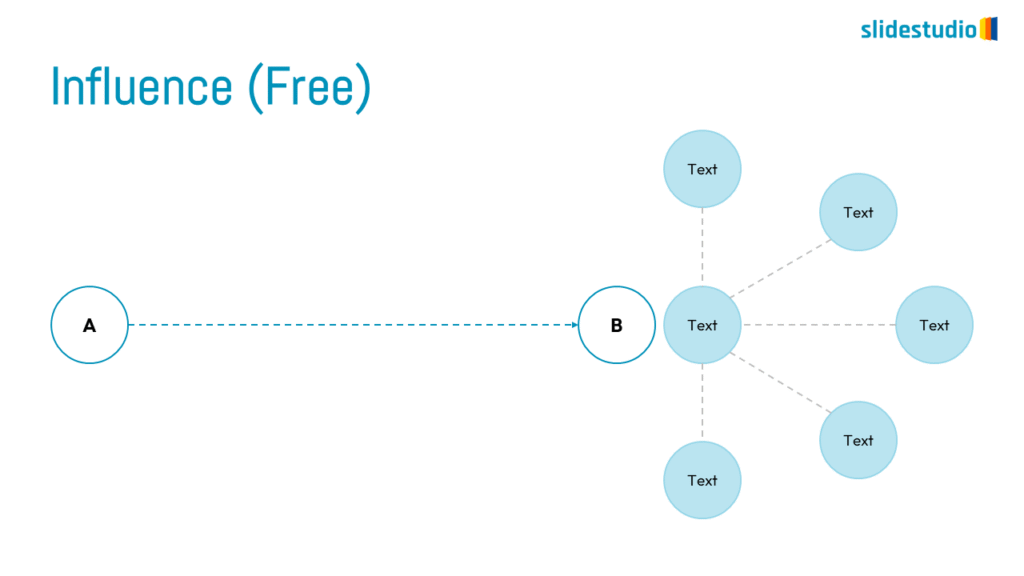
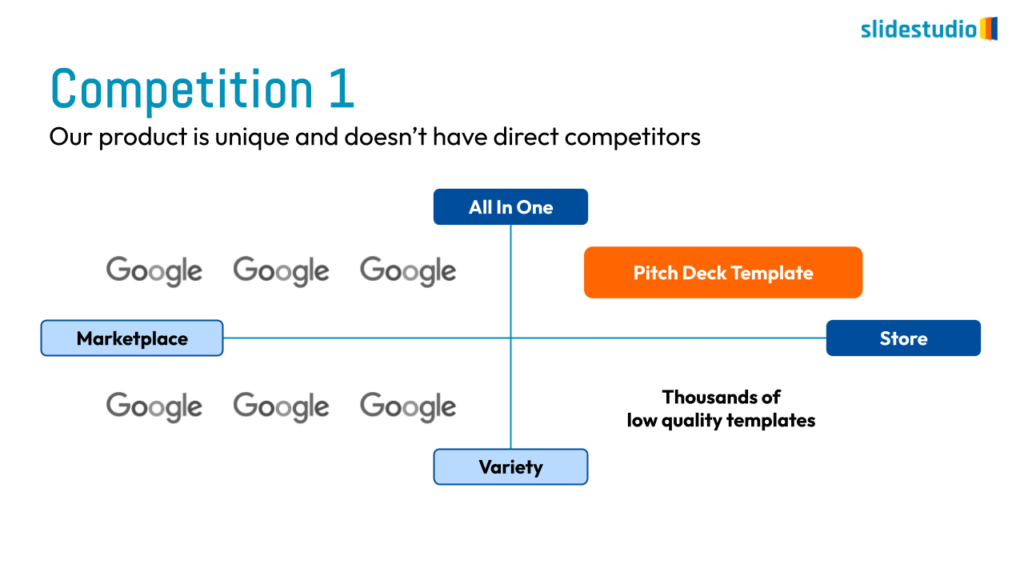
Radiate
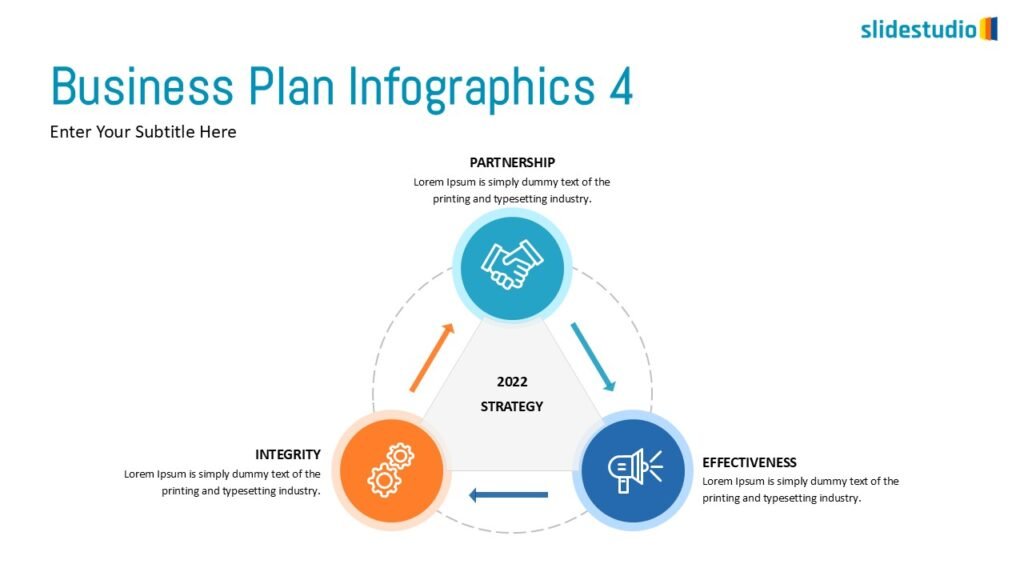
This concept shows elements extending outward from a central point, typically illustrating a spread or influence. It can be depicted with or without a core and represents a central idea that radiates outwards.

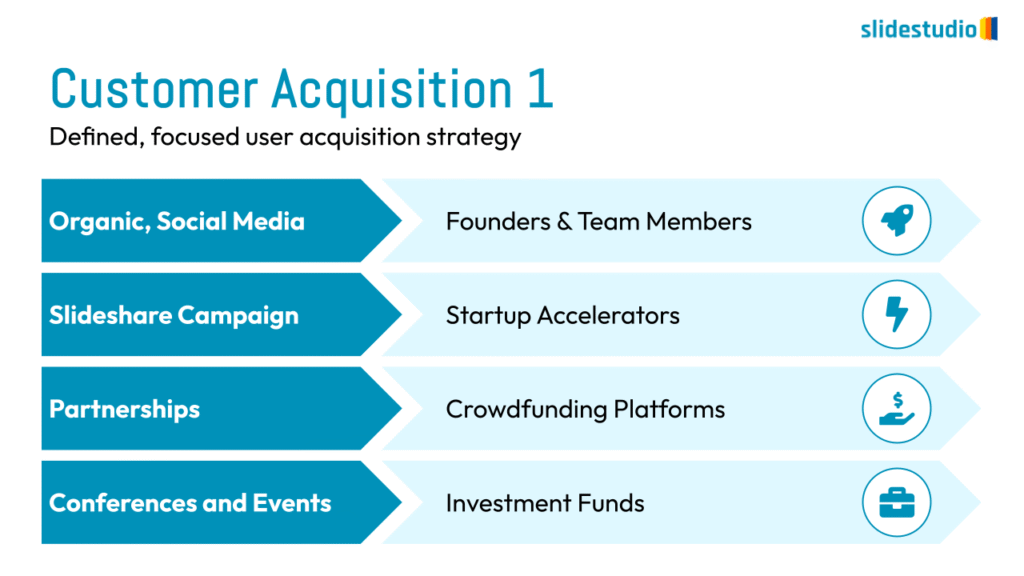
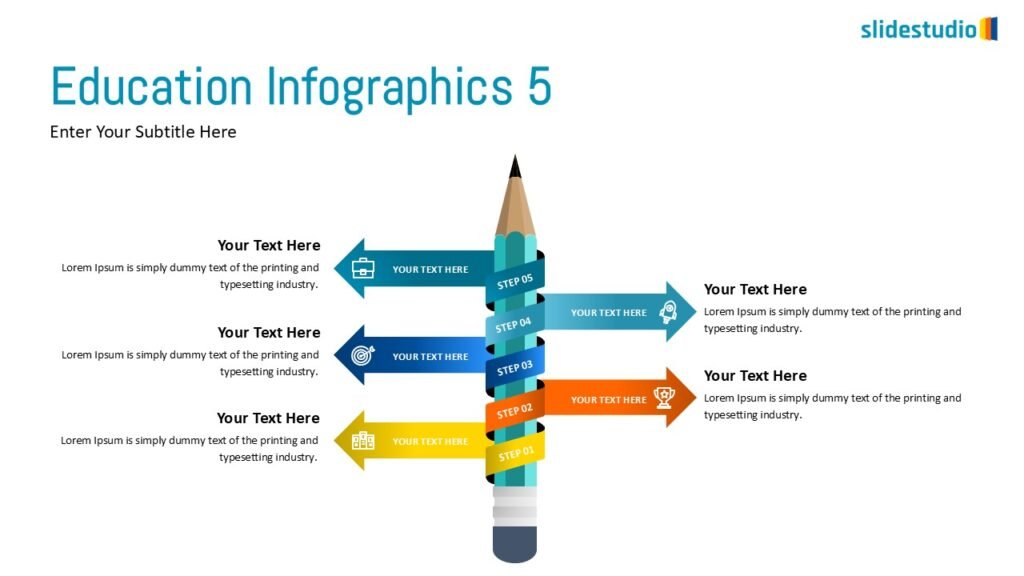
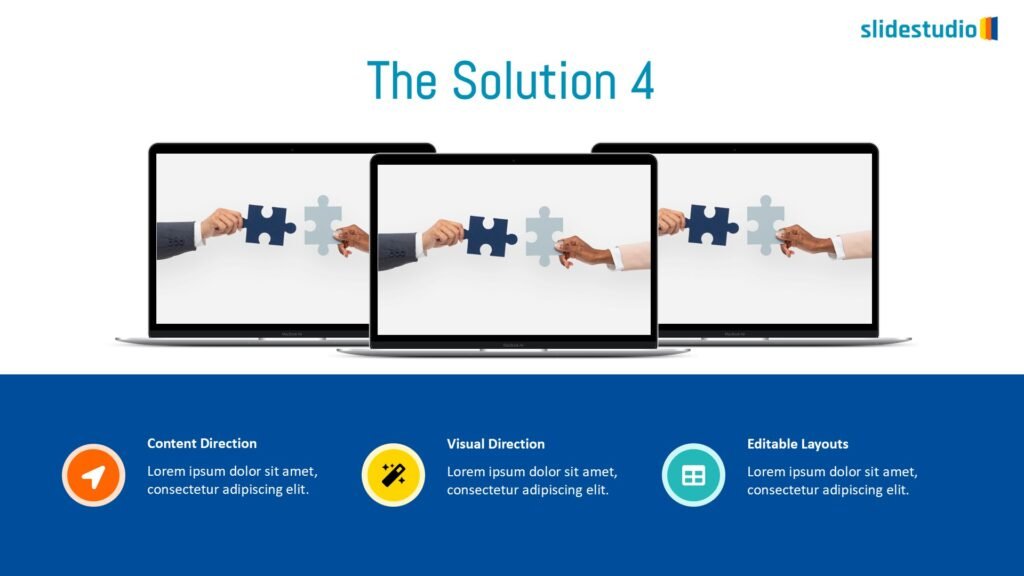
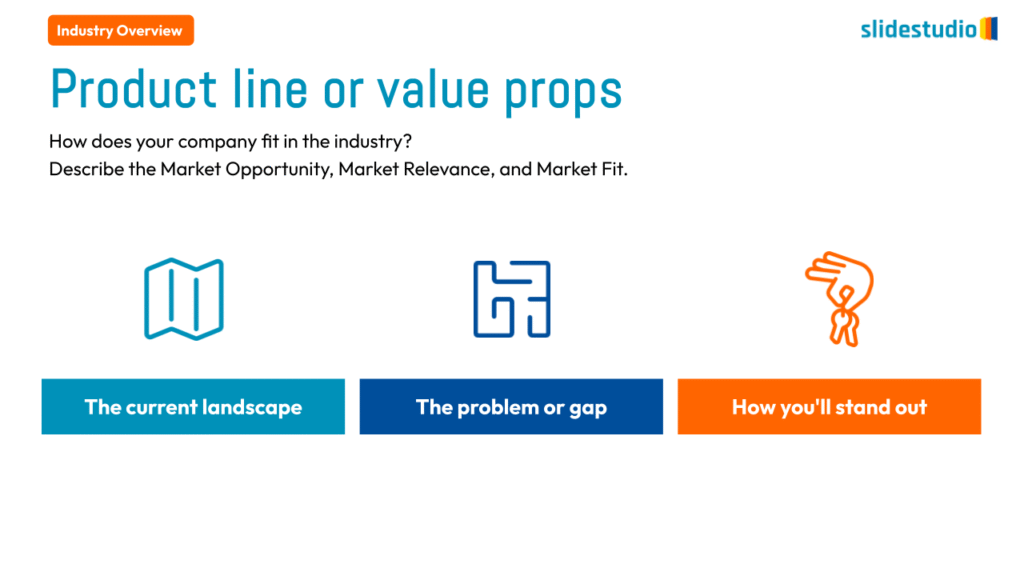
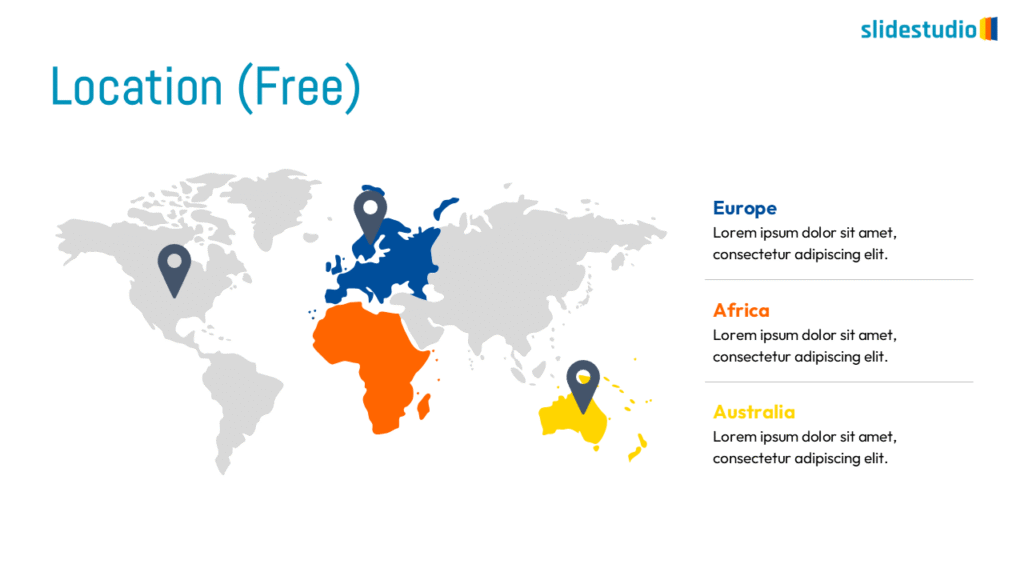
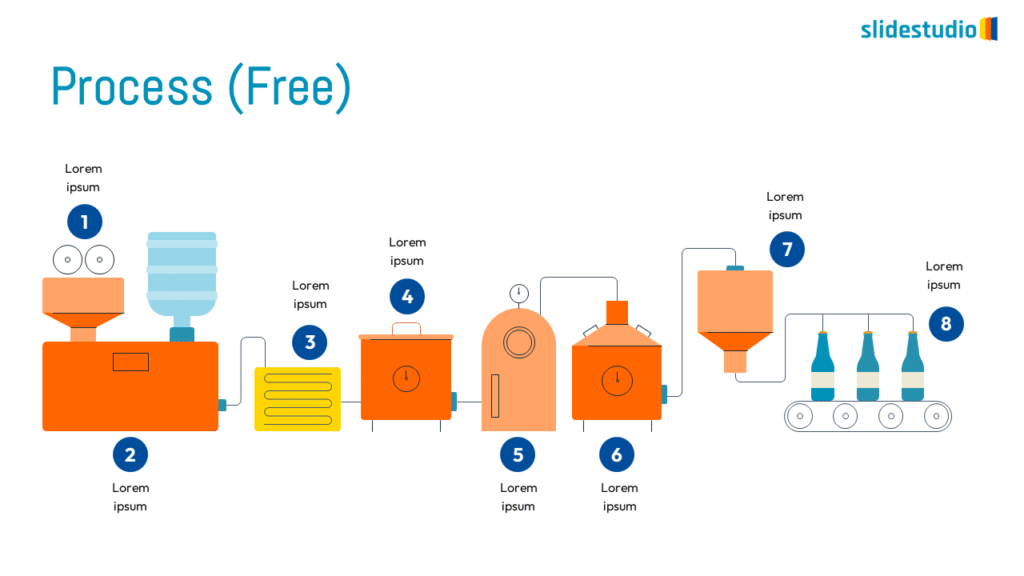
Pictorial
This concept uses images or icons to convey direction, location, reveal processes, or show influence. It provides a visual representation that is easy to understand and adds clarity to directional or procedural content.
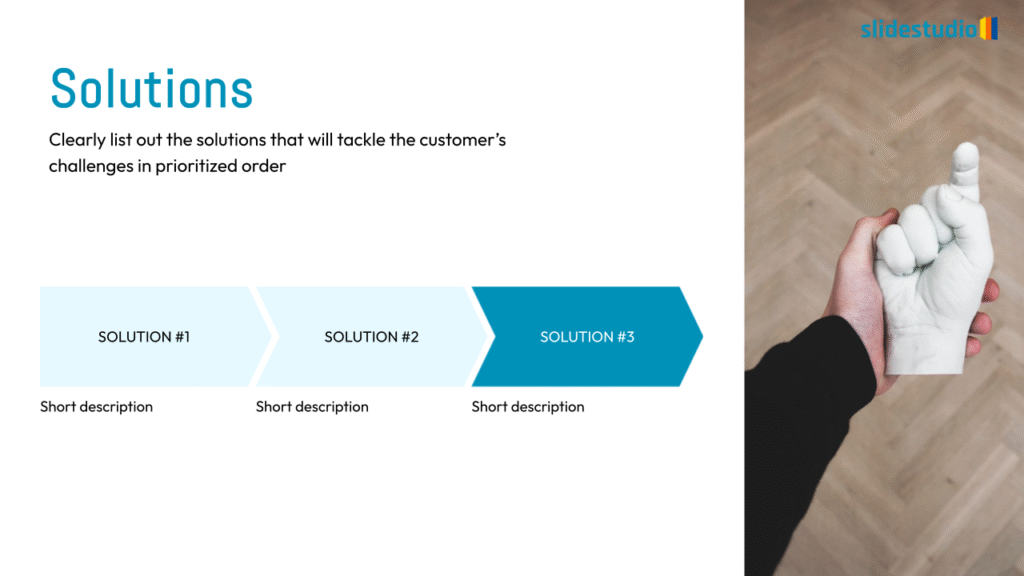
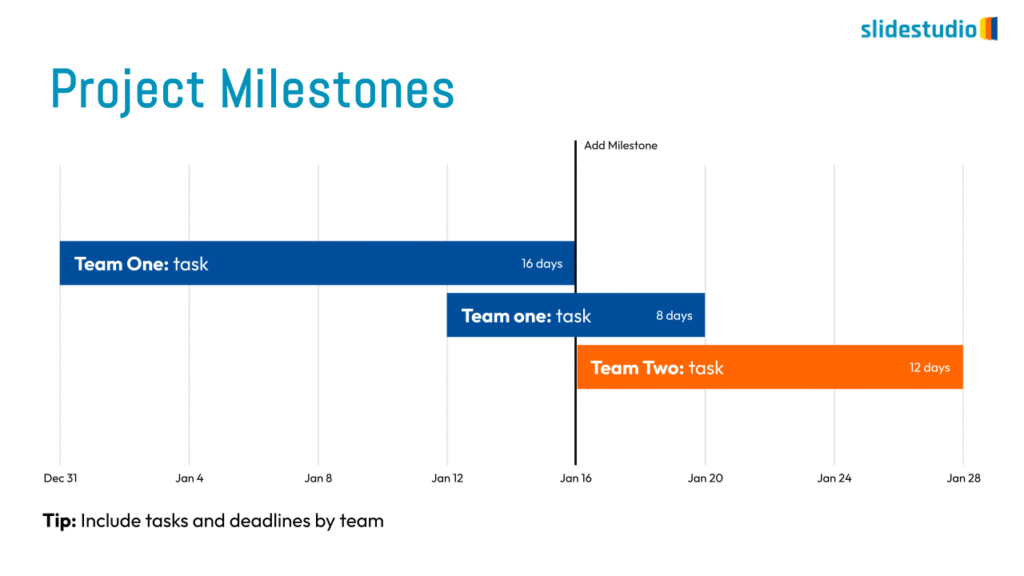
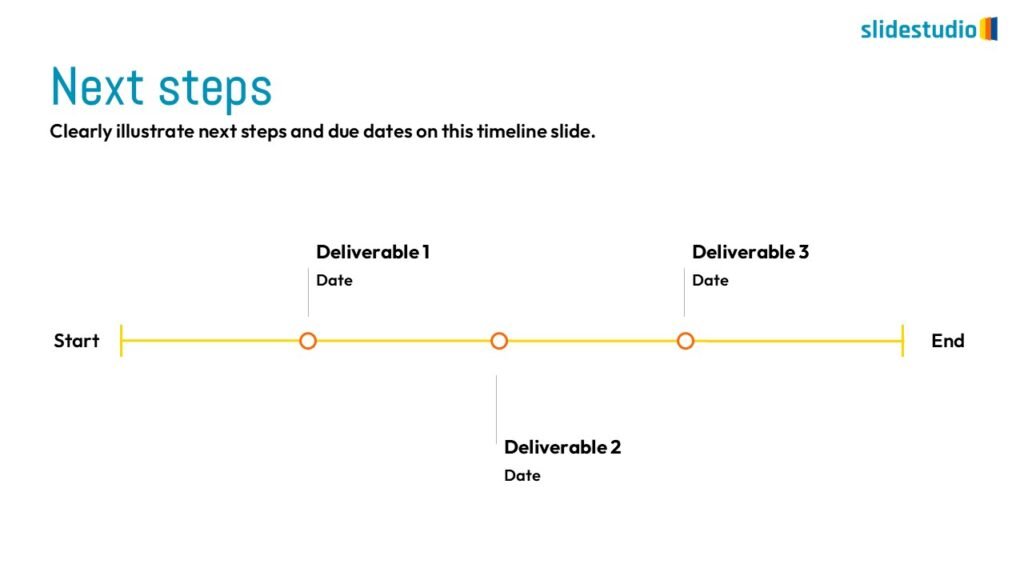
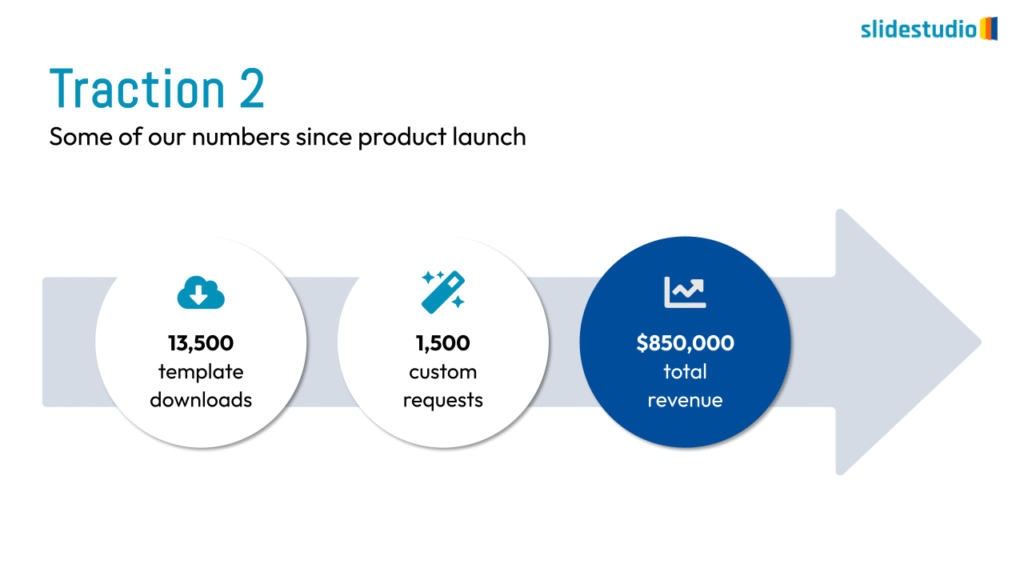
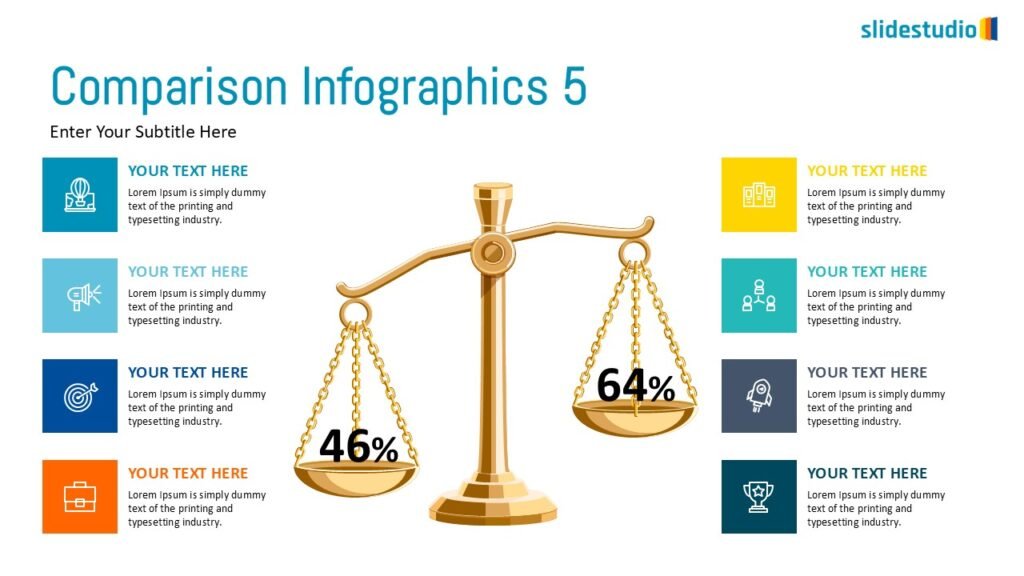
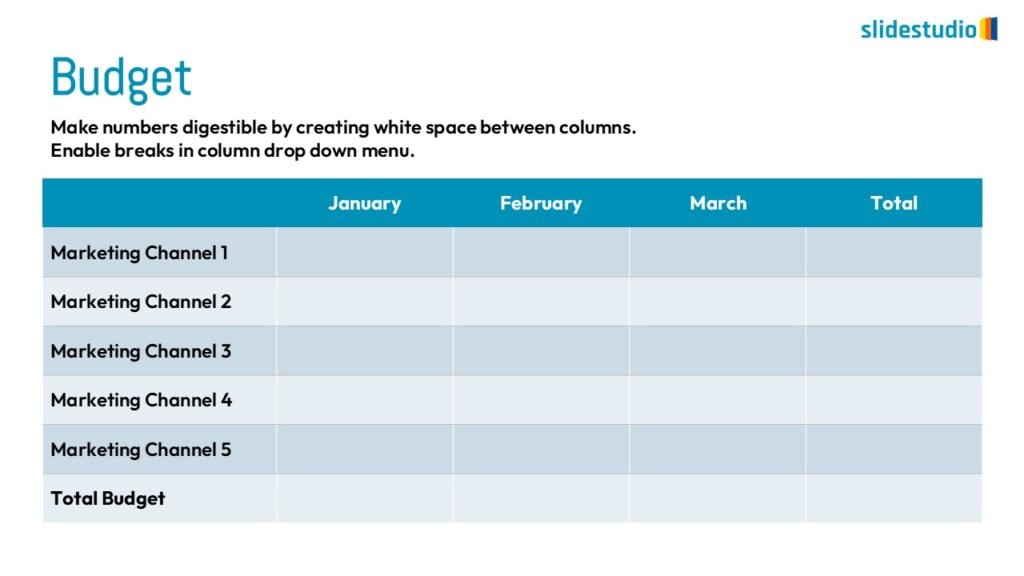
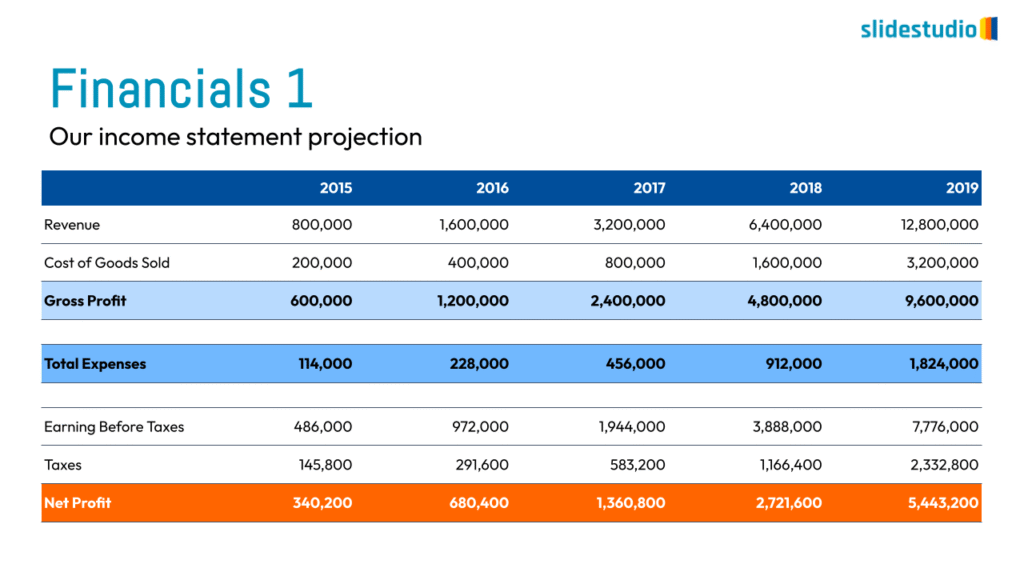
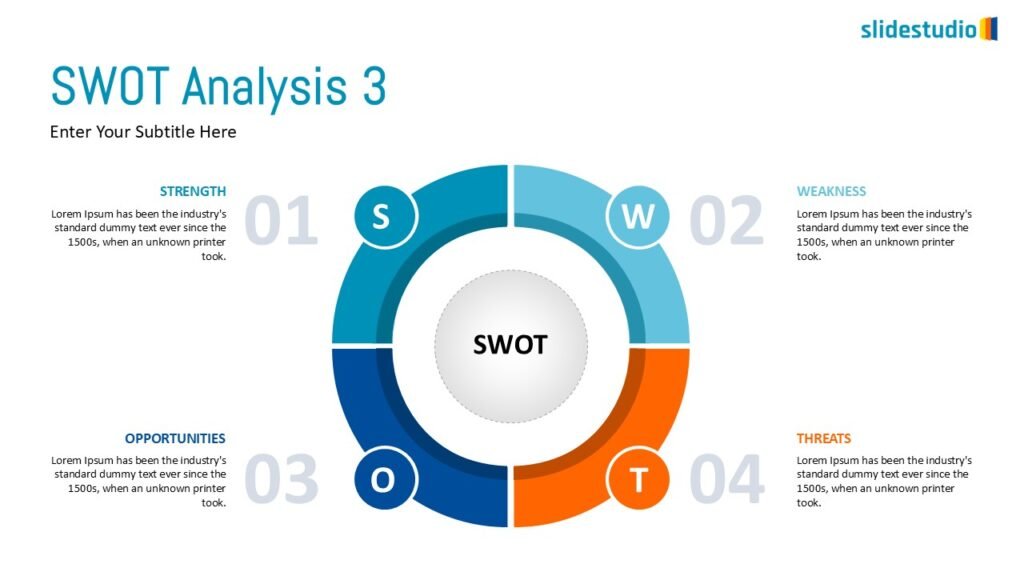
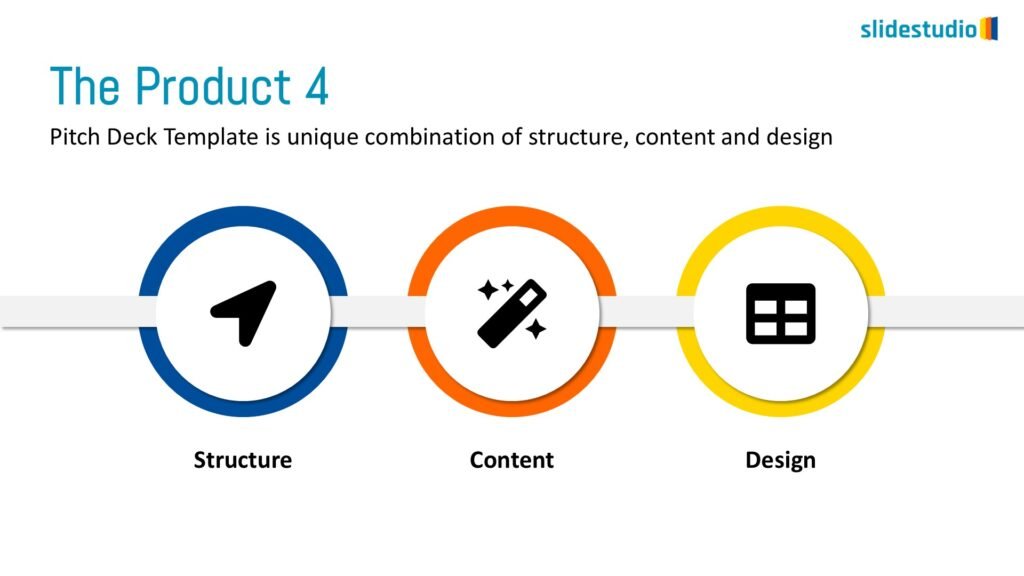
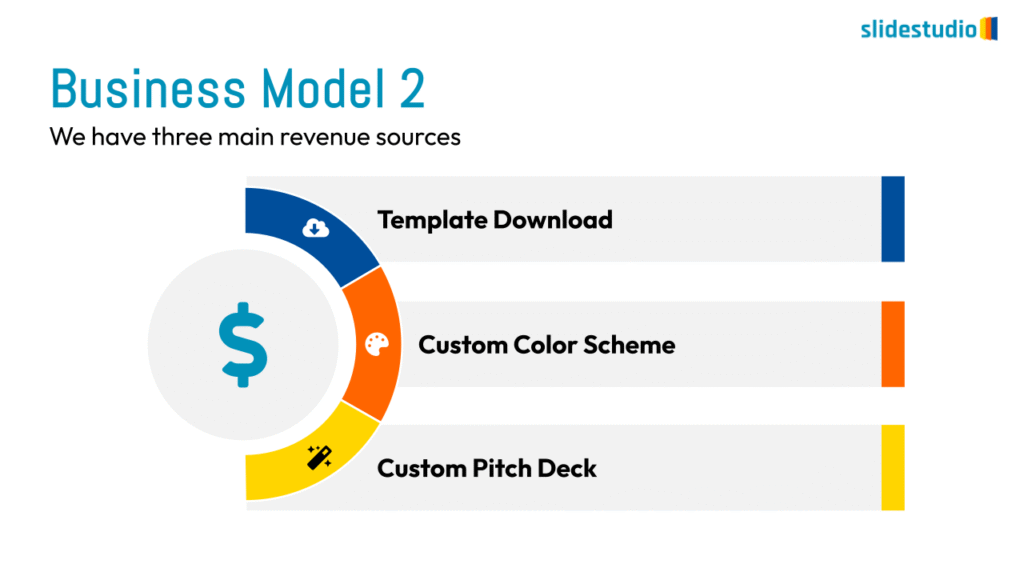
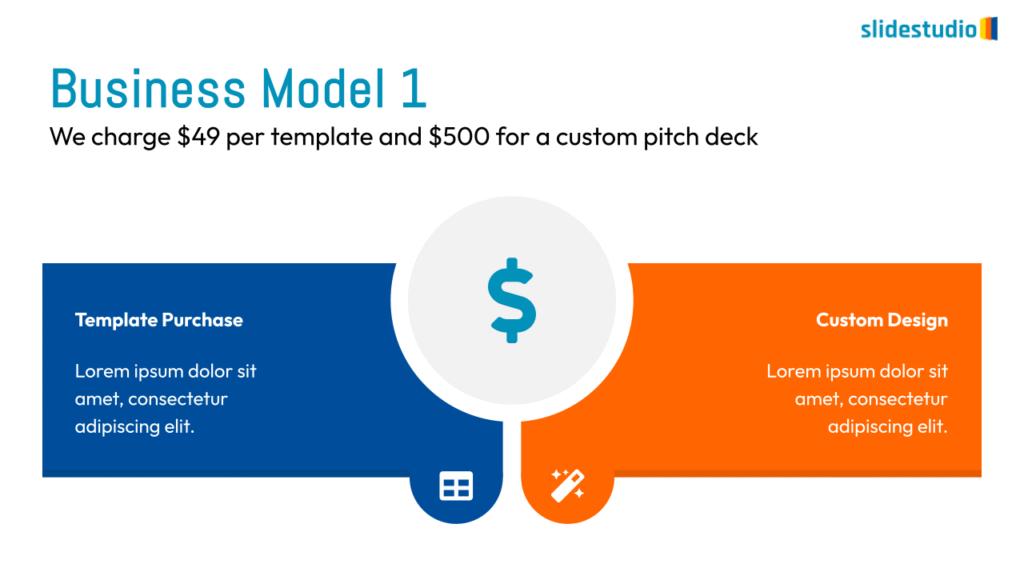
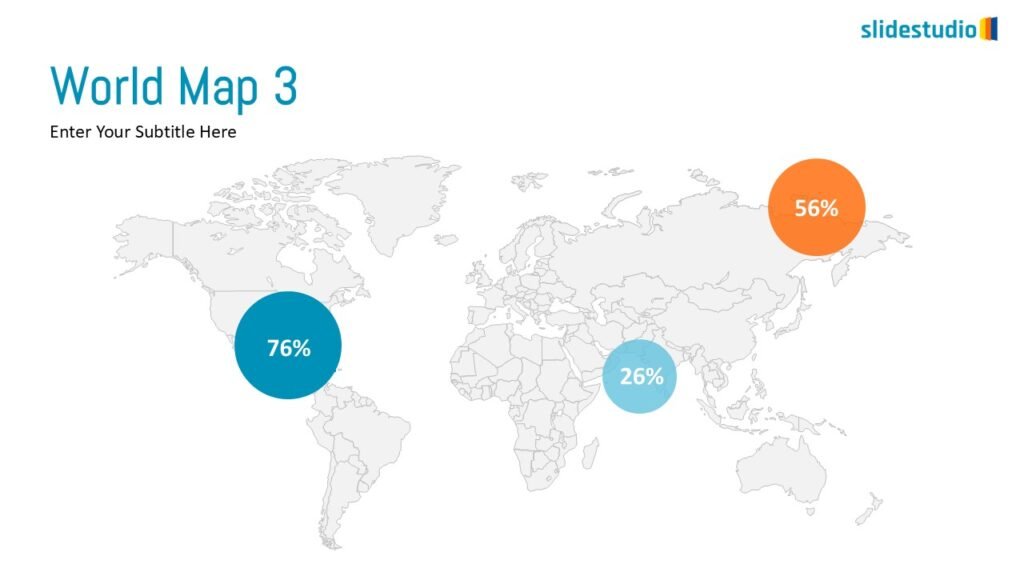
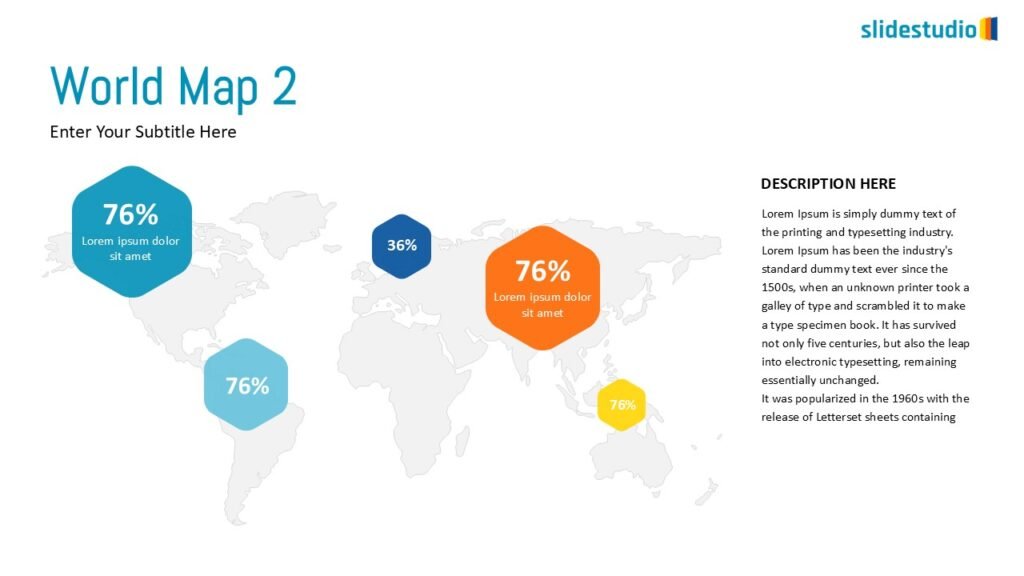
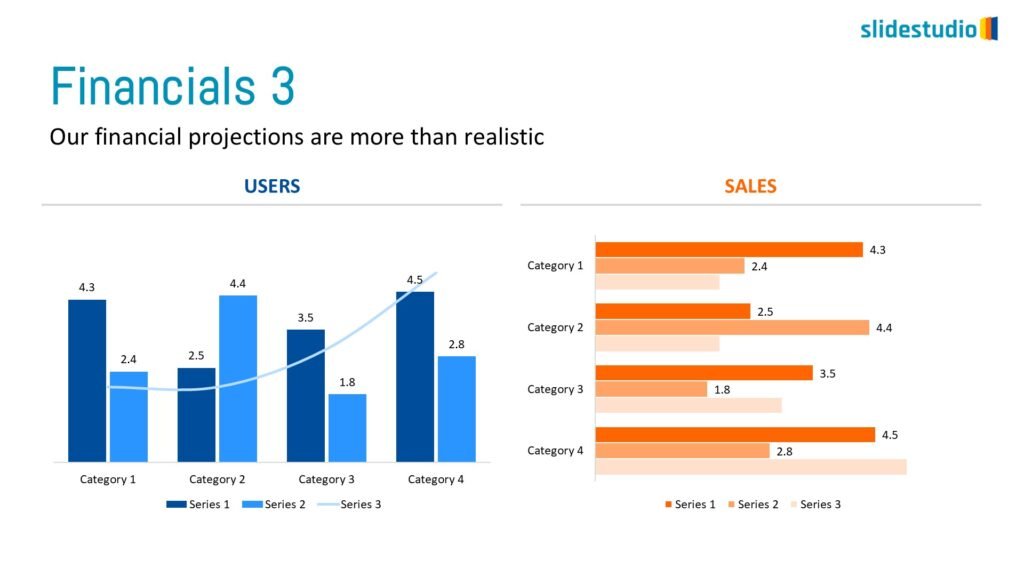
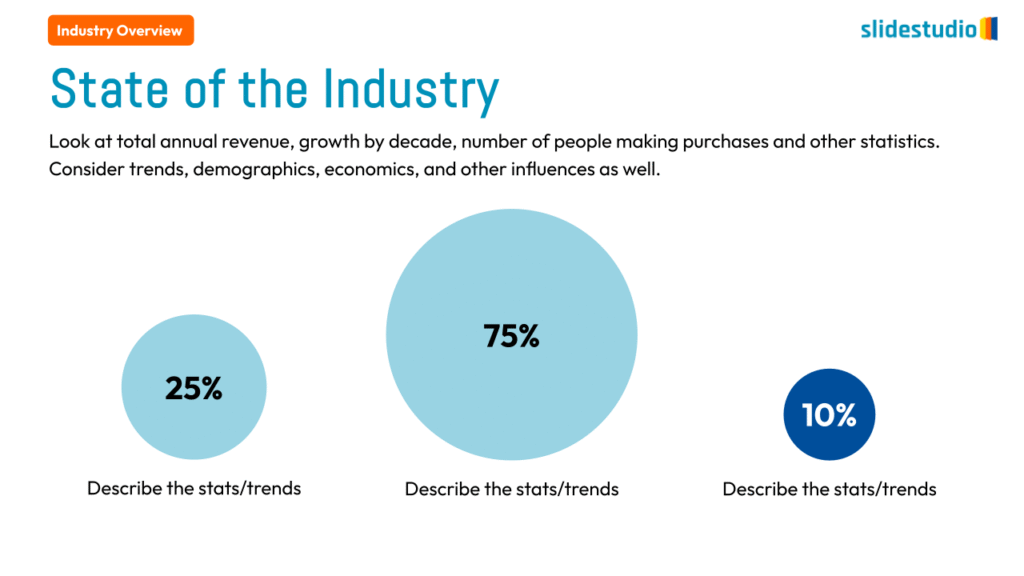
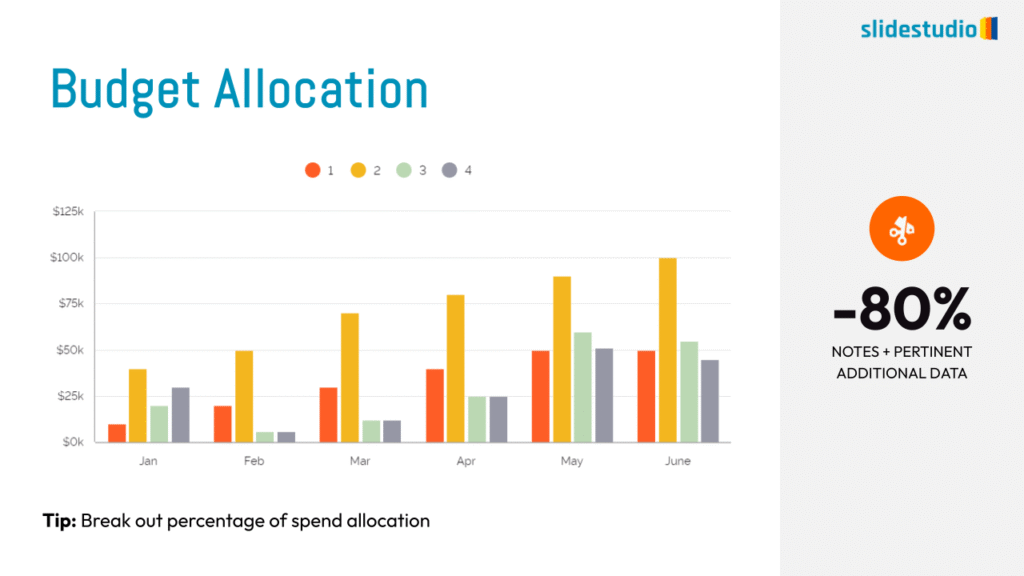
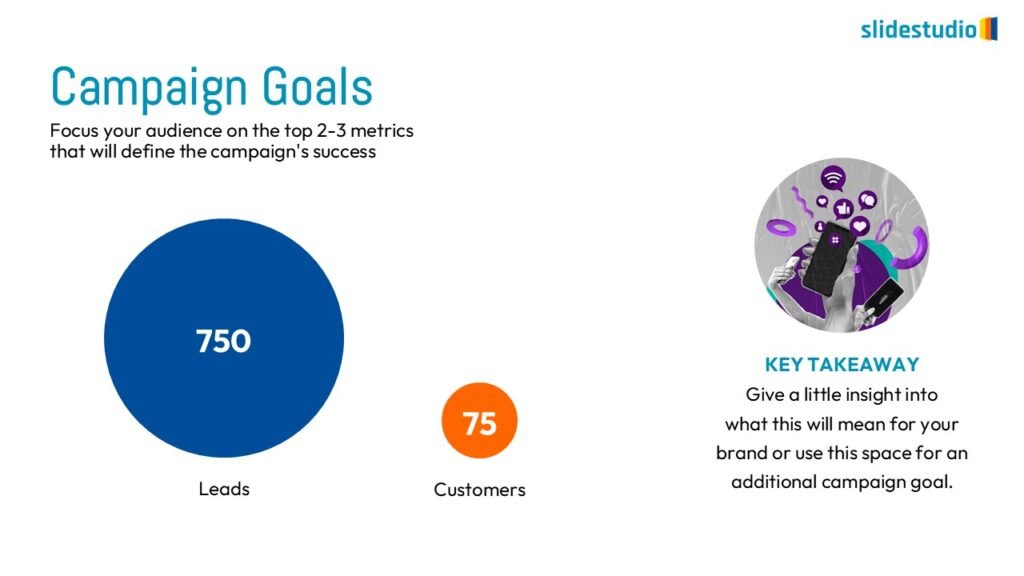
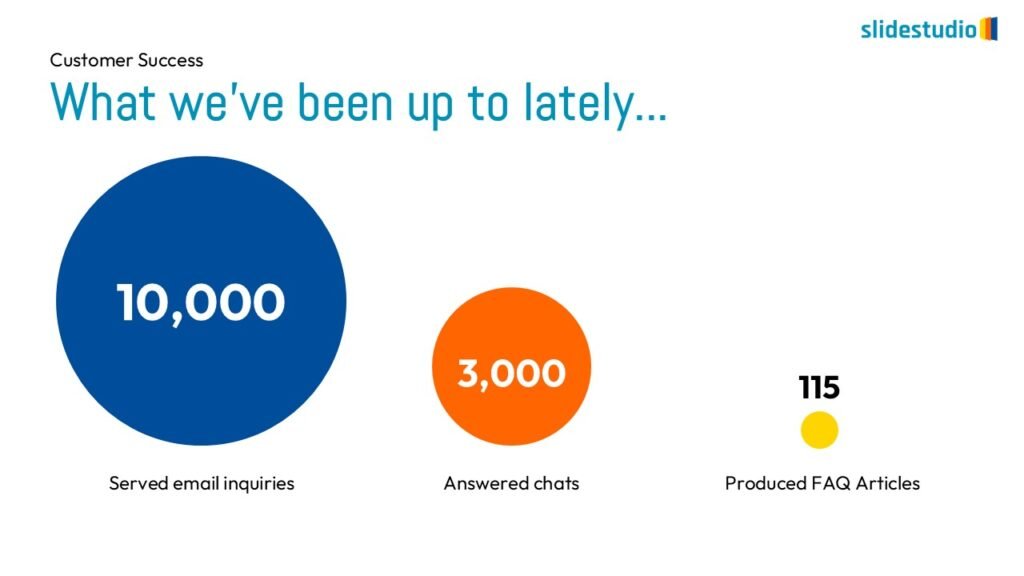
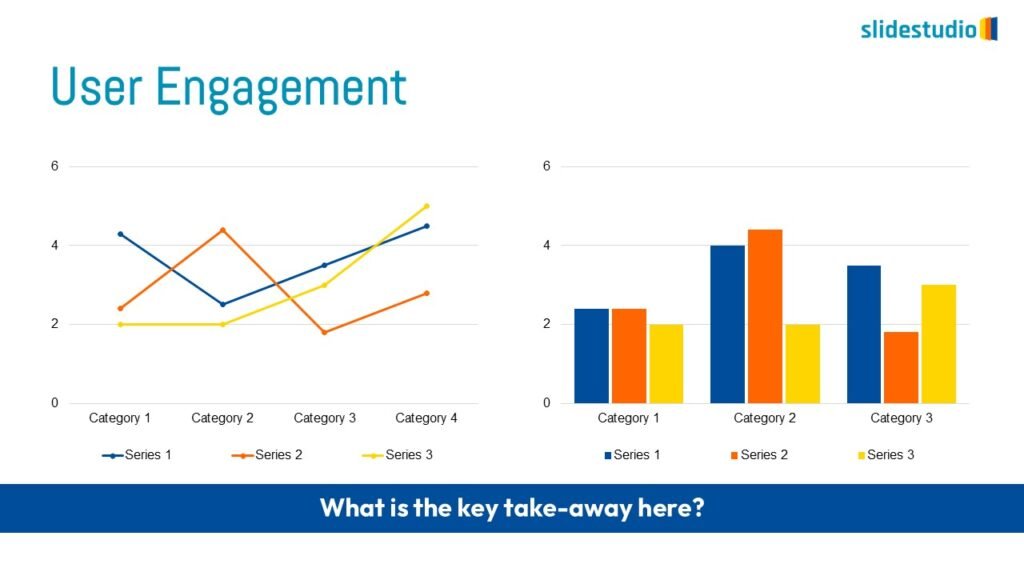
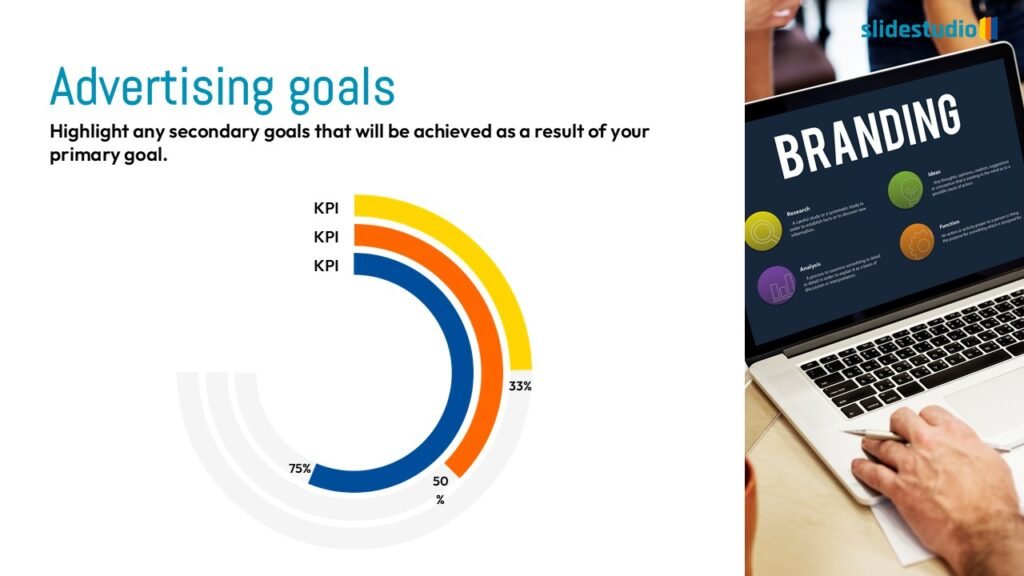
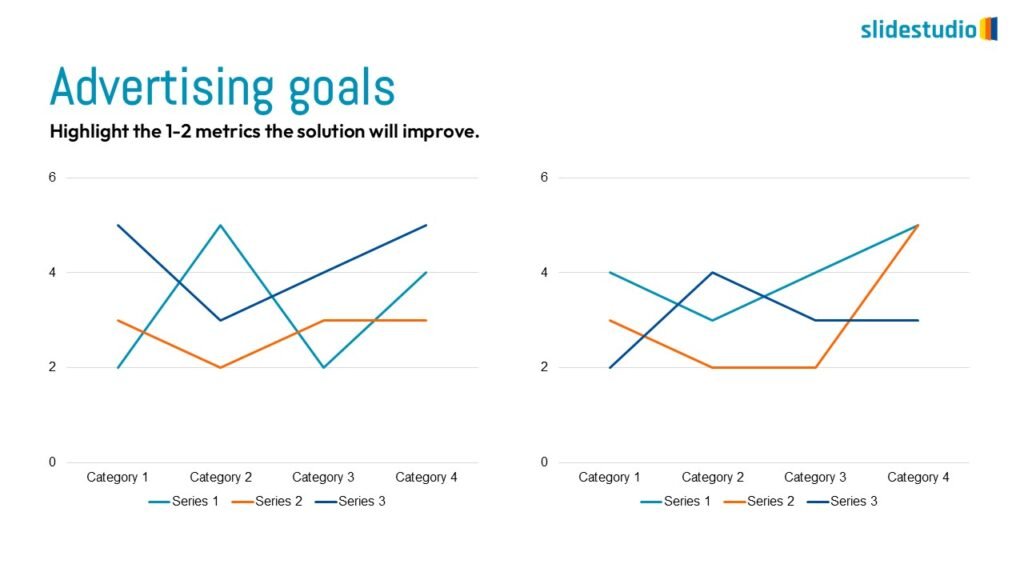
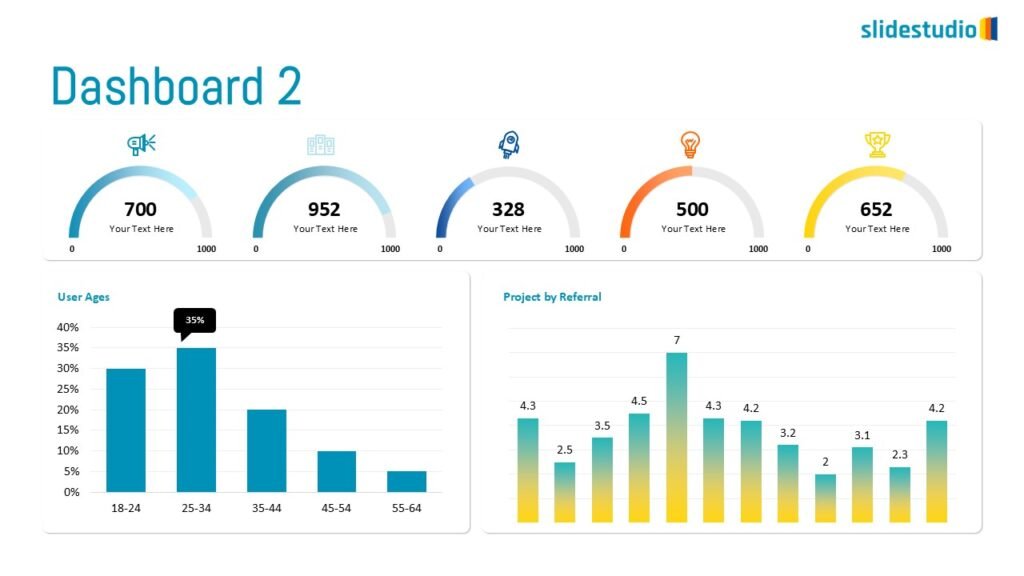
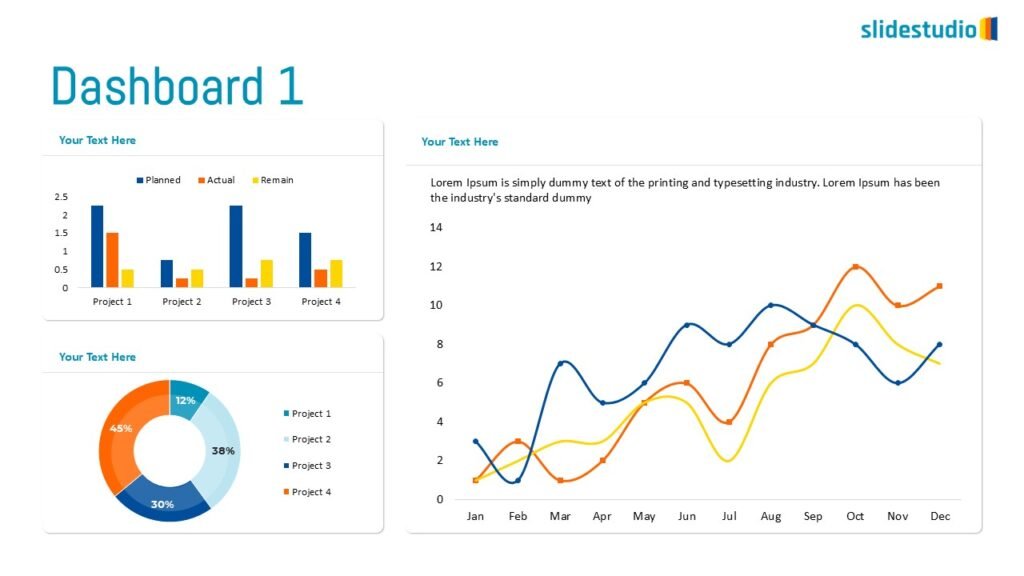
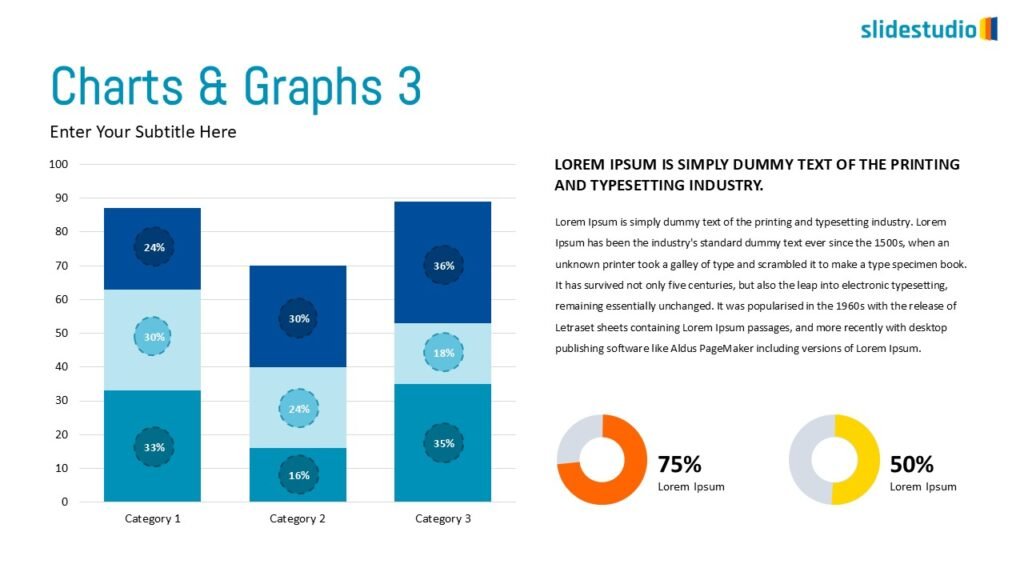
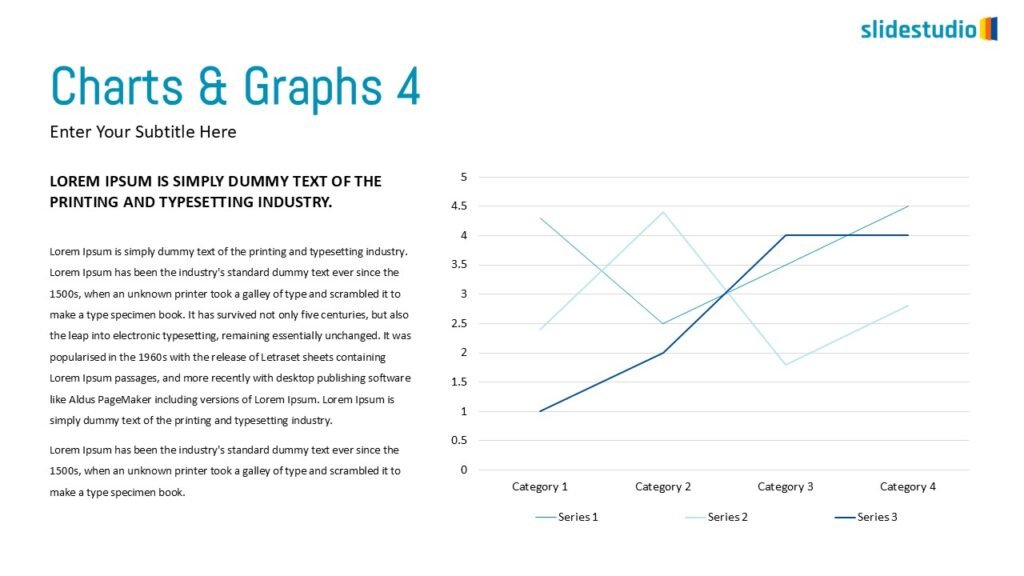
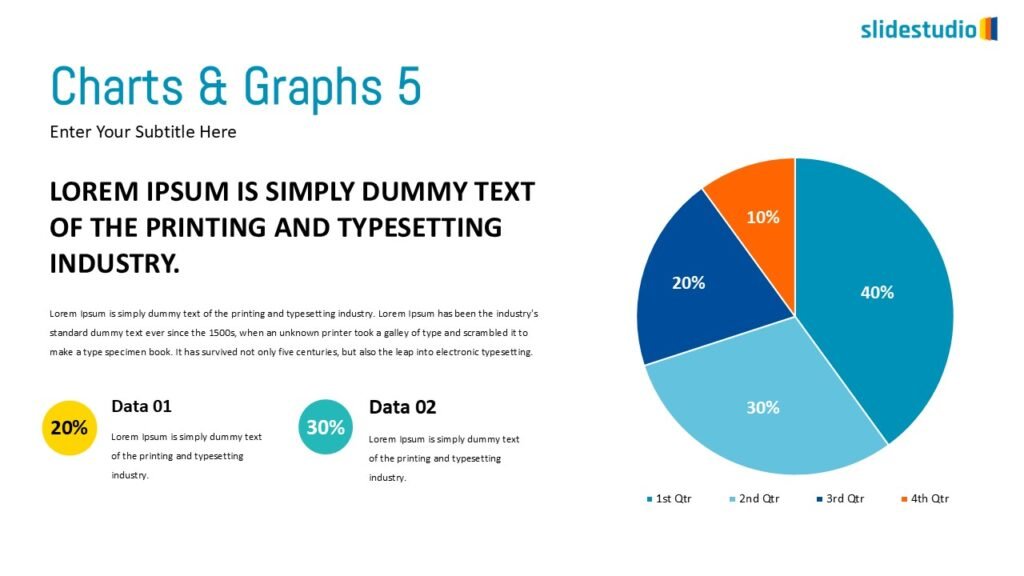
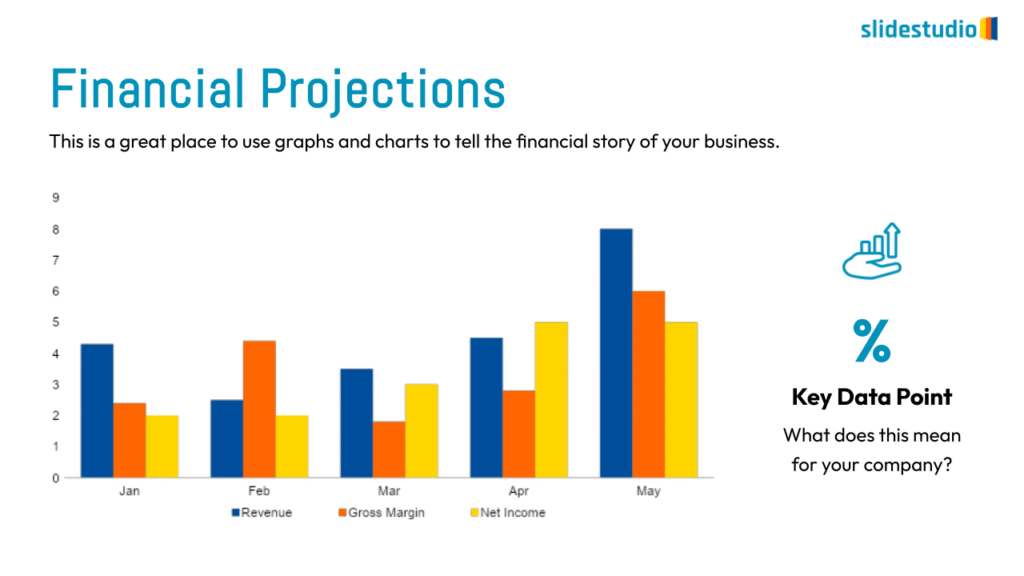
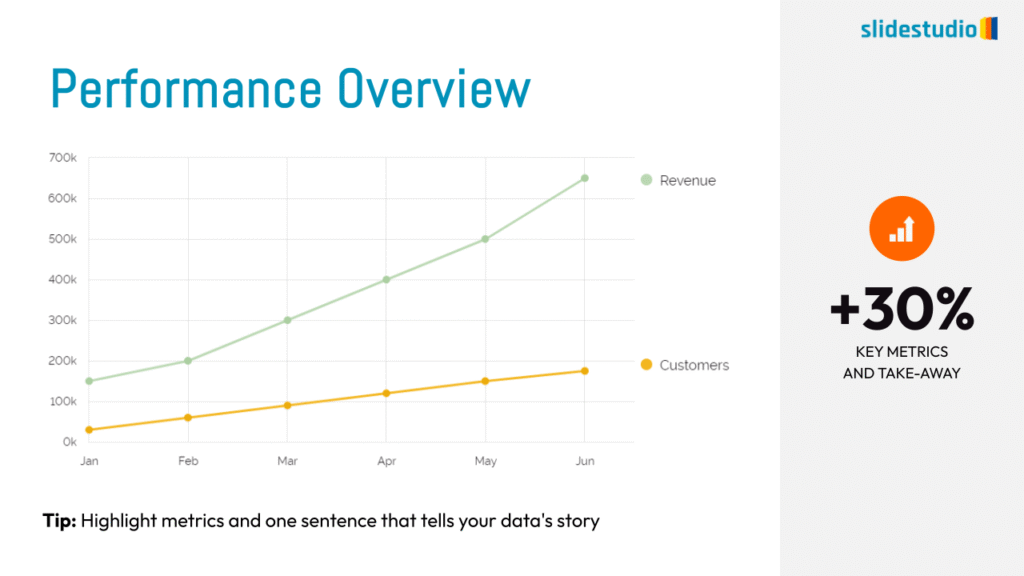
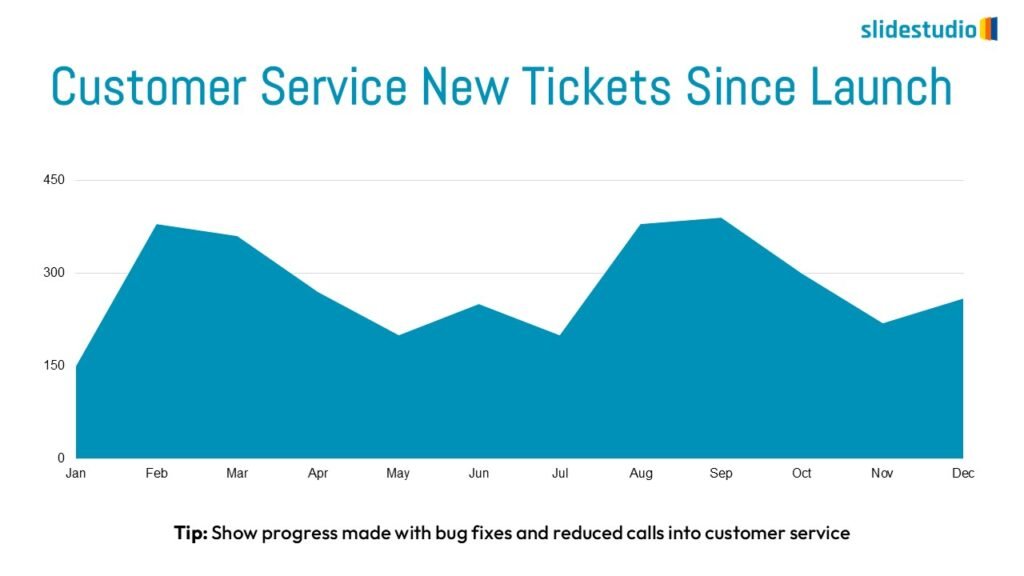
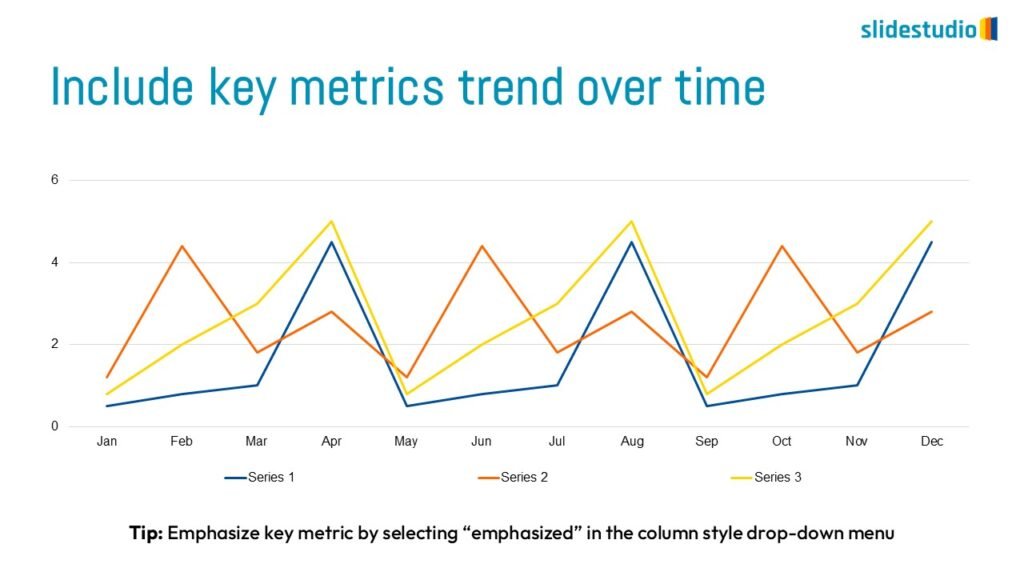
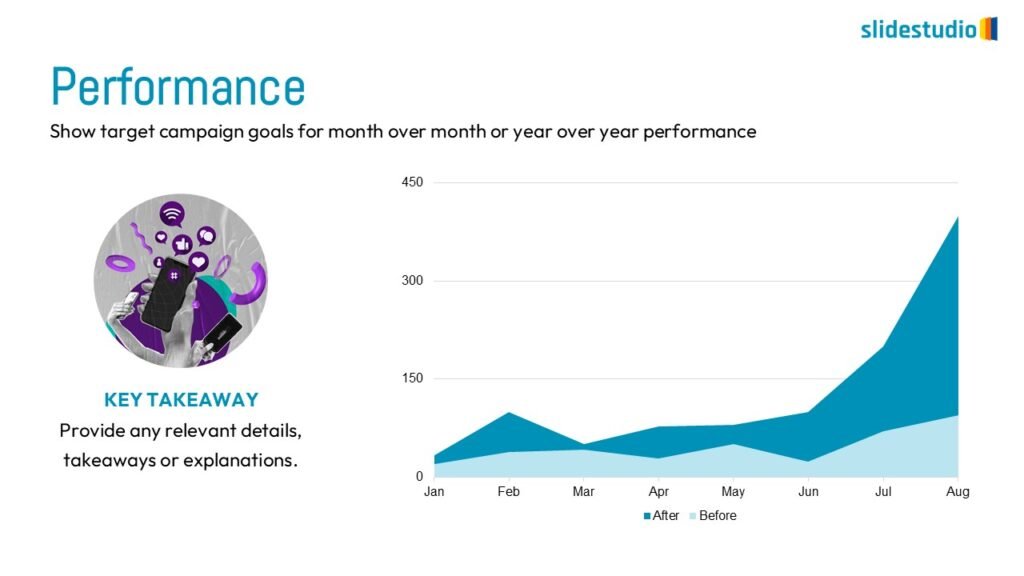
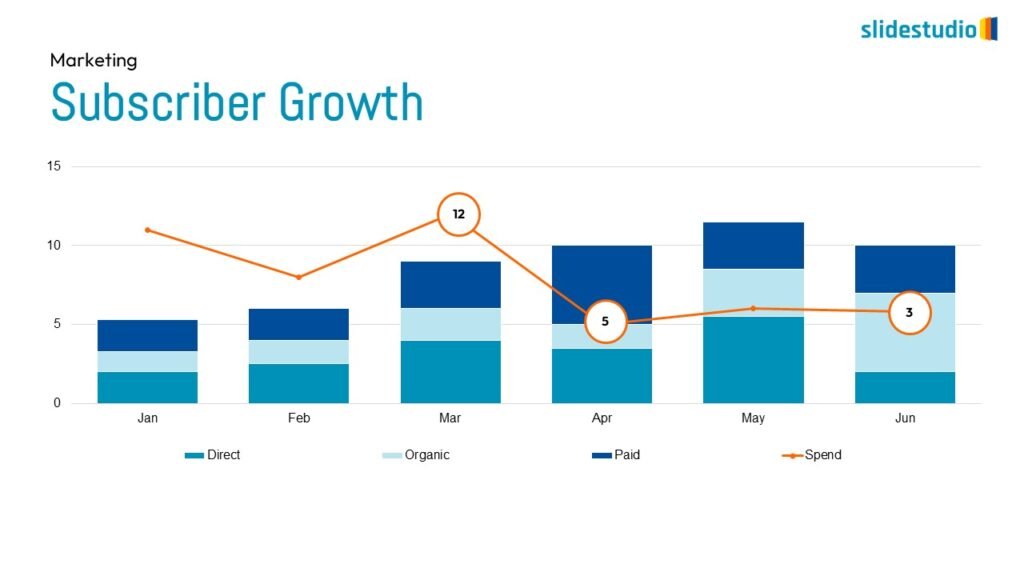
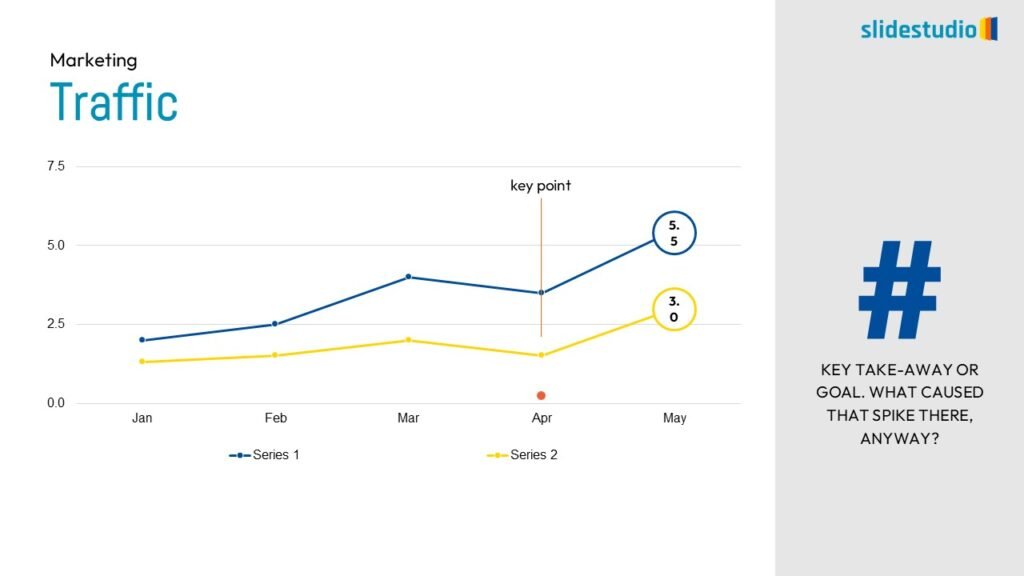
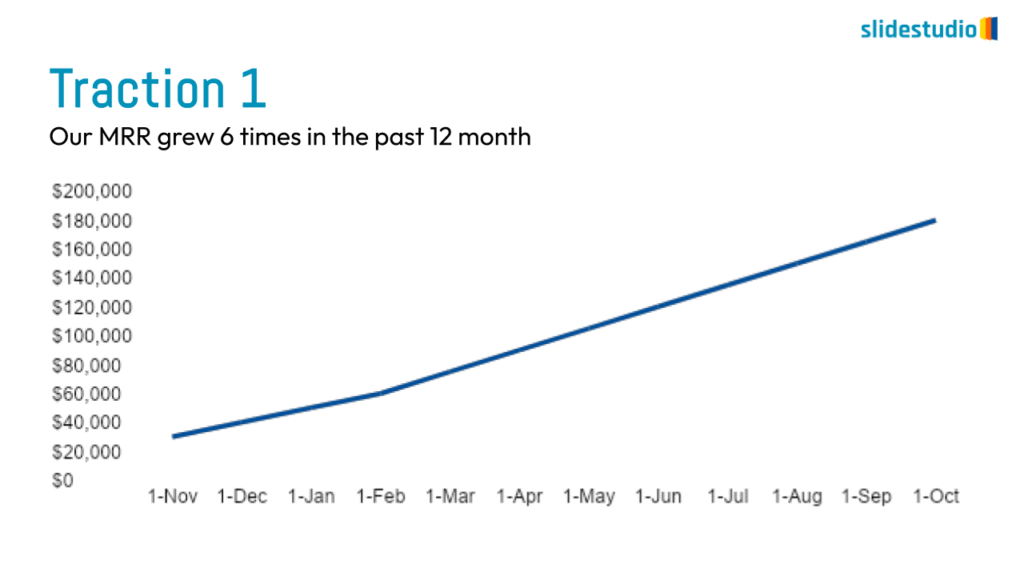
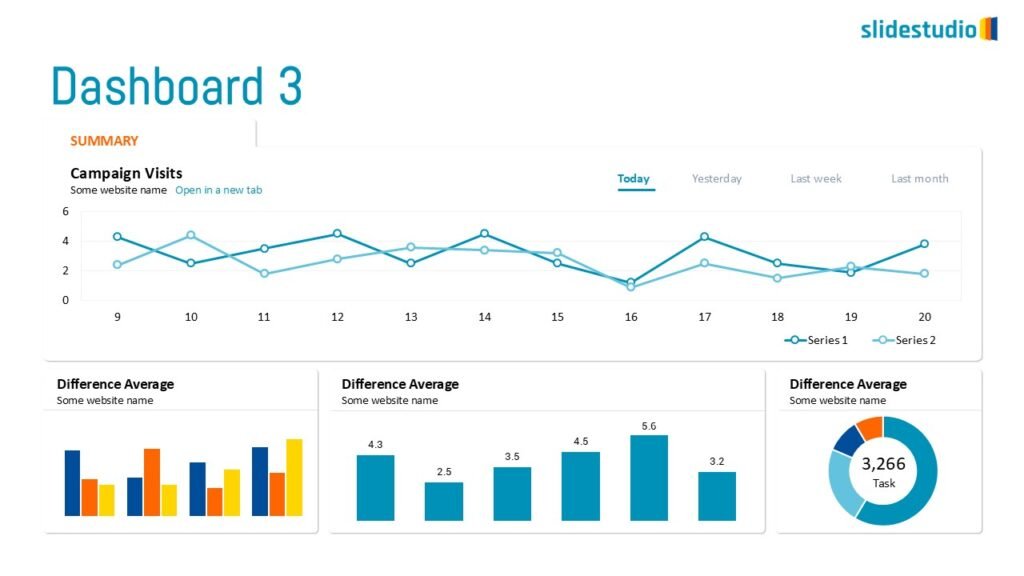
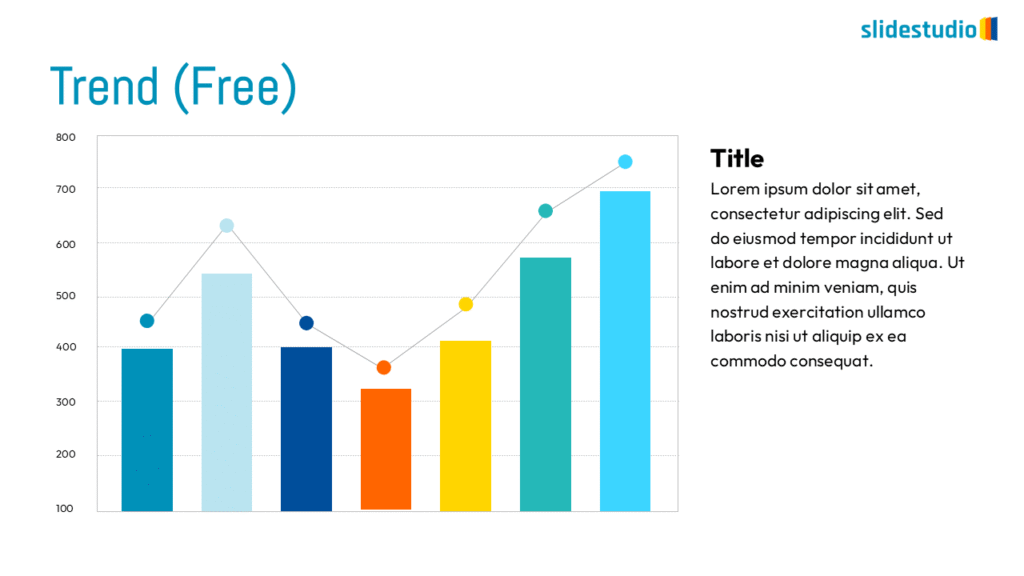
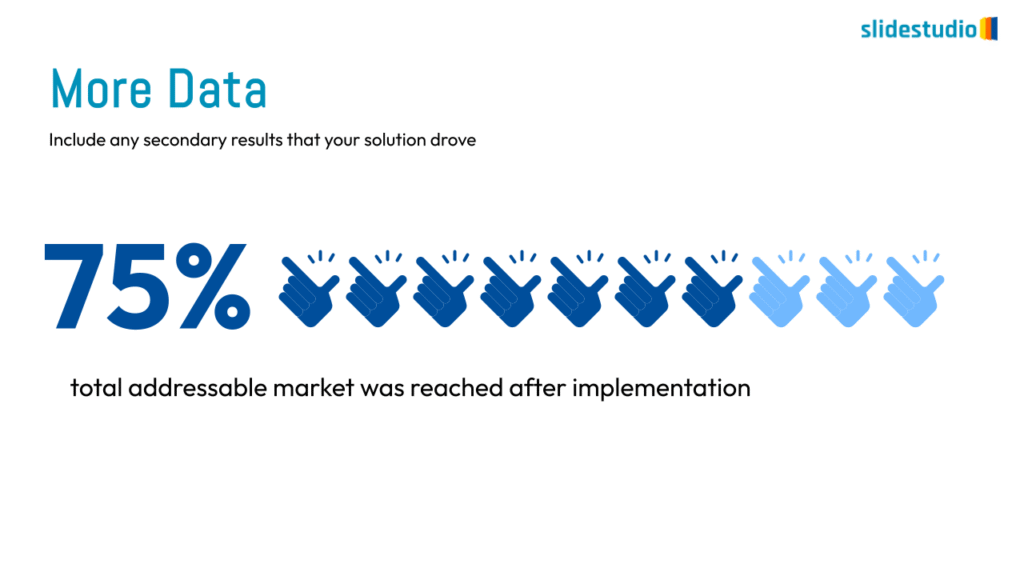
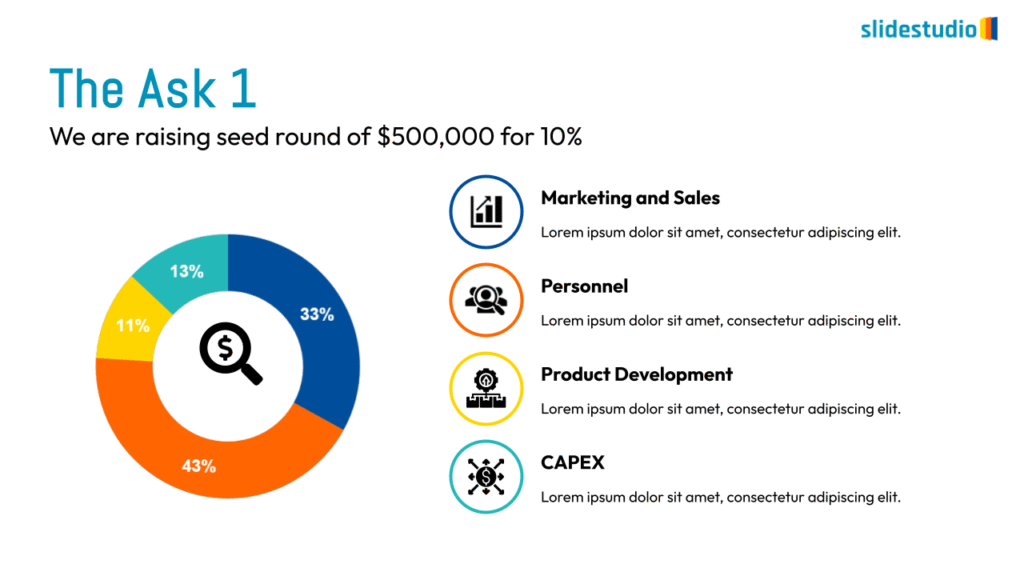
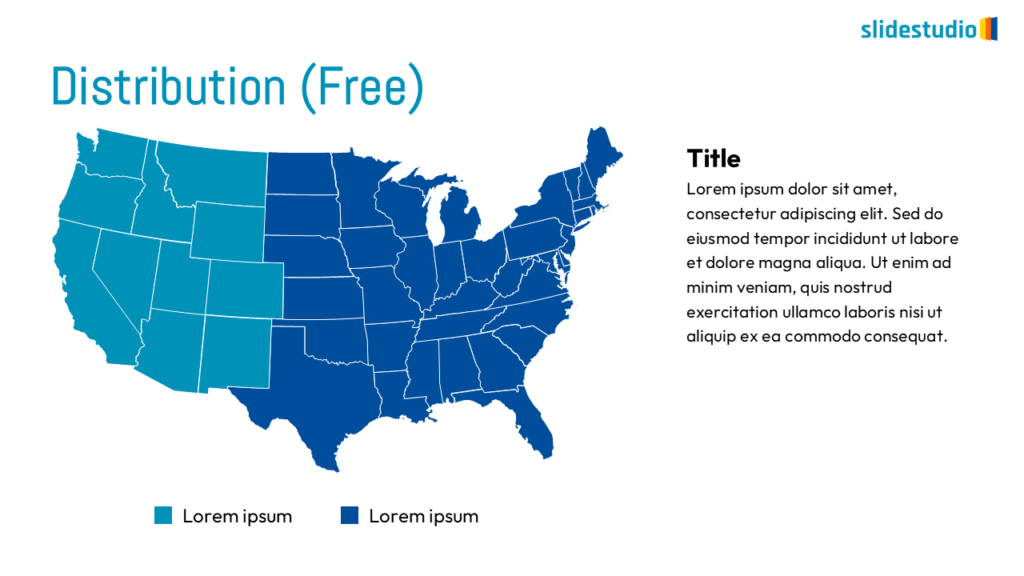
Display Data
This concept focuses on presenting data in a visual format, such as comparisons, trends, or distributions. Common methods include charts, graphs, or other data visualization techniques to make information easier to interpret at a glance.

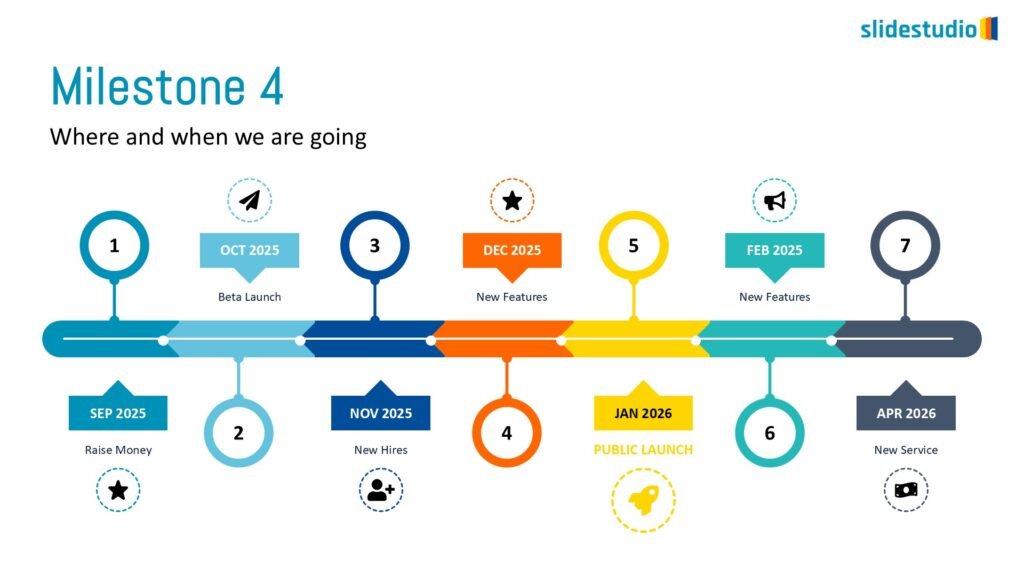
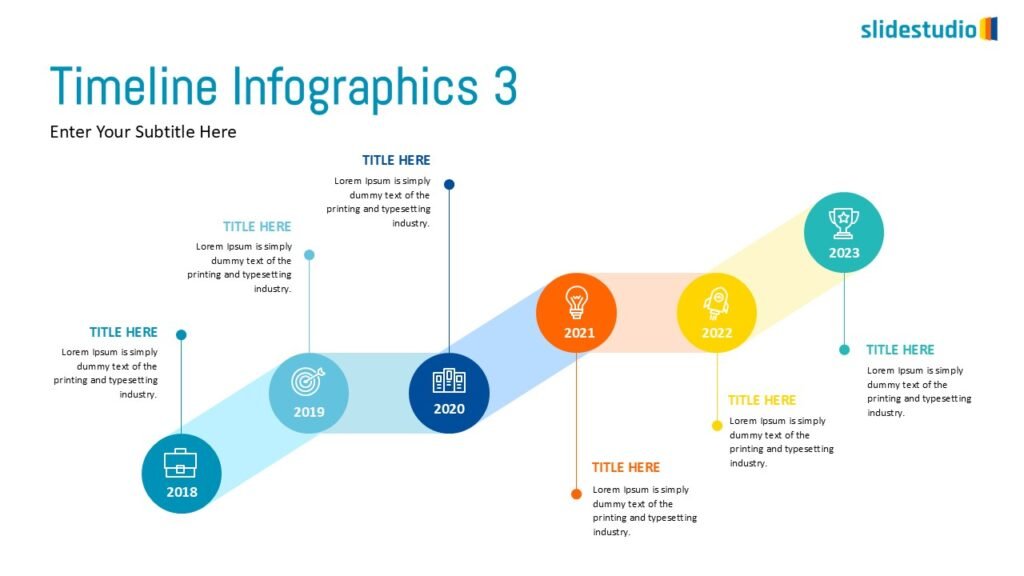
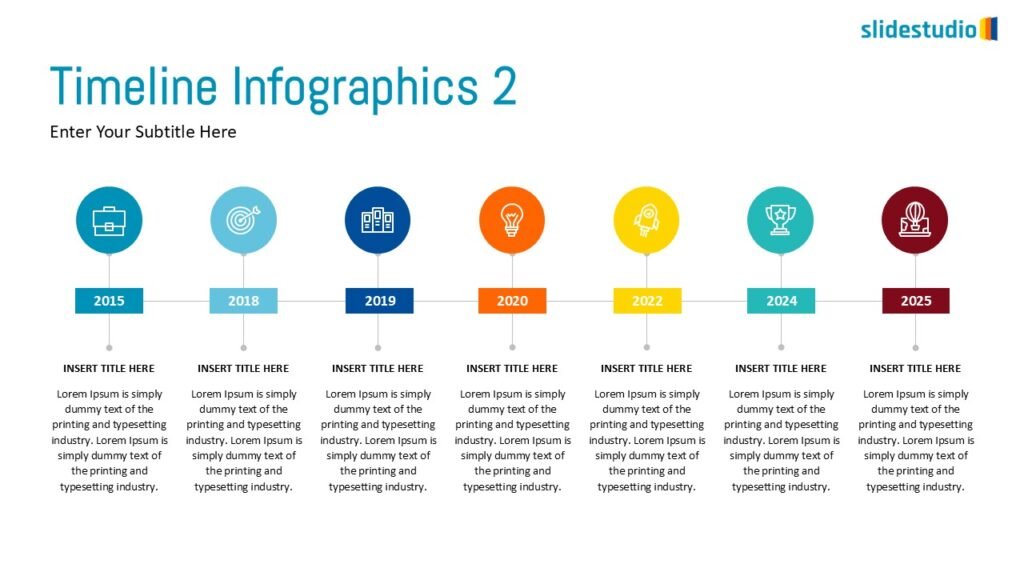
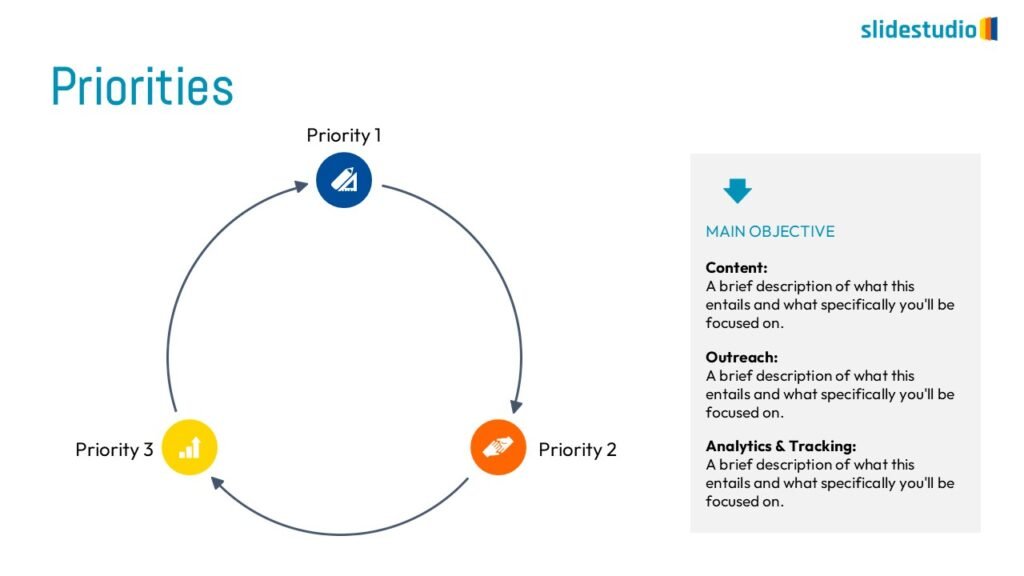
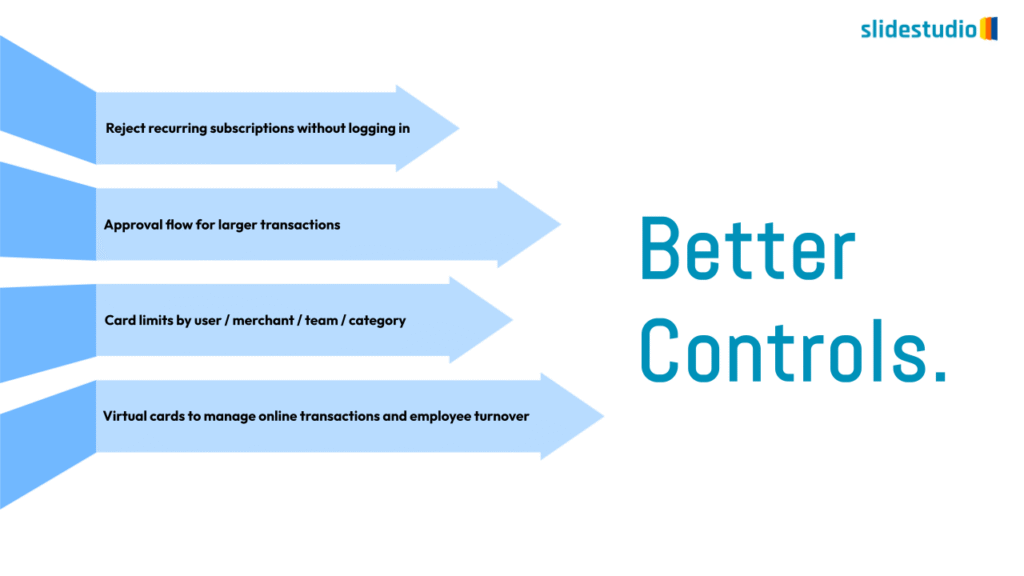
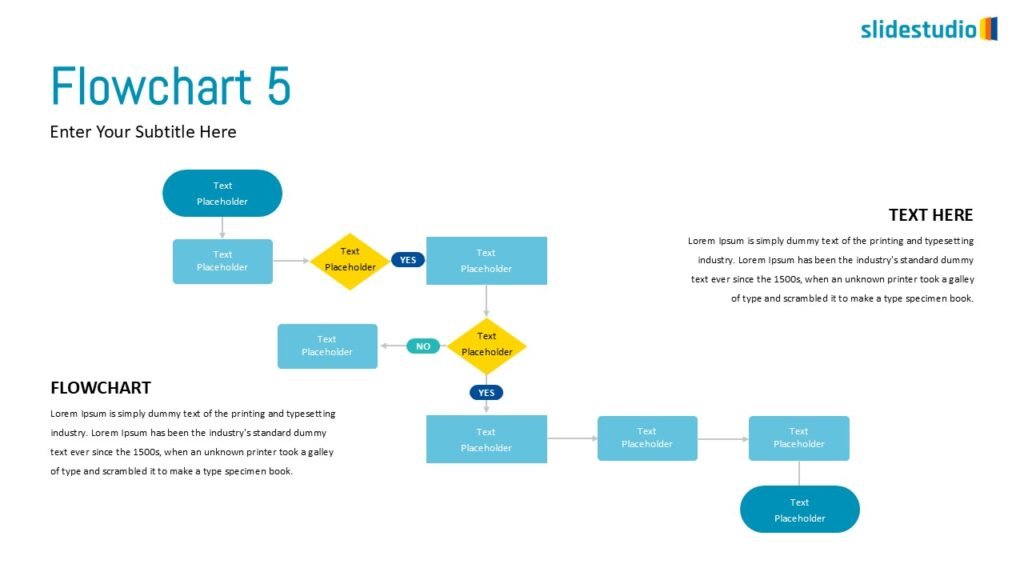
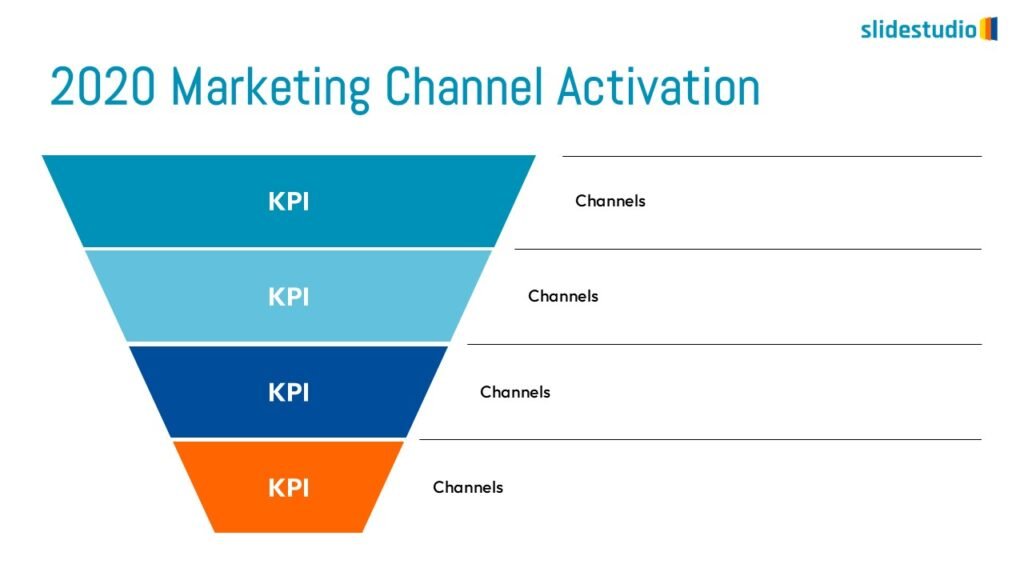
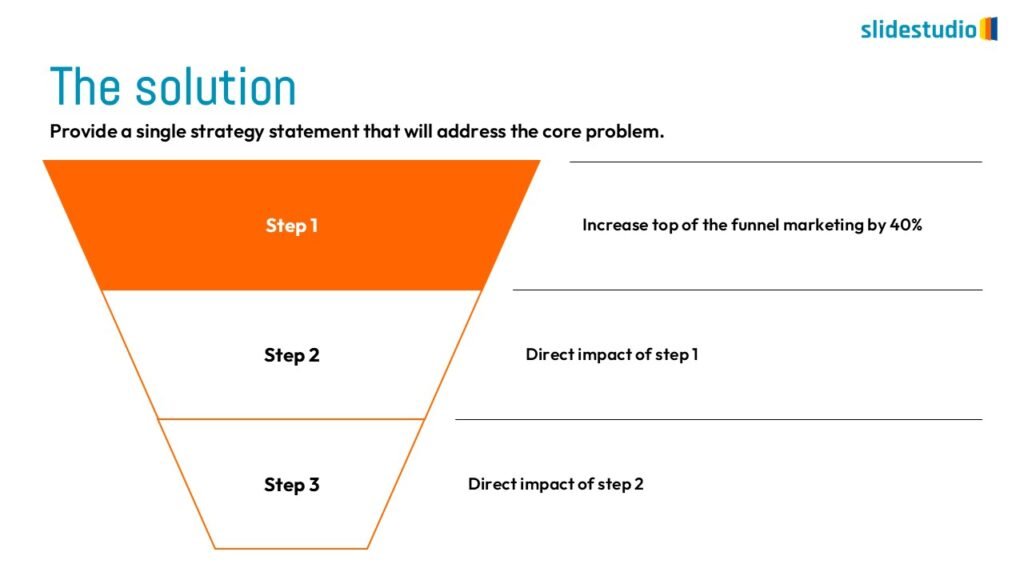
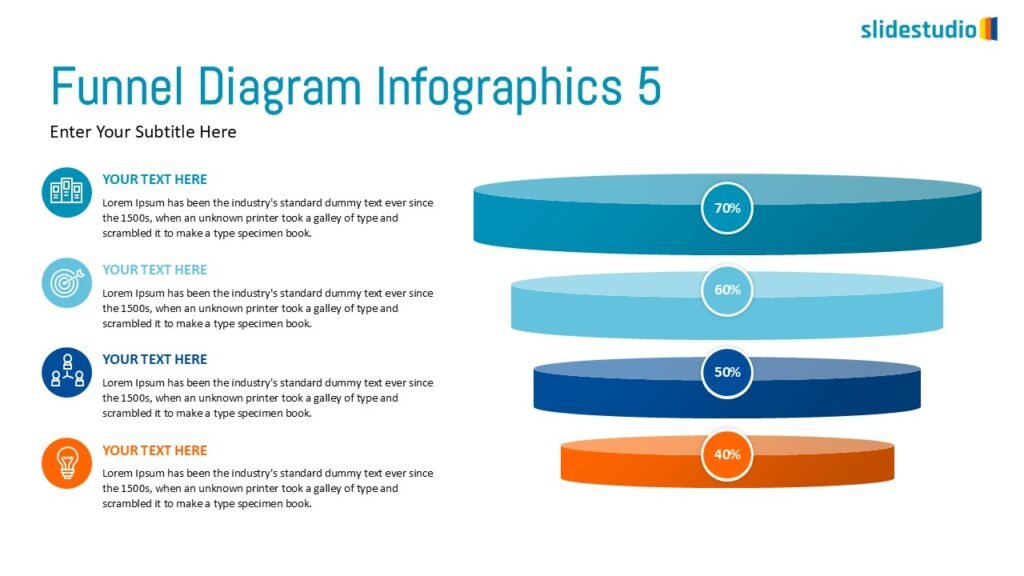
Flow
This concept focuses on illustrating the movement or progression of information. It can be represented in various forms, such as linear, circular, divergent/convergent, or multidirectional pathways, to convey how elements progress or connect in a sequence.
Linear
A step-by-step structure that illustrates a straightforward progression from start to finish.
DIVERGENT/CONVERGENT
A flow that branches out or converges, ideal for showing multiple pathways or merging ideas.

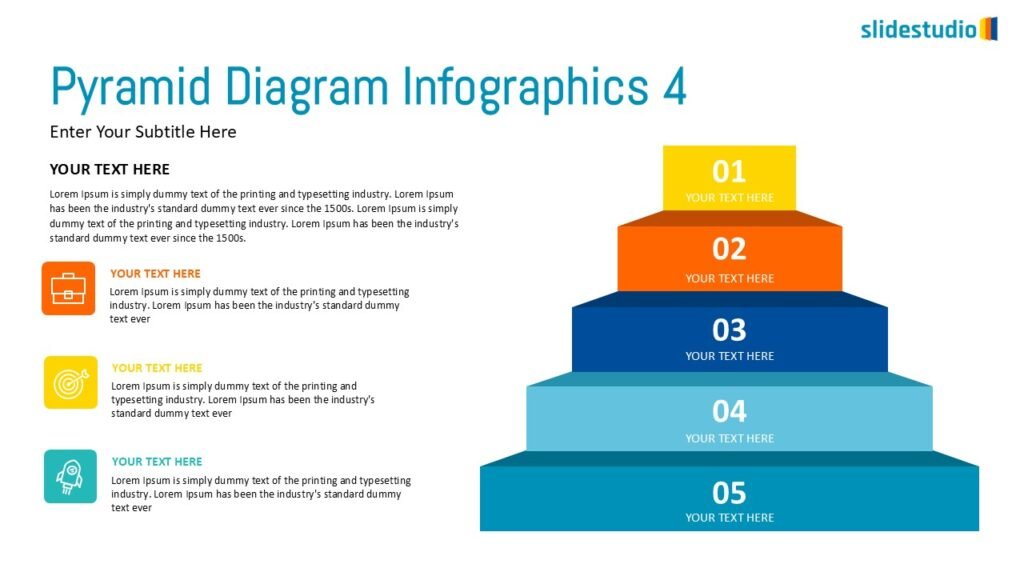
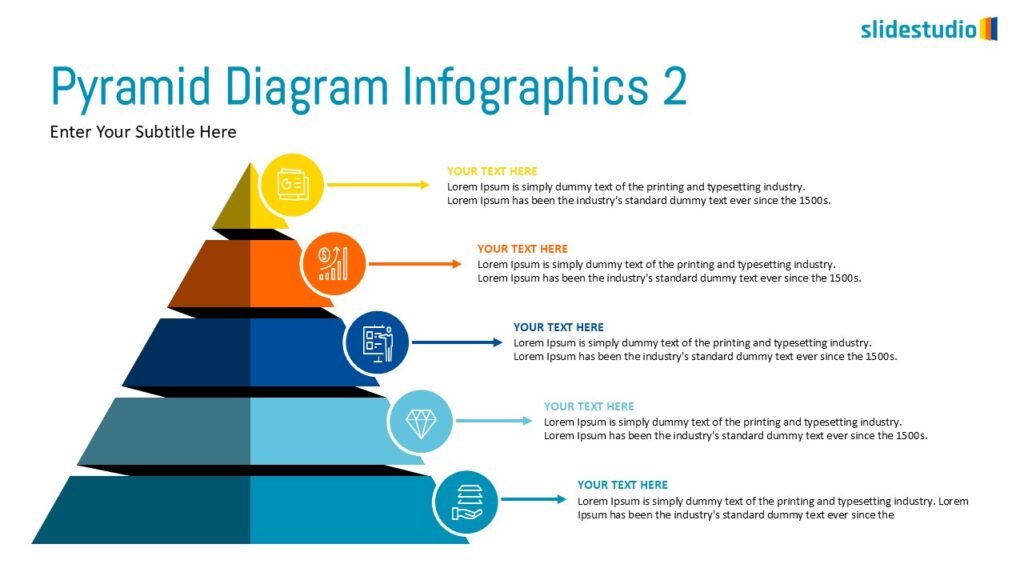
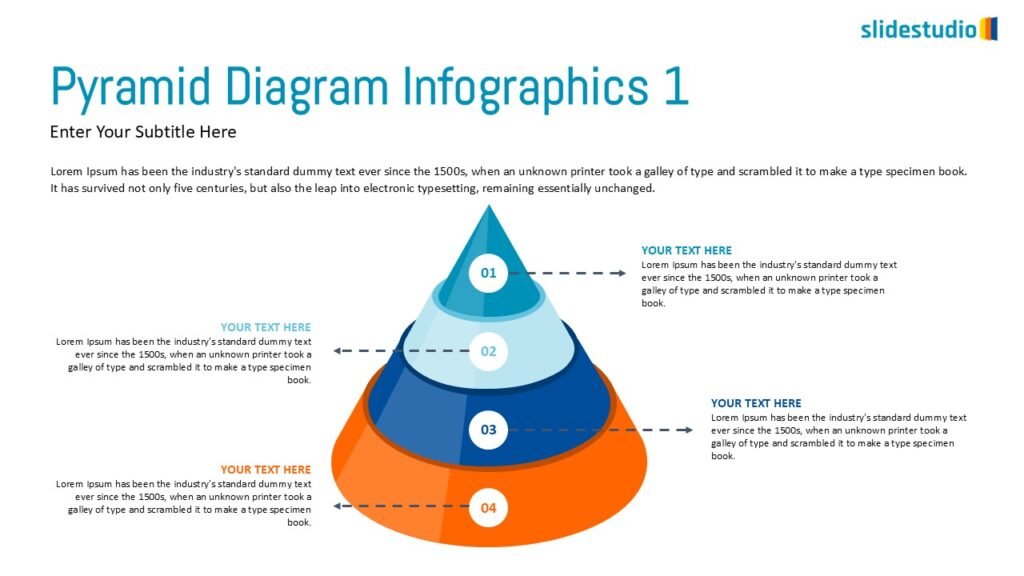
Structure
This concept organizes information hierarchically or categorically, often using matrices, trees, or layered arrangements. It helps to present the framework or arrangement of components within a system or process.
TREES
A hierarchical layout that maps out connections, such as organizational charts or family trees.

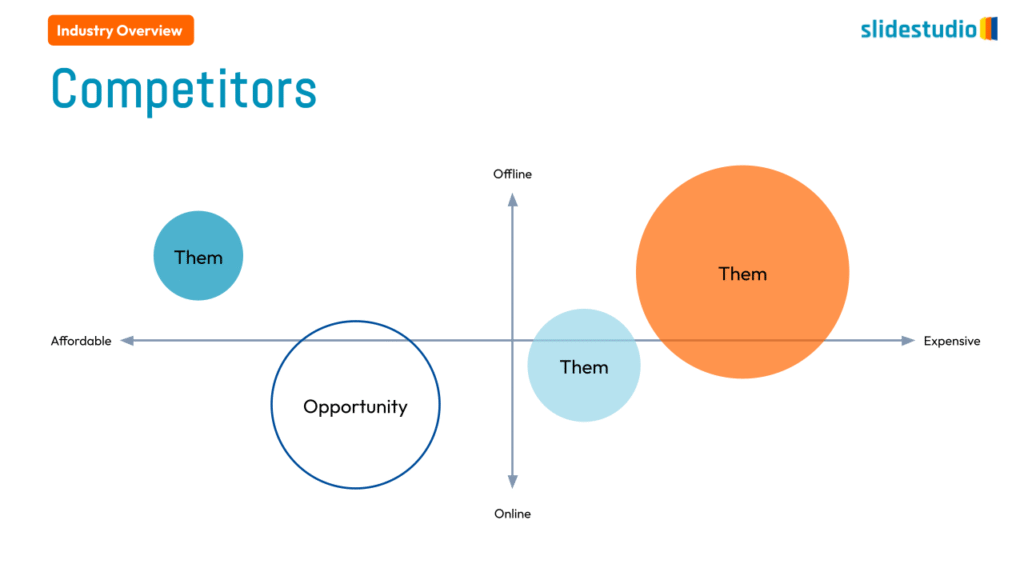
Cluster
This concept visually groups related items together, showing associations or overlaps. Cluster designs c to represent elements that belong together within a context or theme.
OVERLAPPING
Displays shared areas or intersections, useful for showing commonalities in Venn diagrams.

Radiate
This concept shows elements extending outward from a central point, typically illustrating a spread or influence. It can be depicted with or without a core and represents a central idea that radiates outwards.

Pictorial
This concept uses images or icons to convey direction, location, reveal processes, or show influence. It provides a visual representation that is easy to understand and adds clarity to directional or procedural content.
Display Data
This concept focuses on presenting data in a visual format, such as comparisons, trends, or distributions. Common methods include charts, graphs, or other data visualization techniques to make information easier to interpret at a glance.

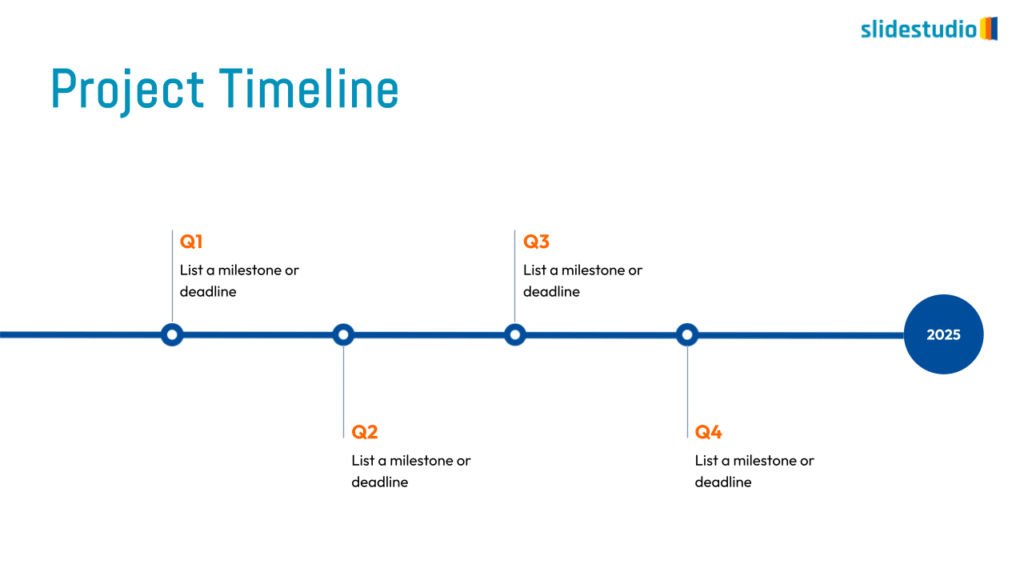
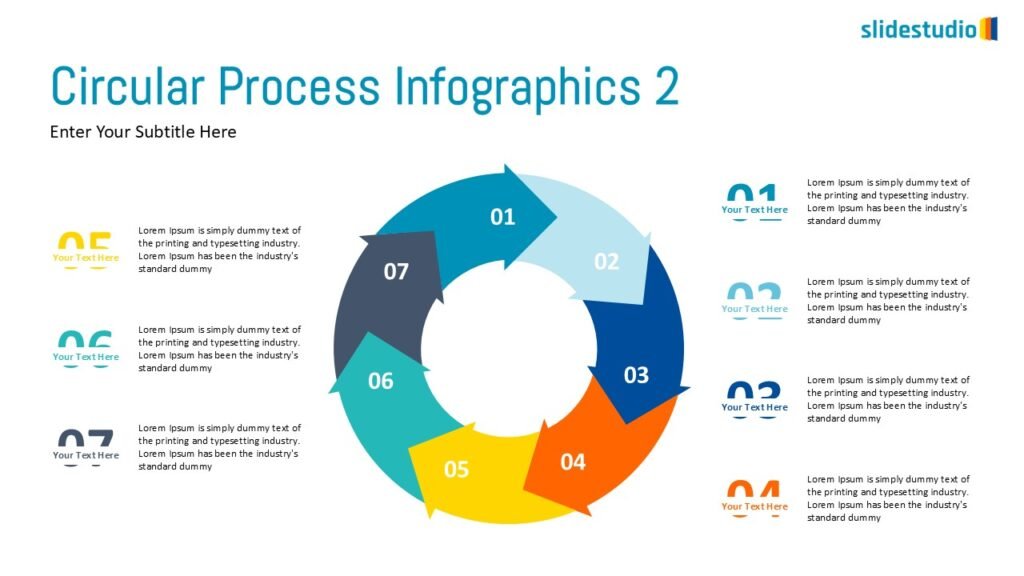
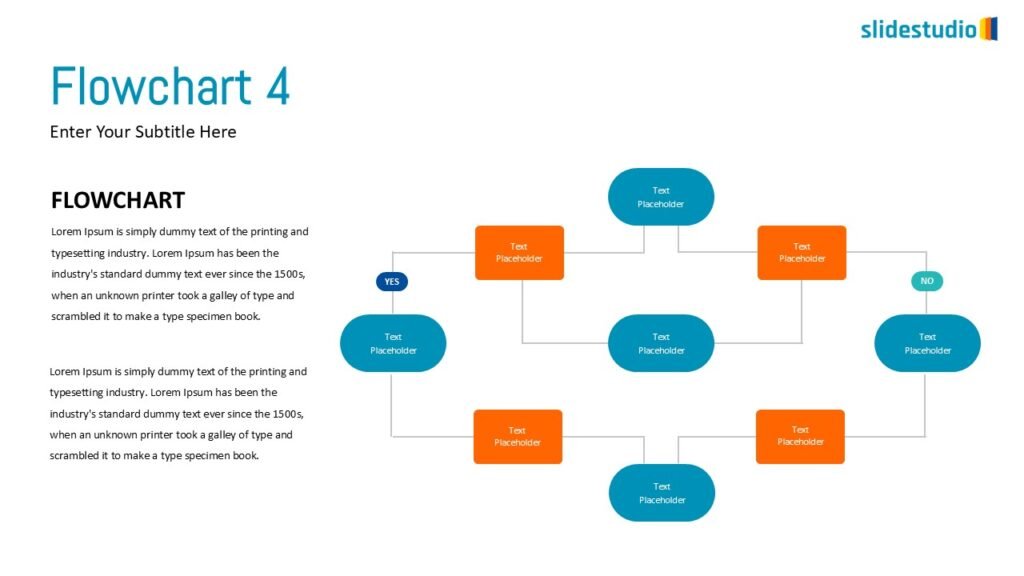
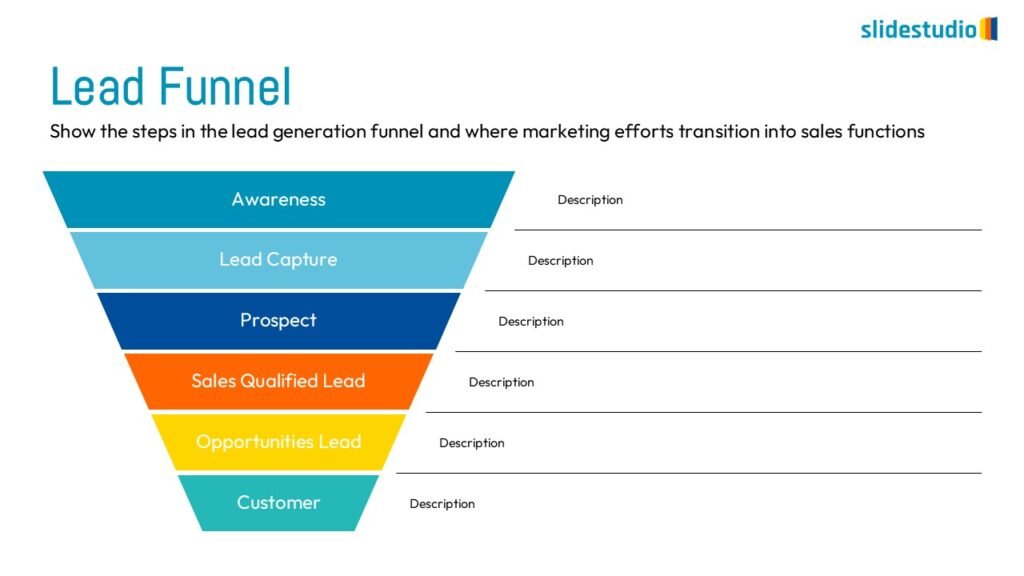
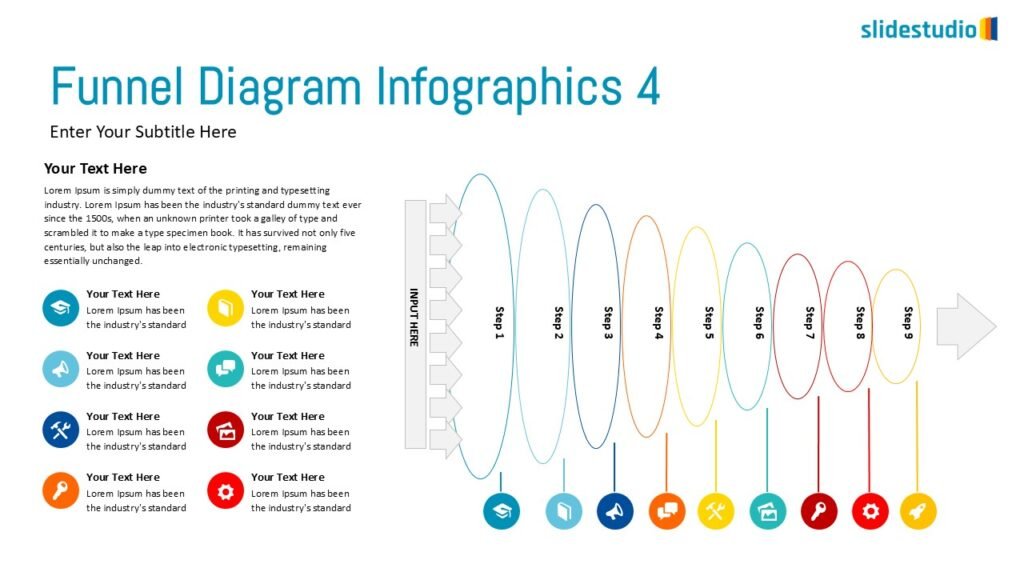
Flow
This concept focuses on illustrating the movement or progression of information. It can be represented in various forms, such as linear, circular, divergent/convergent, or multidirectional pathways, to convey how elements progress or connect in a sequence.
Linear
A step-by-step structure that illustrates a straightforward progression from start to finish.
DIVERGENT/CONVERGENT
A flow that branches out or converges, ideal for showing multiple pathways or merging ideas.

Structure
This concept organizes information hierarchically or categorically, often using matrices, trees, or layered arrangements. It helps to present the framework or arrangement of components within a system or process.
TREES
A hierarchical layout that maps out connections, such as organizational charts or family trees.

Cluster
This concept visually groups related items together, showing associations or overlaps. Cluster designs c to represent elements that belong together within a context or theme.
OVERLAPPING
Displays shared areas or intersections, useful for showing commonalities in Venn diagrams.

Radiate
This concept shows elements extending outward from a central point, typically illustrating a spread or influence. It can be depicted with or without a core and represents a central idea that radiates outwards.

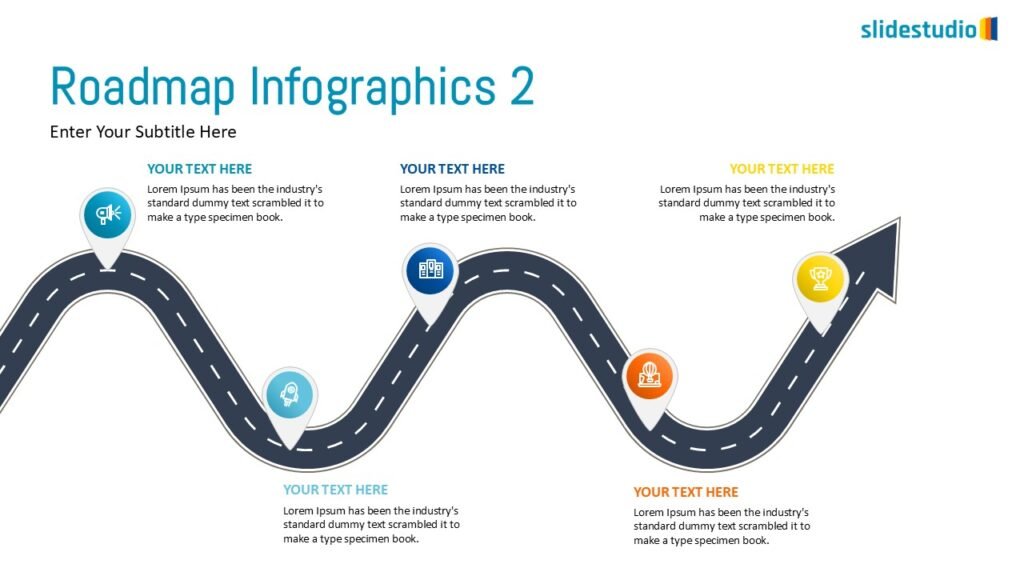
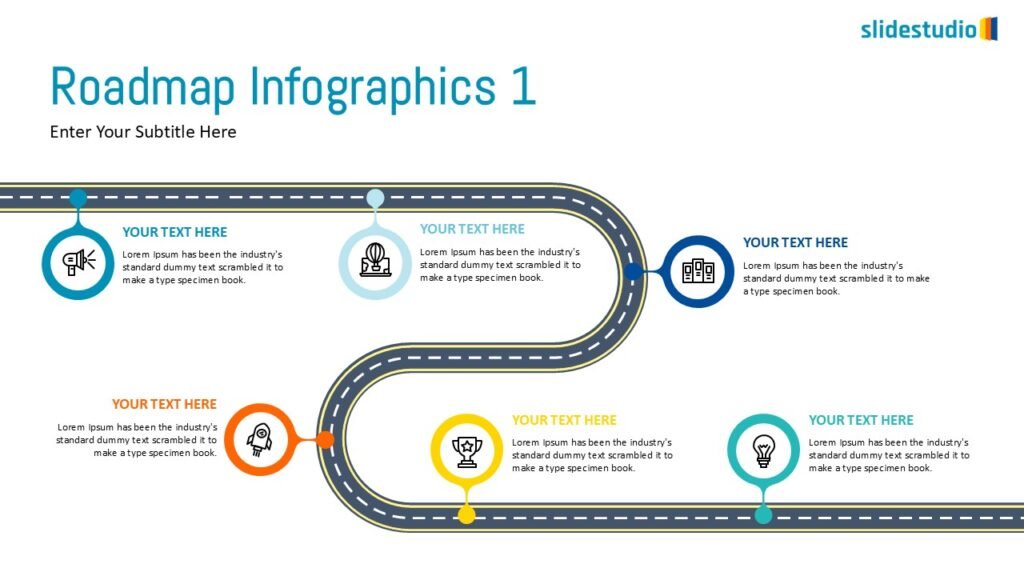
Pictorial
This concept uses images or icons to convey direction, location, reveal processes, or show influence. It provides a visual representation that is easy to understand and adds clarity to directional or procedural content.
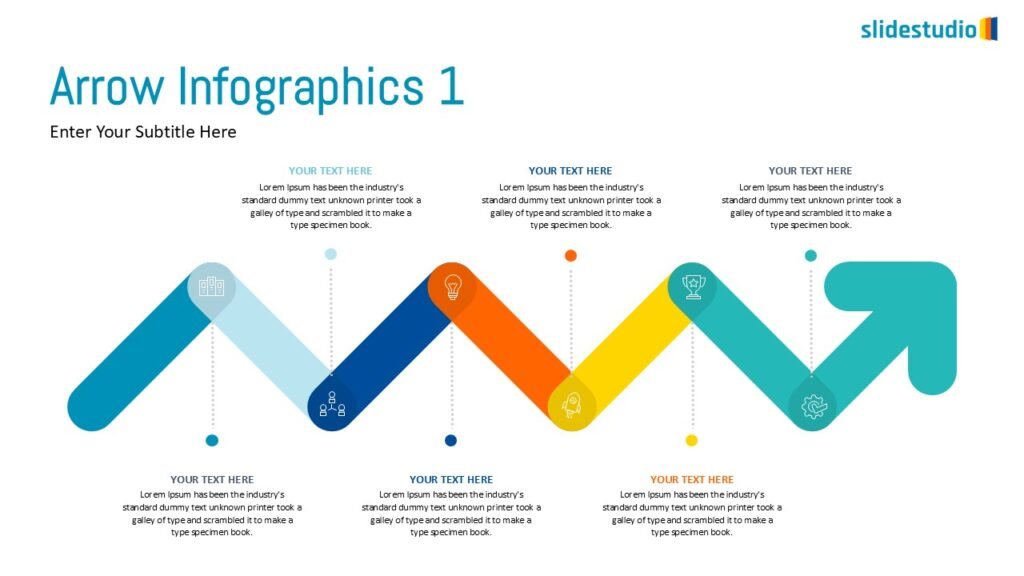
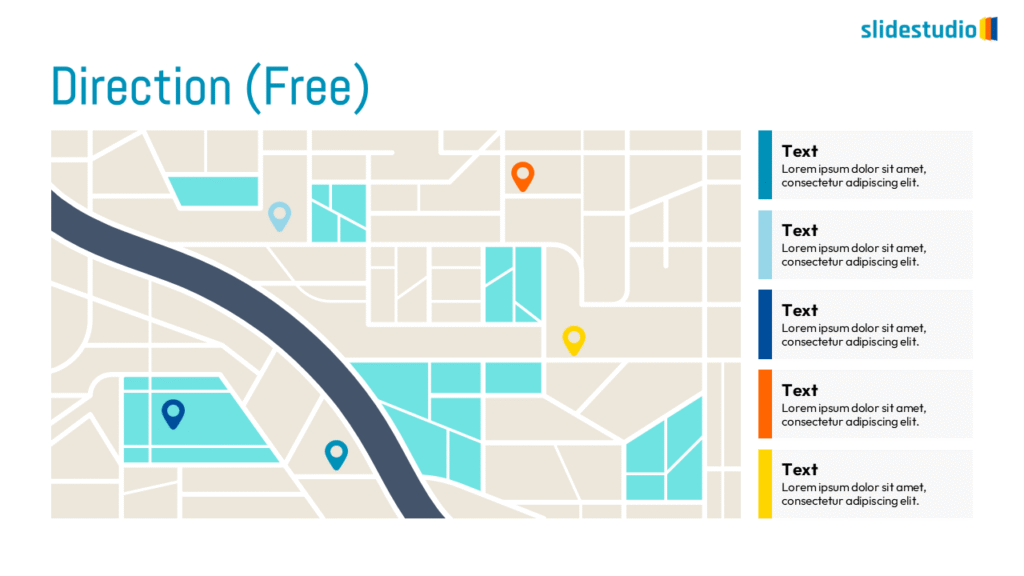
DIRECTION
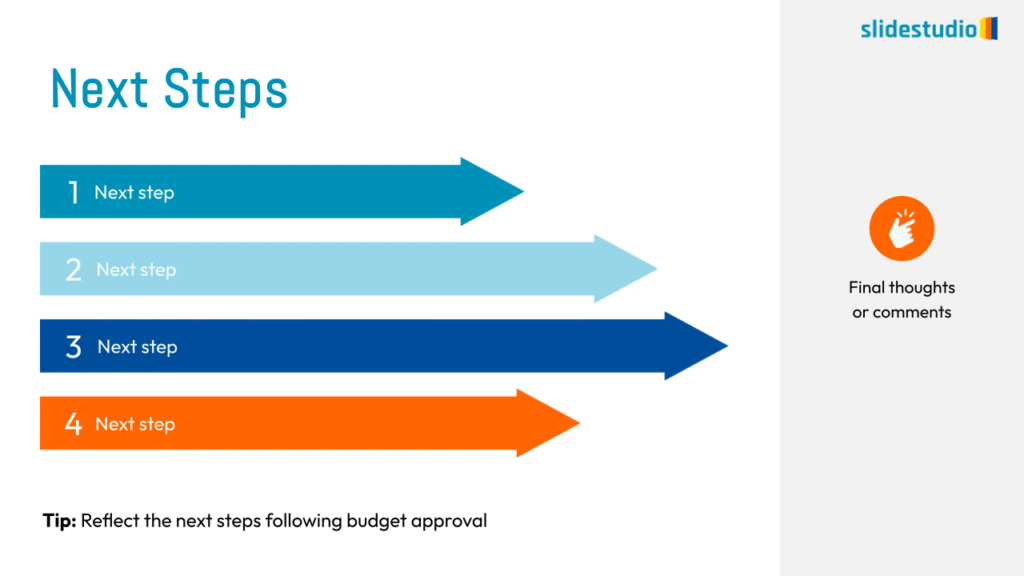
Uses arrows or paths to guide viewers through a specific route or sequence.
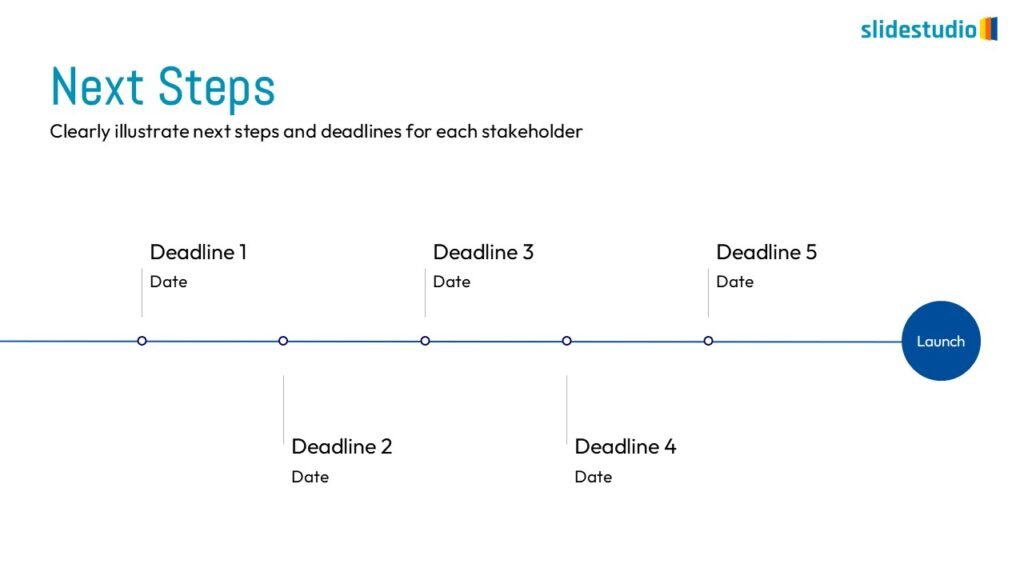
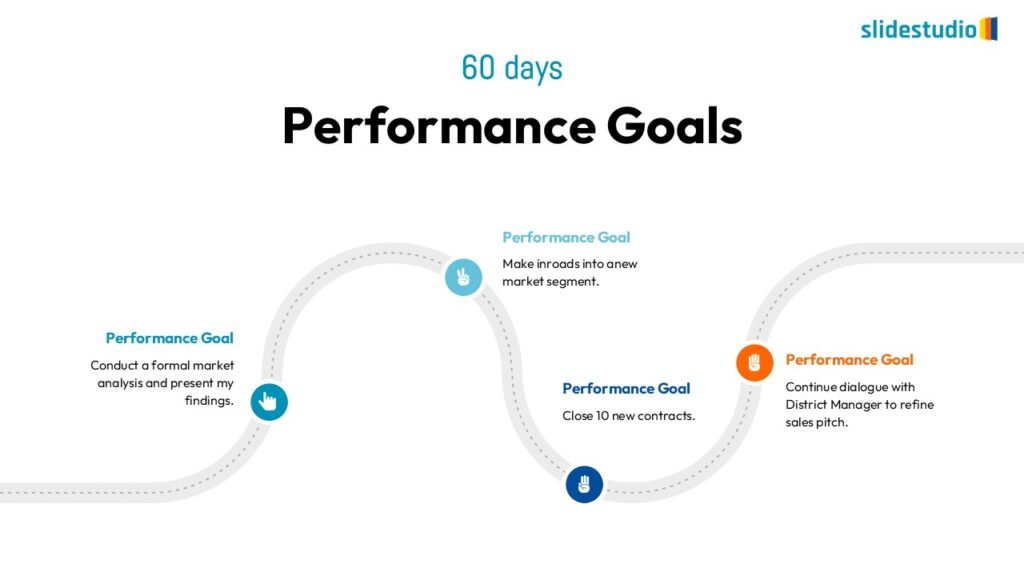
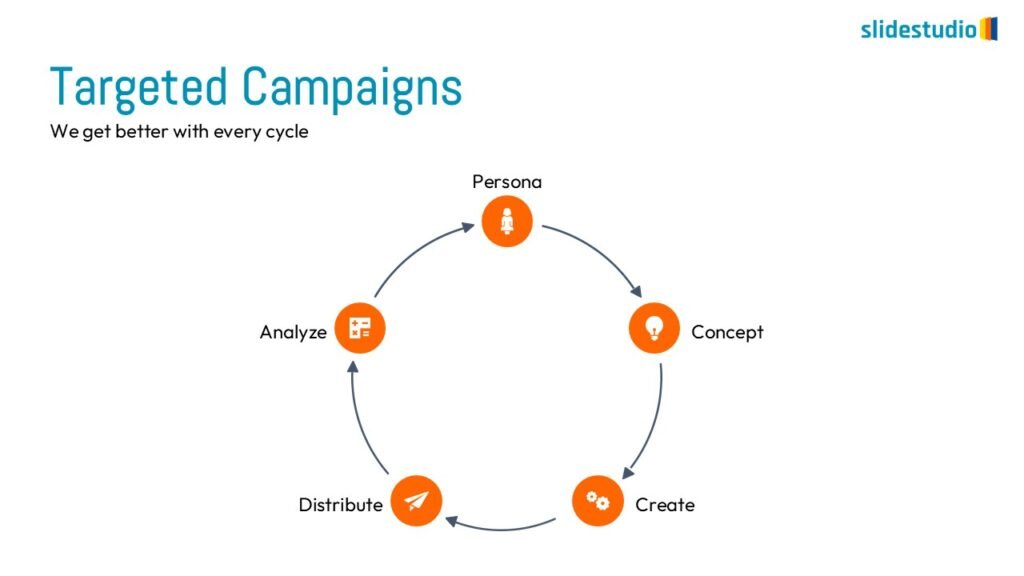
PROCESS
Shows stages within a workflow to visualize a continuous sequence of tasks.
Display Data
This concept focuses on presenting data in a visual format, such as comparisons, trends, or distributions. Common methods include charts, graphs, or other data visualization techniques to make information easier to interpret at a glance.